Abstract
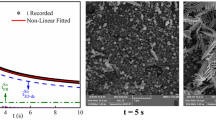
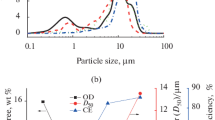
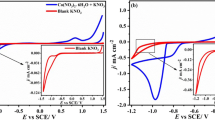
Metallic lead (Pb) has been electrodeposited on FTO substrate at room temperature from aqueous nitrate solution under constant applied potential in the range of − 0.46 to − 0.8 V vs. SCE. Cyclic voltammetry shows that 3D nucleation and growth are the main feature at higher electrolyte concentration when the profile is recorded at 20 mVs−1. While a single step potential facilitates the deposition of faceted crystals of Pb, distinguished lead having cabbage-like morphology can be deposited by applying sequential two step potentials. The I-t response shows that the deposition is initiated through instantaneous 2D nucleation and growth at the shorter time domain followed by 3D nucleation and growth in 0.4 M Pb(NO3)2. Theoretical simulation of the closely matched experimental I-t profile for simple step potential provides a 2D rate constant of 2.00 ± 0.04 × 10−7 mol cm−2 s−1 while for 3D, the vertical and plane growth rate constant of 3.27 ± 0.05 × 10−5 mol cm−2 s−1 and 2.00 ± 0.04 × 10−7 mol cm−2 s−1, respectively. The formation of the cabbage morphology has been discussed on the basis of time evaluation of FE-SEM. The high surface area of unique lead deposits with cabbage morphology shows better life time and oxygen sensitivity in a typical oxygen sensor application.

ᅟ









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delayen J, Dick G, Mercereau J (1981) Test of a ß≃ 0.1 superconducting split ring resonator. IEEE Trans Magn 17(1):939–942
Pavlov D (1993) Premature capacity loss (PCL) of the positive lead/acid battery plate: a new concept to describe the phenomenon. J Power Sources 42(3):345–363
Avellaneda CO, Napolitano MA, Kaibara EK, Bulhões LOS (2005) Electrodeposition of lead on ITO electrode: influence of copper as an additive. Electrochim Acta 50(6):1317–1321
Rashkova B, Guel B, Pötzschke RT, Staikov G, Lorenz WJ (1998) Electrodeposition of Pb on n-Si (111). Electrochim Acta 43(19-20):3021–3028
Mukhopadhyay I, Raghavan MSS, Sharon M, Minoura H, Veluchamy P (1994) Photoelectrochemical studies of photoactive lead oxide prepared by the “potential pulse coupled potentiodynamic anodization technique” in alkaline medium. J Electroanal Chem 379(1-2):531–534
Patel DB, Mukhopadhyay I (2015) Schottky junction solar cells based on non-stoichiometric PbO x films. J Phys D Appl Phys 48(2):025102
Willett M (2014) Oxygen sensing for industrial safety - evolution and new approaches. Sensors 14(4):6084–6103
Winand R (1994) Electrodeposition of metals and alloys—new results and perspectives. Electrochim Acta 39(8-9):1091–1105
Ghali E, Girgis M (1985) Electrodeposition of lead from aqueous acetate and chloride solutions. Metall Trans B 16(3):489–496
Mostany J, Parra J, Scharifker BR (1986) The nucleation of lead from halide-containing solutions. J Appl Electrochem 16(3):333–338
Mostany J, Mozota J, Scharifker BR (1984) Three-dimensional nucleation with diffusion controlled growth: Part II. The nucleation of lead on vitreous carbon. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 177(1-2):25–37
Popov KI, Stojilković ER, Radmilović V, Pavlović MG (1997) Morphology of lead dendrites electrodeposited by square-wave pulsating overpotential. Powder Technol 93(1):55–61
Danilov FI, Protsenko VS, Vasil’eva EA, Kabat OS (2011) Antifriction coatings of Pb–Sn–Cu alloy electro-deposited from methanesulphonate bath. Trans IMF 89(3):151–115
Wong SM, Abrantes LM (2005) Lead electrodeposition from very alkaline media. Electrochim Acta 51(4):619–626
Carlos IA, Siqueira JLP, Finazzi GA, De Almeida MRH (2003) Voltammetric study of lead electrodeposition in the presence of sorbitol and morphological characterization. J Power Sources 117(1-2):179–186
Carlos IA, Matsuo TT, Siqueira JLP, De Almeida MRH (2004) Voltammetric and morphological study of lead electrodeposition on copper substrate for application of a lead–acid batteries. J Power Sources 132(1-2):261–265
Gu Y-Y, Zhou Q-H, Yang T-Z, Wei LIU, Zhang D-C (2011) Lead electrodeposition from alkaline solutions containing xylitol. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 21(6):1407–1413
Bhatt AI, Bond AM, Zhang J (2007) Electrodeposition of lead on glassy carbon and mercury film electrodes from a distillable room temperature ionic liquid, DIMCARB. J of Solid State Electrochem 11(12):1593–1603
Katayama Y, Fukui R, Miura T (2013) Electrodeposition of Lead from 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium Bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide Ionic Liquid. J Electrochem Soc 160(6):D251–D255
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Lačnjevac UČ (2011) Formation of two-dimensional (2D) lead dendrites by application of different regimes of electrolysis. J Solid State Electrochem 16:2121–2126
Nikolić ND, Ivanović ER, Branković G, Lačnjevac UČ, Stevanović SI, Stevanović JS, Pavlović MG (2015) Electrochemical and crystallographic aspects of lead granular growth. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci 46(4):1760–1774
Fletcher S (1983) Some new formulae applicable to electrochemical nucleation/growth/collision. Electrochim Acta 28(7):917–923
O’M Bockris AKNR J, Aldeco MG (2000) Modern electrochemistry, vol 2. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York
Jaya S, Prabhakarrao G, Prasadarao T (1986) Bull Electrochem 2(1):65–68
Hills GJ, Schiffrin DJ, Thompson J (1974) Electrochemical nucleation from molten salts—I. Diffusion controlled electrodeposition of silver from alkali molten nitrates. Electrochim Acta 19(11):657–670
Bewick A, Fleischmann M, Thirsk HR (1962) Kinetics of the electrocrystallization of thin films of calomel. Trans Faraday Soc 58:2200–2216
Armstrong RD, Fleischmann M, Thirsk HR (1966) The anodic bbhaviour of mercury in hydroxide ion solutions. J Electroanal Chem 11(3):208–223
Cobianu C, Serban B, Avramescu V, Hobbs B, Pratt K, Willett M (2012) Lifetime considerations for lead-free oxygen galvanic sensors. Ann Acad Romanian Sci 5:7–8
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Solar Research & Development Centre (SRDC), Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University (PDPU), for providing the technical and financial assistance.
Funding
Financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, (Project number SR/S1/PC-44/2011), is deeply acknowledged to carry out this whole investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhagat, D., Waldiya, M. & Mukhopadhyay, I. Electrochemical deposition of cabbage-like lead microstructures on fluorine-doped tin oxide for oxygen sensor application. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 159–167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4110-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4110-0