Abstract
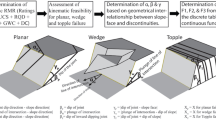
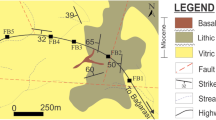
The paper discusses the use of kinematic stability and slope mass rating (SMR) maps in GIS based on field studies recording the relationships between the bedding/joint geometry relative to the orientation of the free face. The results indicated the potential for both planar and wedge type failures in many locations along a railway route. Whilst the results showed the procedure to be a useful first assessment of slope stability, it is recommended that the construction of the maps by kinematic slope stability and SMR analysis within the GIS medium should be used in conjunction with more sophisticated slope stability models taking into account of the material strengths, hydrostatic pressures, seepage forces, active forces, passive forces, etc.
Résumé
L’article considère l’utilisation de cartes présentant les conditions cinématiques de rupture de pente et un indice SMR de pente, dans un système d’information géographique, cartes établies à partir d’études de terrain comparant les attitudes respectives des pentes et des joints dans une masse rocheuse. Les résultats montrent que des ruptures planes et des ruptures de dièdres sont possibles en plusieurs endroits le long de la voie ferrée étudiée. La procédure est utile pour une première évaluation de la stabilité des pentes, mais il est recommandé que les cartes donnant les conditions cinématiques de rupture de pente et l’indice SMR de pente, dans un SIG, soient utilisées conjointement avec des modèles plus sophistiqués de stabilité des pentes prenant en compte les résistances des matériaux, les pressions hydrostatiques, les forces d’écoulement, les forces motrices, les forces résistantes, etc.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
ArcGIS (Version 9.1) (2005) GIS Software. ESRI, N.Y., USA
Barredo JJ, Benavides A, Hervas J, Van Westen CJ (2000) Comparing heuristic landslide hazard assessment techniques using GIS in the Trijana basin, Gran Canaria Island, Spain. JAG 2(1):9–23
Barton MR (1973) Review of a new shear strength criterion for rock joints. Eng Geol 7:287–332
Barton N, Choubey V (1977) The shear strength of rock joints in theory and practice. Rock Mech 10:1–54
Bieniawski ZT (1973) Engineering classification of jointed rock masses. Trans South Afr Inst Civ Eng 15:335–344
Bieniawski ZT (1979) The geomechanics classification in rock engineering applications. In: Proc. 4th Int. Congr. on Rock Mechanics, Balkema, Rotterdam, 2:51–58
Bieniawski ZT (1984) Rock mechanics design in mining and tunneling. Balkema, Rotterdam, p 272
Bieniawski ZT (1989) Engineering rock mass classification. Wiley, New York
Brabb EE, Pampeyan EH, Bonilla M (1972) Landslide susceptibility in the San Mateo County, California, scale 1 : 62.500, U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Field Studies Map MF344
Calcaterra D, Gili JA, Iovinelli R (1998) Shallow landslides in deeply weathered slates of the Sierra de Collcerola (Catalonian Coastal Range, Spain). Eng Geol 50:283–298
Carrara A, Cardinali M, Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P (1995) GIS based techniques for mapping landslide hazard. (http://deis158.deis.unibo.it)
Chung CF, Fabbri AG (1999) Probabilistic prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 65(12):1389–1399
De Graff J, Romesburg H (1980) Regional landslide-susceptibility assessment for wildland management: a matrix approach. In: Coates D, Vitek J (eds) Thresholds in geomorphology. George Allen and Unwin, London, pp 401–414
Fernández T, Irigaray C, Hamdouni RE, Chacón J (2003) Methodology for landslide susceptibility mapping by means of a GIS. Application to the Contraviesa area (Granada, Spain). Nat Hazards 30:297–308
Gomez H, Kavzoglu T (2005) Assessment of shallow landslide susceptibility using artificial neural networks in Jabonosa River Basin, Venezuela. Eng Geol 78(1–2):11–27
Hoek E, Bray J (1981) Rock slope engineering. Institution of Mining and Metalurgy, London
ISRM (2007) The complete ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring. In: Ulusay R, Hudson JA (eds), Kazan Offset Press, Ankara
Jade S, Sarkar S (1993) Statistical models for slope instability classification. Eng Geol 36:91–98
Kliche CA (1999) Rock slope stability. Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc. (SME), Littleton
Mote T, Morley D, Keuscher T, Crampton T (2004) GIS-based kinematic slope stability analysis. The ESRI user conference In: Proceedings 24th annual ESRI international user conference, August 9–13, San Diego
Priest SD, Hudson JA (1976) Discontiniuty spacing in rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 13:135–148
Romana M (1988) Practice of SMR classification for slope appraisal. In: Proc. 5th Int Symp on Landslides, Balkema, Rotterdam, 2:1227–1232
Topal T, Akin M, Ozden UA (2007) Assessment of rockfall hazard around Afyon castle, Turkey. Environ Geol 53:191–200
Van Westen CJ, Soeters R, Sijmons K (2000) Digital geomorphological landslide hazard mapping of the Alpago area, Italy. Int J Appl Earth Obser Geoinform 2(1):51–59
Yilmaz I (2007) GIS based susceptibility mapping of karst depression in gypsum: a case study from Sivas basin (Turkey). Eng Geol 90:89–103
Yilmaz I (2008) A case study for mapping of spatial distribution of free surface heave in alluvial soils (Yalova, Turkey) by using GIS software. Comput Geosci 34(8):993–1004
Yilmaz I (2009a) Landslide susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio, logistic regression, artificial neural networks and their comparison: a case study from Kat landslides (Tokat-Turkey). Comput Geosci 35(6):1125–1138
Yilmaz I (2009b) A case study from Koyulhisar (Sivas-Turkey) for landslide susceptibility mapping by artificial neural networks. Bull Eng Geol Environ 68(3):297–306
Yilmaz I (2010a) The effect of the sampling strategies on the landslide susceptibility mapping by conditional probability (CP) and artificial neural networks (ANN). Environ Earth Sci 60(3):505–519
Yilmaz I (2010b) Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping methodologies for Koyulhisar, Turkey: conditional probability, logistic regression, artificial neural networks, and support vector machine. Environ Earth Sci 61(4):821–836
Yilmaz I, Bagcı A (2006) Soil liquefaction susceptibility and hazard mapping in the residential area of Kütahya (Turkey). Environ Geol 49(5):708–719
Yilmaz I, Yavuzer D (2005) Liquefaction potentials and susceptibility mapping in the city of Yalova, Turkey. Environ Geol 47(2):175–184
Yilmaz I, Yıldırım M, Keskin I (2008) A method for mapping the spatial distribution of RockFall computer program analyses results using ArcGIS software. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:547–554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmaz, I., Marschalko, M., Yildirim, M. et al. GIS-based kinematic slope instability and slope mass rating (SMR) maps: application to a railway route in Sivas (Turkey). Bull Eng Geol Environ 71, 351–357 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0384-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0384-5