Abstract
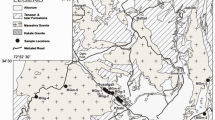
A number of medium to small sized barite deposits are located within the Mor Mountain Range, Pakistan. The present study evaluated eight barite deposits from the Lasbela area, Balochistan, Pakistan, representing the different parts of the Mor Range. Evaluation of the barite content and those properties important in the production of heavyweight concrete aggregate indicated that the material would be suitable for the construction of earthquake resistant buildings and for radiation shielding.
Résumé
Plusieurs gisements de barytine de petite à moyenne taille sont situés dans la chaîne de Mor au Pakistan. L’étude a évalué huit gisements de barytine de la région de Lasbela, au Baloutchistan, représentant les différentes parties de la chaîne de Mor. L’évaluation des teneurs en barytine et des propriétés importantes pour la production de granulats lourds pour béton a montré que les matériaux seraient adaptés pour la construction de bâtiments anti-sismiques et pour des écrans de protection contre les radiations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkurt I, Basyigit C, Kilincarslan S, Mavi B, Akkurt A (2006) Radiation shielding of concretes containing different aggregates. Cem Concr Composites 28:153–157
Akkurt I, Altindag R, Basyigit C, Kilincarslan S (2008) The effect of barite rate on the physical and mechanical properties of concretes under F-T cycle. Mater Des 29:1793–1795
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 1218-99 (2008) Standard test method for water-soluble chloride in mortar and concrete. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 127-07 (2007) Standard test method for specific gravity and absorption of coarse aggregate. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 131-06 (2006) Standard test method for resistance to degradation of small size coarse aggregate by abrasion and impact in the Los Angeles machine. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 136-06 (2006) Standard test method for sieve analysis of fine and coarse aggregates. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 142-97 (1997) Standard test method for clay lumps and friable particles in aggregates. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 289-07 (2007) Standard test method for potential alkali-silica reactivity of aggregates (chemical method). In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 637-98a (1998) Standard specification for aggregates for radiation-shielding concrete. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM C 88-05 (2005) Standard test method for soundness of aggregates by use of sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate. In: Annual book of ASTM Standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM D 4791-05 (2006) Standard test method for flat particles, elongated particles, or flat and elongated particles in coarse aggregate. In: Annual book of ASTM Standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM D 5821-01 (2005) Standard test method for determining the percentage of fractured particles in coarse aggregate. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Basyigit C (2006) The physical and mechanical properties of heavyweight concretes used in radiation shielding. J Appl Sci 6(46):762–766
Bradley DC, Leach DL (2003) Tectonic controls of Mississippi valley-type lead-zinc mineralization in orogenic forelands. Miner Deposita 38:652–667
Gnos E, Immenhauser A, Peters Tj (1997) Late Cretaceous/early Tertiary convergence between Indian and Arabian plates recorded in ophiolites and related sediments. Tectonophysics 271:1–19
Junsomboon J, Jakmunee J (2008) Determination of chloride in admixtures and aggregates for cement by a simple flow injection potentiometric system. Talanta 76:365–368
Kilincarslan S, Akkurt I, Basyigit C (2006) The effect of barite rate on the some physical and mechanical properties of concrete. Mater Sci Eng A 42:83–86
Kilincarslan S, Basyigit C, Akkurt I (2007) Investigation of heavyweight concrete with barite aggregates for radiation shielding. J Fac Eng Arch Gazi Univ 22(2):393–399
Martínez-Barrera G, Martínez-Hernández AL, Carlos Velasco-Santos C, Brostow W (2009) Polymer concretes improved by fiber reinforcement and gamma irradiation. E-Polymers 103:1–14. http://www.e-polymers.org
Ozbas KE, Hicyilmaz C (1994) Concentration of barite and fluorite minerals Eskisehir-Beylikahir District. Fizykochem Probl Mineralurgii 28:65–74
Sana Traders (2009) Minerals. http://www.mineralspakistan.com/minerals/products.html
Shah MT, Gohar A (2003) Geotechnical and geochemical studies of Eocene limestone of Kohat formation for its use as concrete aggregates. Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 36:11–22
Topçu IB (2003) Properties of heavyweight concrete produced with barite. Cem Concr Res 33:815–822
WAPA (2002) Material-aggregate, Washington asphalt pavement association, retrieve from Inc. file:///H:/los%20angeles/3_2%20Materials%20-%20Aggregate.htm
Zafir N, Majid A (2000) The influence of aggregates properties on strength of concrete. Series on K-economy. Civil Struct Eng Works, Malayasia, pp 1–22
Acknowledgments
Special appreciation is extended to Mr. Shabir Ahmed Baloch, proprietor of the Industrial Mineral Syndicate, Karachi for many years of cooperation with the authors on the studies of barite deposits of Lasbela, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseem, S., Bashir, E. & Hussain, K. Evaluation of geotechnical characteristics of Lasbela barite deposits of Balochistan, Pakistan, as heavyweight aggregate. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70, 651–655 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0359-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0359-6