Abstract
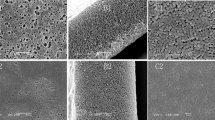
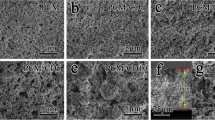
Since Li+ ions can transport through porous channels in the separator containing liquid electrolyte, the electrochemical and structural properties of the separator needs to be improved to develop a high rate performance lithium-ion battery (LIB). In this study, a gel-type polymer membrane using poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (P (VDF-HFP)) acting as a matrix and ethylene carbonate (EC) as a separator was applied for a high-performance LIB with LiMn2O4 as a cathode. The cell assembled with the porous polymer gel electrolyte membrane prepared using P (VDF-HFP) with an appropriate amount of EC exhibited an improved capacity (78.8 mAh g−1) and energy density (308.4 mWh g−1) at a current density of 720 mA g−1, and a high capacity retention (94.8%) at a current density of 240 mA g−1, compared to the cell assembled with polyethylene as a separator. The enhanced LIB performance can result from an increased Li+-ion migration between the chains in low-crystalline polymer membranes and an increased volume of the liquid electrolyte for ionic motion in the porous membrane due to an increased porosity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tripathi AK, Singh RK (2018) Lithium salt assisted enhanced performance of supercapacitor based on quasi solid-state electrolyte. J Saudi Chem Soc 22(7):838–845
Tripathi AK, Verma YL, Shalu SVK, Balo L, Gupta H, Singh SK, Singh RK (2017) Quasi solid-state electrolytes based on ionic liquid (IL) and ordered mesoporous matrix MCM-41 for supercapacitor application. J Solid State Electrochem 21(11):3365–3371
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM (2008) Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 47(16):2930–2946
Van Noorden R (2014) The rechargeable revolution: a better battery. Nature 507(7490):26–28
Wagner R, Preschitschek N, Passerini S, Leker J, Winter M (2013) Current research trends and prospects among the various materials and designs used in lithium-based batteries. J Appl Electrochem 43(5):481–496
Whittingham MS (2004) Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem Rev 104(10):4271–4301
Goodenough JB, Park KS (2013) The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective. J Am Chem Soc 135(4):1167–1176
Shin WK, Yoo JH, Kim DW (2015) Surface-modified separators prepared with conductive polymer and aluminum fluoride for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 279:737–744
Tripathi AK, Singh RK (2018) Development of ionic liquid and lithium salt immobilized MCM-41 quasi solid-liquid electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Energy Storage 15:283–291
Gupta H, Kataria S, Balo L, Singh VK, Singh SK, Tripathi AK, Verma YL, Singh RK (2018) Electrochemical study of ionic liquid based polymer electrolyte with graphene oxide coated LiFePO4 cathode for li battery. Solid State Ionics 320:168–192
Zhang SS (2007) A review on the separators of liquid electrolyte li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 164(1):351–364
Venugopal G, Moore J, Howard J, Pendalwar S (1999) Characterization of microporous separators for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77(1):34–41
Kim JH, Kim JH, Choi ES, Kim JH, Lee SY (2014) Nanoporous polymer scaffold-embedded nonwoven composite separator membranes for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 4(97):54312–54321
Arora P, Zhang Z (2004) Battery separators. Chem Rev 104(10):4419–4462
Ryou MH, Lee YM, Park JK, Choi JW (2011) Mussel-inspired polydopamine-treated polyethylene separators for high-power Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 23(27):3066–3070
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77(2):183–197
Croce F, Sacchetti S, Scrosati B (2006) Advanced, high-performance composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 161(1):560–564
Li W, Pang Y, Liu J, Liu G, Wang Y, Xia Y (2017) A PEO-based gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 7(38):23494–23501
Wang Y, Qiu J, Peng J, Li J, Zhai M (2017) One-step radiation synthesis of gel polymer electrolytes with high ionic conductivity for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 5(24):12393–12399
Singh SK, Shalu BL, Gupta H, Singh VK, Tripathi AK, Verma YL, Singh RK (2018) Improved electrochemical performance of EMIMFSI ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte with temperature for rechargeable lithium battery. Energy 150:890–900
Saito Y, Stephan AM, Kataoka H (2003) Ionic conduction mechanisms of lithium gel polymer electrolytes investigated by the conductivity and diffusion coefficient. Solid State Ionics 160(1-2):149–153
Huang B (1996) The mechanism of lithium ion transport in polyacrylonitrile-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 91(3-4):279–284
Shi Q, Yu M, Zhou X, Yan Y, Wan C (2002) Structure and performance of porous polymer electrolytes based on P (VDF-HFP) for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 103(2):286–292
Li Z, Su G, Wang X, Gao D (2005) Micro-porous P (VDF-HFP)-based polymer electrolyte filled with Al2O3nanoparticles. Solid State Ionics 176(23-24):1903–1908
Yang CC, Lian ZY, Lin SJ, Shih JY, Chen WH (2014) Preparation and application of PVDF-HFP composite polymer electrolytes in LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2lithium-polymer batteries. Electrochim Acta 134:258–265
Huang H, Wunder SL (2001) Preparation of microporous PVDF based polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 97–98:649–653
Zhang J, Sun B, Huang X, Chen S, Wang G (2014) Honeycomb-like porous gel polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium ion batteries with enhanced safety. Sci Rep 4:1–7
Aliahmad N, Shrestha S, Varahramyan K, Agarwal M (2016) Poly (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) polymer electrolyte for paper-based and flexible battery applications. AIP Adv 6:1–8
li SB, Mingija H (2008) Lewis acid–base property of P (VDF-co-HFP) measured by inverse gas chromatography. J Appl Polym Sci 107:1642–1646
Croce F, Curini R, Martinelli A, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B, Caminiti R (1999) Physical and chemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 103(48):10632–10638
Pokorný V, Štejfa V, Fulem M, Červinka C, Růžička K (2017) Vapor pressures and thermophysical properties of ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate, γ-valerolactone, and γ-butyrolactone. J Chem Eng Data 62(12):4174–4186
Gummow RJ, de Kock A, Thackeray MM (1994) Improved capacity retention in rechargeable 4 V lithium/lithium-manganese oxide (spinel) cells. Solid State Ionics 69(1):59–67
Zhan C, Lu J, Jeremy Kropf A, Wu T, Jansen Andrew N, Sun YK, Qiu X, Amine K (2013) Mn (II) deposition on anodes and its effects on capacity fade in spinel lithium manganate-carbon systems. Nat Commun 4:1–8
Shin H, Park J, Sastry AM, Lu W (2015) Degradation of the solid electrolyte interphase induced by the deposition of manganese ions. J Power Sources 284:416–427
Saikia D, Kumar A (2004) Ionic conduction in P (VDF-HFP)/PVDF-(PC + DEC)-LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 49(16):2581–2589
Ramesh S, Lu SC (2011) Effect of lithium salt concentration on crystallinity of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-based solid polymer electrolytes. J Mol Struct 994(1-3):403–409
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ (2015) Ion-transport study in nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes based on chitosan: electrical and dielectric analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41774
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, Xiao S, Chang Z, Wu Y (2013) Composite of a nonwoven fabric with poly (vinylidene fluoride) as a gel membrane of high safety for lithium ion battery. Energy Environ Sci 6(2):618–624
Ding Y, Zhang P, Long Z, Jiang Y, Xu F, Di W (2008) Preparation of PVdF-based electrospun membranes and their application as separators. Sci Technol Adv Mater 9(1):015005
Kim I, Kim BS, Nam S, Lee HJ, Chung HK, Cho SM, Luu THT, Hyun S, Kang C (2018) Cross-linked poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropene) (PVDF-co-HFP) gel polymer electrolyte for flexible li-ion battery integrated with organic light emitting diode (OLED). Materials 11(4):543
Kim JR, Choi SW, Jo SM, Lee WS, Kim BC (2005) Characterization and properties of P (VdF-HFP)-based fibrous polymer electrolyte membrane prepared by electrospinning. J Electrochem Soc 152(2):A295–A300
Ali S, Tan C, Waqas M, Lv W, Wei Z, Wu S, Boateng B, Liu J, Ahmed J, Xiong J, Goodenough JB, He W (2018) Highly efficient PVDF-HFP/colloidal alumina composite separator for high-temperature lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater Interfaces 5(5):1701147
Oh SG, Lee YG, Kim KM, Lee YM, Kim SH, Kim YJ, Ko JM (2013) Separator properties of silk-woven fabrics coated with PVdF-HFP and silica and the charge-discharge characteristics of Lithium-ion batteries adopting them. Korean Chem Eng Res 51(3):330–334
Luo R, Wang C, Zhang Z, Lv W, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Luo X, He W (2018) Three-dimensional nanoporous polyethylene-reinforced PVDF-HFP separator enabled by dual-solvent hierarchical gas liberation for ultrahigh-rate Lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1(3):921–927
Xu W, Wang J, Ding F, Chen X, Nasybulin E, Zhang Y, Zhang JG (2014) Lithium metal anodes for rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ Sci 7(2):513–537
Li Z, Huang J, Liaw BY, Metzler V, Zhang J (2014) A review of lithium deposition in lithium-ion and lithium metal secondary batteries. J Power Sources 254:168–182
Shaju KM, Bruce PG (2008) A stoichiometric nano-LiMn 2 O 4 spinel electrode exhibiting high power and stable cycling. Chem Mater 20(17):5557–5562
Sun Y, Jin S (1998) Synthesis and electrochemical characteristics of spinel phase. J Mater Chem 8(11):2399–2404
Shalu S, Singh VK, Singh RK (2015) Development of ion conducting polymer gel electrolyte membranes based on polymer PVdF-HFP, BMIMTFSI ionic liquid and the Li-salt with improved electrical, thermal and structural properties. J Mater Chem C 3(28):7305–7318
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017M1A2A2086648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 123 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, YK., Kim, MC., Moon, SH. et al. Pore-controlled polymer membrane with Mn (II) ion trapping effect for high-rate performance LiMn2O4 cathode. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 475–484 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4153-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4153-2