Abstract
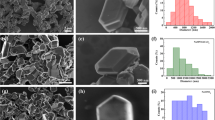
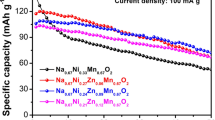
The influence of partial substitution of manganese by nickel or magnesium in Na0.44MnO2on cathode performance in sodium ion batteries has been investigated. Partial substitution changes the structure of parent Na0.44MnO2 from tunnel into layered P2-type, or a mixture of P2- and P3-type materials. Substitution smoothes the charge/discharge curves and may significantly improve capacity, albeit with a lower capacity retention relative to pristine Na0.44MnO2. In particular, high discharge capacities are found in the voltage range 2.0–4.2 V at 0.1 C rate for Na0.44Mn0.89Ni0.11O2 (193 mAh g−1) and Na0.44Mn0.89Mg0.11O2 (188 mAh g−1), with a capacity retention of 74% and 81%, respectively, after 70 cycles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M, Tarascon JM (2008) Building better batteries. Nature 451:652–657
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Electrolyte for energy storage/conversion (Li+, Na+, Mg2+) devices based on PVC and their associated polymer: a comprehensive review. J Solid State Electrochem 23:997–1059
Xiao LN, Ding X, Tang ZF, He XD, Liao JY, Cui YH, Chen CH (2018) Layered LiNi0.80Co0.15Al0.05O2 as cathode material for hybrid Li+/Na+ batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 22:3431–3442
Slater MD, Kim DH, Lee EJ, Johnson CS (2013) Sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 23:947–958
Pan HL, Hu YS, Chen LQ (2013) Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 6:2338–2360
Palomares V, Cabanas MC, Martíınez EC, Han MH, Rojo T (2013) Update on Na-based battery materials. A growing research path. Energy Environ Sci 6:2312–2337
Kulova TL, Kudryashova YO, Kuz’mina AA, Skundin AM, Stenina IA, Chekannikov AA, Yaroslavtsev AB, Libich J (2019) Study of degradation of Na2Тi3O7-based electrode during cycling. J Solid State Electrochem 23:455–463
Zukalová M, Lásková BP, Mocek K, Zukal A, Bouša M, Kavan L (2018) Electrochemical performance of sol-gel-made Na2Ti3O7 anode material for Na-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2545–2552
Galashev AY, Vorob’ev AS (2018) Physical properties of silicene electrodes for Li-, Na-, Mg-, and K-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 22:3383–3391
Wen MM, Liu XD, Zhao YM, Liu SH, Liu HT, Dong YZ, Kuang Q, Fan QH (2018) Synthesis of alluaudite-type Na2VFe2(PO4)3/C and its electrochemical performance as cathode material for sodium-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 22:891–898
Clément RJ, Bruce PG, Grey CP (2015) Review—manganese-based P2-type transition metal oxides as sodium-ion battery cathode materials. J Electrochem Soc 162:A2589–A2604
Wu L, Hao Y, Shi S, Zhang X, Li H, Sui Y, Yang L, Zhong S (2017) Na3V2(PO4)3/C nanofiber bifunction as anode and cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 21:2985–2995
Delmas C, Braconnier JJ, Fouassier C, Hagenmuller P (1981) Electrochemical intercalation of sodium NaxCoO2 bronzes. Solid State Ionics 3/4:165–169
Delmas C, Fouassier C, Hagenmuller P (1980) Structural classification and properties of the layered oxides. Physica 99B:81–85
Singh VK, Singh SK, Gupta H, Shalu BL, Tripathi AK, Verma YL, Singh RK (2018) Electrochemical investigations of Na0.7CoO2 cathode with peo-natfsi-bmimtfsi electrolyte as promising material for na-rechargeable battery. J Solid State Electrochem 22:1909–1919
Bouwmeester HJM, Dekker EJP, Bronsema KD, Haange RJ, Wiegers GA (1982) Structures and phase-relations of compounds NaxTiS2 and NaxTiSe2. Rev Chim Mineral 19:333–342
Rouxel J (1976) Sur un diagramme ionicité-structure pour les composes intercalaire salcalins des sulfures lamellaires. J Solid State Chem 17:223–229
Wang X, Tamaru M, Okubo M, Yamada A (2013) Electrode properties of P2–Na2/3MnyCo1–yO2 as positive electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries. J Phys Chem C 117:15545–15551
Sauvage F, Laffont L, Tarascon JM, Baudrin E (2007) Study of the insertion/deinsertion mechanism of sodium into Na0.44MnO2. Inorg Chem 46:3289–3294
Kim H, Kim DJ, Seo DH, Yeom MS, Kang K, Kim DK, Jung Y (2012) Ab initio study of the sodium intercalation and intermediate phases in Na0.44MnO2 for sodium-ion battery. Chem Mater 24:1205–1211
Wang Y, Liu J, Lee B, Qiao R, Yang Z, Xu S, Yu X, Gu L, Hu YS, Yang W, Kang K, Li H, Yang XQ, Chen L, Huang X (2015) Ti-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2 oxide as a negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries. Nat Commun 6:6401–6411
Dai Z, Mani U, Tan HT, Yan Q (2017) Advanced cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries: what determines our choices? Small Methods 1:1700098
Clément RJ, Billaud J, Armstrong AR, Singh G, Rojo T, Bruce PG, Grey CP (2016) Structurally stable Mg-doped P2-Na2/3Mn1-yMgyO2 sodium-ion battery cathodes with high rate performance: insights from electrochemical NMR and diffraction studies. Energy Environ Sci 9:3240–3251
Zhou YT, Sun X, Zou BK, Liao JY, Wen ZY, Chen CH (2016) Cobalt-substituted Na0.44Mn1-xCoxO2: phase evolution and a high capacity positive electrode for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 213:496–503
Zhao L, Ni J, Wang H, Gao L (2013) Flux synthesis of Na0.44MnO2 nanoribbons and their electrochemical properties for Na-ion batteries. Funct Mater Lett 6:1350012–1135001
Wang PF, Yao HR, Liu XY, Zhang JN, Gu L, Yu XQ, Yin YX, Guo YG (2017) Ti-substituted NaNi0.5Mn0.5-xTixO2 cathodes with reversible O3−P3 phase transition for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 29:1700210
Yabuuchi N, Kajiyama M, Iwatate J, Nishikawa H, Hitomi S, Okuyama R, Usui R, Yamada Y, Komaba S (2012) P2-type Nax[Fe1/2Mn1/2]O2 made from earth-abundant elements for rechargeable Na batteries. Nat Mater 11:512–517
Billaud J, Singh G, Armstrong AR, Gonzalo E, Roddatis V, Armand M, Rojo T, Bruce PG (2014) Na0.67Mn1-xMgxO2 (0≤x≤0.2): a high capacity cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 7:1387–1391
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51577175), the Hefei Center of Materials Science and Technology (grant no. 2014FXZY006), the Educational department of the Anhui Province (grant no. KJ2014ZD36), and by Elementec Co., Ltd. in Suzhou, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 8820 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Zhou, YT., Deng, MM. et al. Performance of Na0.44Mn1−xMxO2 (M = Ni, Mg; 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.44) as a cathode for rechargeable sodium ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 2979–2988 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04375-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04375-6