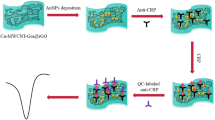
Abstract
Epidemiological studies have demonstrated an association between the risk of cardiovascular events and increasing C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration. This paper reports the development of an immunosensor for the assessment of the cardiovascular process using anti-C-reactive protein antibody immobilized onto a gold-printed screen electrode. Positive and negative human sera were successfully evaluated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and atomic force microscopy (AFM). EIS results show that, after the incubation with positive serum for myocardial infarction, the resistance increased about two times in relation to the negative serum. A linear range from 6.25 to 50 μg mL−1 and detection limit of 0.78 μg mL−1 using DPV were obtained. The immunosensor developed for the CRP detection using gold electrode revealed efficacy and a potential use for the diagnosis and monitoring of the progression of cardiovascular diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamishima K, Yamaguchi J, Honda A, Ogawa H, Hagiwara N (2015) Effect of concurrent elevation of serum creatinine and C-reactive protein values on the long-term outcome in patients with ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 1(188):102–104
Brieger D, Eagle KA, Goodman SG, Steg PG, Budaj A, White K, Montalescot G (2004) Acute coronary syndromes without chest pain, an underdiagnosed and undertreated high-risk group: insights from the global registry of acute coronary events. Chest 126(2):461–469
Gilstrap LG, Wang TJ (2012) Biomarkers and cardiovascular risk assessment for primary prevention: an update. Clin Chem 58(1):72–82
Ge Y, Wang TJ (2012) Identifying novel biomarkers for cardiovascular disease risk prediction. J Intern Med 272(5):430–439
Montgomery JE, Brown JR (2013) Metabolic biomarkers for predicting cardiovascular disease. Vasc Health Risk Manag 9:37–45
Nystron T (2007) C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Clin Sci 113:79–81
Ramasamy I (2011) Biochemical markers in acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta 412(15–16):1279–1296
Ridker PM (2003) C-reactive protein: a simple test to help predict risk of heart attack and stroke. Circulation 108(12):81–85
Weinstein G, Lutski M, Goldbourt U, Tanne D (2017) C-reactive protein is related to future cognitive impairment and decline in elderly individuals with cardiovascular disease. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 69:31–37
Bryan T, Luo X, Bueno PR, Davis JJ (2013) An optimised electrochemical biosensor for the label-free detection of C-reactive protein in blood. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):94–98
Calabrò P, Golia E, Yeh ETH (2012) Role of C-reactive protein in acute myocardial infarction and stroke: possible therapeutic approaches. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13(1):4–16
Chan D, Ng LL (2010) Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. BMC Med 8(34):1–11
Hindman N, Grande P, Harrell FE, Anderson C, Harrison D, Ideker RE, Selvester RH, Wagner GS (1986) Relation between electrocardiographic and enzymatic methods of estimating acute myocardial infarct size. Am J Cardiol 58(1):31–35
Kehl DW, Iqbal N, Fard A, Kipper BA, De La Parra Landa A, Maisel AS (2012) Biomarkers in acute myocardial injury. Transl Res 159(4):252–264
Lewandrowski KB (2014) Cardiac markers of myocardial necrosis. A history and discussion of milestones and emerging new trends. Clin Lab Med 34(1):31–41
Loria V, Leo M, Biasillo G, Dato I, Biasucci LM (2008) Biomarkers in acute coronary syndrome. Biomark Insights 3:453–468
Madjid M, Willerson JT (2011) Inflammatory markers in coronary heart disease. Br Med Bull 100:23–38
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM, Tennent GA, Gallimore JR, Kahan MC, Bellotti V, Hawkins PN, Myers RM, Smith MD, Polara A, Cobb AJ, Ley SV, Aquilina JA, Robinson CV, Sharif I, Gray GA, Sabin CA, Jenvey MC, Kolstoe SE, Thompson D, Wood SP (2006) Targeting C-reactive protein for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Nature 440:1217–1221
Dekker MS, Mosterd A, van 't Hof AW, Hoes AW (2010) Novel biochemical markers in suspected acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and critical appraisal. Heart 96(13):1001–1010
Thévenot DR, Toth K, Durst RA, Wilson GS (2001) Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification. Biosens Bioelectron 16:121–131
Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, Jablonski KA, Rice MM, Warnica JW, Domanski MJ, Hsia J, Gersh BJ, Rifai N, Ridker PM, Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E (2007) Prognostic significance of the Centers for Disease Control/American Heart Association high-sensitivity C-reactive protein cut points for cardiovascular and other outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circulation 115(12):1528–1536
Schulz S, Lüdike H, Lierath M, Schlitt A, Werdan K, Hofmann B, Gläser C, Schaller HG, Reichert S (2016) C-reactive protein levels and genetic variants of CRP as prognostic markers for combined cardiovascular endpoint (cardiovascular death, death from stroke, myocardial infarction, and stroke/TIA). Cytokine 88:71–76
Mody P, Joshi PH, Khera A, Ayers CR, Rohatgi A (2016) Beyond coronary calcification, family history, and C-reactive protein: cholesterol efflux capacity and cardiovascular risk prediction. J Am Coll Cardiol 67(21):2480–2487
Rama EC, Gonzalez-Garcia MB, Costa-Garcia A (2014) Competitive electrochemical immunosensor for amyloid-beta 1-42 detection based on gold nanostructurated screen-printed carbon electrodes. Sens Actuators B Chem 201:567–571
Chen X, Wang Y, Zhou J, Yan W, Li X, Zhu JJ (2008) Electrochemical impedance immunosensor based on three-dimensionally ordered macroporous gold film. Anal Chem 80(6):2133–2140
Zhang Y, Rojas OJ (2017) Immunosensors for C-reactive protein based on ultrathin films of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils. Biomacromolecules 18(2):526–534
Qureshi A (2012) Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: a review. Sens Actuators B Chem 171-172:62–76
Sadana A, Sadana N Medical applications of biosensors - Chapter 8. In: Handbook of biosensors and biosensor kinetics, 1st edn. E-Publishing: Elsevier, pp 197–222
Mehrotra P (2016) Biosensors and their applications—a review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 16(2):153–159
Ibupoto ZH, Jamal N, Khun K, Willander M (2012) Development of a disposable potentiometric antibody immobilized ZnO nanotubes based sensor for the detection of C-reactive protein. Sens Actuators B Chem 166-167:809–814
Nakamura T, Suchiya T, Ohana T (2014) Fabrication of sulfur-functionalized DLC films by photochemical modification and attachment of gold nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 317:443–448
Ashwell GJ, Williams AT, Barnes SA, Chappell SL, Phillips LJ, Robinson BJ, Urasinska-Wojcik B, Wierzchowiec P, Gentle IR, Wood BJ (2011) Self-assembly of amino-thiols via gold-nitrogen links and consequence for in situ elongation of molecular wires on surface-modified electrodes. J Phys Chem C 115:4200–4208
Oliveira AAS, Costa DAS, Teixeira IF, Moura FCC (2015) Gold nanoparticles supported on modified red mud for biphasic oxidation of sulfur compounds: a synergistic effect. Appl Catal B Environ 162:475–482
Di Felice R, Selloni A (2004) Adsorption modes of cysteine on Au(111): thiolate, amino-thiolate, disulfide. J Chem Phys 120(10):4906–4914
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Leff DV, Brandt L, Heath JR (1996) Synthesis and characterization of hydrophobic, organically-soluble gold nanocrystals functionalized with primary amines. Langmuir 12(20):4723–4730
Hamm UW, Lazarescu V, Kolb DM (1996) Adsorption of pyrazine on Au(111) and Ag(111) electrodes an ex situ XPS study. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 92:3785–3790
Vallee A, Humblot V, Pradier CM (2010) Peptide interactions with metal and oxide surfaces. Acc Chem Res 43(10):1297–1306
Hennessey H, Afara N, Omanovic S, Padjen AL (2009) Electrochemical investigations of the interaction of C-reactive protein (CRP) with a CRP antibody chemically immobilized on a gold surface. Anal Chim Acta 643(1–2):45–53
Brito-Madurro AG, Ferreira LF, Vieira SN, Ariza RG, Goulart Filho LR, Madurro JM (2007) Immobilization of purine bases on a poly-4-aminophenol matrix. J Mater Sci 42(9):3238–3243
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Humana Press, New York City
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank teacher Abílio Borghi for the review of the English manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The research project was approved by the Ethics Committee of UFU (number 721.990).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resende, L.O., de Castro, A.C.H., Andrade, A.O. et al. Immunosensor for electrodetection of the C-reactive protein in serum. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 1365–1372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3820-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3820-z