Abstract
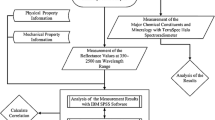
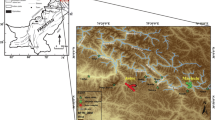
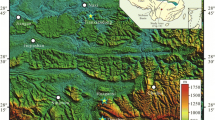
Reflectance spectroscopy was applied to assess the degree of weathering of the granite sculpture of Buddha in Gyeongju, South Korea, using diagnostic absorption features of representative weathering products (iron oxides and clay minerals). The relative weathering degree map obtained using reflectance spectroscopy corresponds closely with the visual interpretation of exfoliations and cracks. Eight chemical weathering indices (Vogt ratio, weathering potential index, Ruxton ratio, Parker index, modified weathering potential index, chemical index of alteration, plagioclase index of alteration, and chemical index of weathering) determined on granite specimens from three sites in Korea were compared with the quantitative absorption depths of iron oxides and clay minerals. Relatively good correlations were found for the modified weathering potential index and Parker index and the absorption features of iron oxides and good correlations between the weathering potential index and Parker index and the absorption depth of clay minerals. The work has shown the applicability of reflectance spectroscopy as a new non-destructive technique for assessing the weathering of stone monuments.
Résumé
La spectroscopie de réflectance a été utilisée pour évaluer le degré d’altération de la sculpture de granite du Bouddha de Gyeongju en Corée du Sud, utilisant les caractéristiques d’absorption de produits d’altération représentatifs (oxydes de fer et minéraux argileux). La cartographie du degré d’altération relative obtenue par la spectroscopie de réflectance correspond étroitement à l’interprétation visuelle des exfoliations et des fissures. Huit indices d’altération chimique (rapport de Vogt, indice de potentiel d’altération météorique, rapport de Ruxton, indice de Parker, indice modifié de potentiel d’altération météorique, indice chimique d’altération, indice d’altération des plagioclases, indice chimique d’altération météorique) déterminés sur des échantillons de granite provenant de trois sites de Corée ont été comparés avec les profondeurs d’absorption d’oxydes de fer et de minéraux argileux. Des corrélations relativement bonnes ont été trouvées pour l’indice modifié de potentiel d’altération météorique, l’indice de Parker et les caractéristiques d’absorption des oxydes de fer. De bonnes corrélations ont été trouvées entre l’indice de potentiel d’altération météorique, l’indice de Parker et la profondeur d’absorption des minéraux argileux. Le travail réalisé a montré l’applicabilité de la spectroscopie de réflectance comme nouvelle technique non destructive pour l’évaluation de l’altération météorique des monuments en pierre.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baynes J, Dearman WR (1978) The microfabric of a chemically weathered granite. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 18:91–100
Burns R (1993) Mineralogical applications of crystal field theory, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 551 pp
Clark RN (1999) Chapter 1: spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. Manual of remote sensing, vol 3, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 3–58
Clark RN, Roush TL (1984) Reflectance spectroscopy: quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J Geophys Res 89(B7):6329–6340
Clark RN, King TVV, Klejwa M, Swayze G, Vergo N (1990) High spectral resolution reflectance spectroscopy of minerals. J Geophys Res 95(B8):12653–12680
Clark RN, Swayze GA, Wise R, Livo KE, Hoefen TM, Kokaly RF, Sutley SJ (2003) USGS digital spectral library splib05a. USGS open file report 03-395
Dearman WR (1974) Weathering classification in the characterization of rock for engineering purpose in British practice. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 9:33–42
Dearman WR, Baynes FJ, Irfan TY (1978) Engineering grading of weathered granite. Eng Geol 12:345–374
Duke EF (1994) Near infrared spectral of muscovite, Tschermak substitution, and metamorphic reaction progress: implications for remote sensing. Geology 22:621–624
Farmer VC (ed) (1974) The infra-red spectra of minerals. Mineralogical Society. London, 539 pp
Fedo CM, Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1995) Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 23:921–924
Harnois L (1988) The CIW index: a new chemical index of weathering. Sed Geol 55:319–322
Harnois L, Moore JM (1988) Geochemistry and origin of the ore chimmey formation, a transported paleoregolith in the Greenville Province of Souteastern Ontario, Canada. Chem Geol 69:267–289
Hunt GR (1977) Spectral signatures of particulate minerals, in the visible and near-infrared. Geophysics 42(3):501–513
Irfan TY (1996) Mineralogy, fabric properties and classification of weathered granites in Hong Kong. Q J Eng Geol 29(11):5–35
Jun BK, Han MS, Lee JJ, Song CY (2006) Present state and statistical analysis of stone cultural heritage by National Appointment in Republic of Korea. Conserv Stud 27:43–61 (in Korean with English abstract)
Kim CS, Kim GS (1997) Petrogenesis of the early Tertiary A-type Nsmsan alkali granite in the Kyongsang Basin, Korea. Geosci J 1–2:99–107
Kim S, Park HD (2003) The relationship between physical and chemical weathering indices of granite around Seoul, Korea. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 62:207–212
Kim SJ, Lee MS, Kim WS, Lee SJ (1994) The change of natural environment in the Seoul Area: environmental mineralogy of the granite weathering. J Geol Soc Korea 30:284–296 (in Korean with English abstract)
KMA (Korea Meteorological Administration) (2004) Annual climatological report. 292 pp (in Korean)
KMA (Korea Meteorological Administration) (2005) Annual climatological report. 295 pp (in Korean)
KMA (Korea Meteorological Administration) (2006) Annual climatological report. 295 pp (in Korean)
KMA (Korea Meteorological Administration) (2007) Annual climatological report. 308 pp (in Korean)
Lee SG (1993) Weathering of granite. J Geol Soc Korea 29(4):396–413
Lee SG, de Freitas MH (1989) A revision of the description and classification of weathered granite and its application to granites in Korea. Q J Eng Geol 22(1):31–48
Lee CH, Yi JE (2007) Weathering damage evaluation of rock properties in the Bunhwangsa temple stone pagoda, Gyeongju, Republic of Korea. Environ Geol 52(6):1193–1205
Lee MJ, Lee JI, Lee MS (1995) Mineralogy and major element geochemistry of A-type alkali granite in the Kyeongju area, Korea. J Geol Soc Korea 31:583–607 (in Korean with English abstract)
Lee CH, Lee MS, Suh M, Choi SW (2005) Weathering and deterioration of rock properties of the Dabotap pagoda (World Cultural Heritage), Republic of Korea. Environ Geol 47:547–557
Lee CH, Lee MS, Kim YT, Kim J (2006) Deterioration assessment and conservation of a heavily degraded Korean Stone Buddha from the ninth century. Stud Conserv 51(4):305–316
Lee SY, Kim SJ, Baik MH (2008) Chemical weathering of granite under acid rainfall environment, Korea. Environ Geol 55(4):853–862
Loughnan FC (1969) Chemical weathering of the silicate minerals. Elsevier, London, 154 pp
Malomo S (1980) Abrasive pH of feldspars as an engineering index for weathered granite. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 22:207–211
Matsuo S, Nishida K (1968) Physical and chemical properties of decomposed granite soils. Soils Found 8:10–20
Michalski JR, Kraft MD, Sharp TG, Christensen PR (2006) Effects of chemical weathering on infrared spectra of Columbia River Basalt and spectral interpretations of martian alteration. Earth Planet Sci Lett 248(3–4):822–829
Middelburg JJ, Van der Weijden CH, Woittiez JRW (1988) Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem Geol 68(3–4):253–273
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299:715–717
Nikiforoff CC, Drosdoff M (1943) Genesis of a clay-pan soil. Soil Sci 55:459
NRICP (National Research Institute of Cultural Heritages) (2007) Development on evaluation technology of deterioration for conservation of stone cultural properties. 695 pp (in Korean)
Parker A (1970) An index of weathering for silicate rocks. Geol Mag 107:501–504
Peltier L (1950) The geographic cycle in periglacial regions as it is related to climatic geomorphology. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 40:214–236
Reiche P (1943) Graphic representation of chemical weathering. J Sediment Petrol 13(2):58–68
Riaza A, Strobl P, Müller A, Beisl U, Hausold A (2001) Spectral mapping of rock weathering degrees on granite using hyperspectral DAIS 7915 spectrometer data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 3(4):345–354
Roaldset E (1972) Mineralogy and geochemistry of Quaternary clays in the Numedal area Southern Norway. Norsk Geologisk Tidsskirft 52:335–369
Rocha Filho P, Antuenes FS, Falcao MFG (1985) Quantitative influence of the weathering upon the mechanical properties of a young gneiss residual soil. In: First International Conference on Geomechanics in Tropical Lateritic and Saprolitic Soils, Brasilia 1:281–294
Ruxton PP (1968) Measures of the degree of chemical weathering of rock. J Geol 76:518–527
Sueoka T, Lee IK, Muramatsu M, Imamura S (1985) Geomechanical properties and engineering classification for decomposed granite soils in Kaduna district Nigeria. First International Conference on Geomechanics in Tropical Lateritic and Saprolitic Soils, Brasilia 1:175–186
Sun Y, Seccombe PK, Yang K (2001) Application of short-wave infrared spectroscopy to define alteration zones associated with the Elura zinc-lead-silver deposit NSW Australia. J Geochem Explor 73(1):11–26
Vogel DE (1973) Precambrian weathering in acid metavolcanic rocks from the Superior Province, Villebond Township, south central Quebec. Can J Earth Sci 12:2080–2085
Vogt T (1927) Sulitjelmefeltets geologiog petrografi. Nor Geol Tidssk 121 pp. 1–560
Woo I, Fleurisson JA, Park YJ, Han KC, Song WK, Park HJ, Kim IS (2008) Essais d’altération chimique accélérée au laboratoire par le double extracteur Soxhlet. Application à des roches granitiques de Corée du Sud. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 67:443–452
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage (project title: Development on Evaluation Technology for Weathering Degree of Stone Cultural Properties, project no.: 09B011Y-00150-2009), the Brain Korea 21 Project in 2009 and the Research Institute of Engineering Science, Seoul National University, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyun, C.U., Park, H.D. Assessment of chemical weathering of granite stone monuments using reflectance spectroscopy. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70, 63–78 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0276-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0276-0