Abstract
Styrene-butadiene rubber is a copolymer widely used in making car tires and has excellent abrasion resistance. The Young’s modulus and tribology of pure styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) polymer and carbon nanotube reinforced polymer composites have been investigated using molecular dynamics simulations. The mechanism of enhanced tribology properties using carbon nanotube has been studied and discussed. The obtained Young’s modulus shows the enhancement in mechanical properties of SBR polymer when carbon nanotubes are used as reinforcement. The concentration, temperature and velocity profiles, radial distribution function, frictional stresses, and cohesive energy density are calculated and analyzed in detail. The Young’s modulus of SBR matrix increases about 29.16% in the presence of the 5% CNT. The atom movement velocity and average cohesive energy density in the friction area of pure SBR matrix was found to be more than that of the CNT/SBR composite.

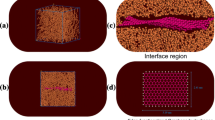
Initial and final conditions of (a) pure SBR matrix and (b) CNT/SBR matrix subjected toshear loading and frictional stresses of top Fe layers of both pure SBR and CNT/SBR composite










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen SL, Brazel CS (2012) Fundamental principles of polymeric materials. Wiley, Hoboken, p 126
Ward IM, Sweeney J (2004) An introduction to the mechanical properties of solid polymers. Wiley, Chichester, p 302
David LB, Grefory SW (2006) A low friction and ultra-low wear rate PEEK/PTFE composite. Wear 26:410–418
Li J, Xia Y (2009) The reinforcement effect of carbon fiber on the friction and wear properties of carbon fiber reinforced PA6 composites. Fiber Polym 10:519–525
Samyn P, Schoukens G (2009) Thermochemical sliding interactions of short carbon fiber polyimide composites at high PV-conditions. Mater Chem Phys 115:185–195
Luo W, Liu Q, Li Y, Zhou S, Zou H, Liang M (2016) Enhanced mechanical and tribological properties in polyphenylene sulfide/polytetrafluoroethylene composites reinforced by short carbon fiber. Compos Part B Eng 91:579–588
Liu N, Wang J, Yang J, Han G, Yan F (2015) Effects of nano-sized and micro-sized carbon fibers on the interlaminar shear strength and tribological properties of high strength glass fabric/phenolic laminate in water environment. Compos Part B Eng 68:92–99
Zhou JH, Sui ZJ, Li P, Chen D, Dai YC, Yuan WK (2006) Structural characterization of carbon nanofibers formed from different carbon-containing gases. Carbon 44:3255–3262
Mall S, Lee H, He P, Shi D, Narasimhadevara S, Yeo-Heung Y, Shanov V, Schulz MJ (2007) Characterization of carbon nanotube/nanofiber-reinforced polymer composites using an instrumented indentation technique. Compos Part B Eng 38:58–65
Minaie B, Rodriguez AJ, Guzman ME, Lim CS (2011) Mechanical properties of carbon nanofiber/fiber-reinforced hierarchical polymer composites manufactured with multiscale-reinforcement fabrics. Carbon 49:937–948
Zhu Y, Bakis CE, Adair JH (2012) Effects of carbon nanofiller functionalization and distribution on interlaminar fracture toughness of multi-scale reinforced polymer composites. Carbon 50:1316–1331
Finegan IC, Tibbetts GG, Gibson RF (2003) Modeling and characterization of damping in carbon nano-fiber/polypropylene composites. Compos Sci Technol 63:1629–1635
Sharma S, Chandra R, Kumar P, Kumar N (2016) Mechanical properties of carbon nanofiber reinforced polymer composites-molecular dynamics approach. JOM 68:1717–1727
Park SH, Bandaru PR (2010) Improved mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/polymer composites through the use of carboxyl-epoxide functional group linkages. Polymer 51:5071–5077
Breuer O, Sundaraj U (2004) Big returns from small fibers: a review of polymer/carbon nanotube composites. Polym Compos 25:630–645
Lourie O, Cox DM, Wagner HD (1998) Buckling and collapse of embedded carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 81:1638–1641
Jindal P, Pande S, Sharma P, Mangla V, Chaudhary A, Patel D, Singh BP, Mathur RB, Goyal M (2013) High strain rate behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotubes-polycarbonate composites. Compos Part B Eng 45:417–422
Chawla R, Sharma S (2017) Molecular dynamics simulation of carbon nanotube pull-out from polyethylene matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 144:169–177
Sharma S, Chandra R, Kumar P, Kumar N (2016) Molecular dynamics simulation of functionalized SWCNT-polymer composites. J Compos Mater. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998316628973jcm.sagepub.com
Sharma S, Chandra R, Kumar P, Kumar N (2015) Thermo-mechanical characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotube reinforced polycarbonate composites: a molecular dynamics approach. C R Mecanique 343:371–396
Li Y, Wang S, He E, Quan W (2016) The effect of sliding velocity on the tribological properties of polymer/carbon nanotube composites. Carbon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.04.077
Li HL, Wang C, Dong B, Gao GY, Xu MW (2008) A study on microhardness and tribological behavior of carbon nanotubes reinforced AMMA-CNTs copolymer nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 478:314–318
Li Y, Wang S, Wang Q (2017) Enhancement of tribological properties of polymer composites reinforced by functionalized graphene. Compos Part B Eng 120:83–91
Li Y, Wang S, Wang Q, Xing M (2016) Molecular dynamics simulations of tribology properties of NBR (nitrile-butadiene rubber) /carbon nanotube composites. Compos Part B 97:62–67
Rigby D, Sun H, Eichinger BE (1997) Computer simulations of poly(ethylene oxide): force field, pvt diagram and cyclization behaviour. Polym Int 44:311–330
Li Y, Wu Y, Luo Y, Chan TW, Li Z, Wu S (2015) A combined experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study on the structures and properties of three types of styrene butadiene rubber. Mater Today Commun 4:35–41
Zhang J, Liang Y, Yan J, Lou Z (2007) Study of the molecular weight dependence of glass transition temperature for amorphous poly(L-lactide) by molecular dynamics simulation. Polymer 48(16):4900–4905
Fletcher R, Reeves CM (1964) Function minimization by conjugate gradients. Comput. J. 7(2):149–154
Andersen HC (1980) Molecular dynamics simulations at constant pressure and/or temperature. J. Chem. Phys. 72(4):2384–2393
Berendsen HJ, Postma JV, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola ARHJ, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81(8):3684–3690
Verlet L (1967) Computer" experiments" on classical fluids. I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules. Phys Rev 159(1):98
Sharma S, Chandra R, Kumar P, Kumar N (2015) Molecular dynamics simulation of polymer/carbon nanotube composites. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica 28(4):409–419
Zhang W, Qing Y, Zhong W, Sui G, Yang X (2017) Mechanism of modulus improvement for epoxy resin matrices: a molecular dynamics simulation. React Funct Polym 111:60–67
Girun N, Ahmadun FR, Rashid SA, Ali Atieh M (2007) Multi-Wall carbon nanotubes/styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) nanocomposite. Fuller, Nanotub, Car N 15(3):207–214
Li Y, Wang S, Arash B, Wang Q (2016) A study on tribology of nitrile-butadiene rubber composites by incorporation of carbon nanotubes: molecular dynamics simulations. Carbon 100:145–150
Delle Site L, Abrams CF, Alavi A, Kremer K (2002) Polymers near metal surfaces: selective adsorption and global conformations. Phys Rev Lett 89:156103/1–156103/4
Koch N, Kahn A, Ghijsen J, Pireaux JJ, Schwartz J, Johnson RL, Elschner A (2003) Conjugated organic molecules on metal versus polymer electrodes: demonstration of a key energy level alignment mechanism. Appl Phys Lett 82:70–72
Ludema KC, Tabor D (1968) Friction and viscoelastic properties of polymeric solids. Rubber Chem Technol 41:462–476
Jon AH, Wayne L, Gladfelter GH (1999) Probing polymer viscoelastic relaxations with temperature-controlled friction force microscopy. Macromolecules 32:3360–3367
Fleisher G (1973) Energetische Methode der Bestimmung des Verschleiβes/Schmierungste chnik. Bandolier 4:9–12
Chilan C, Wenxia W, Jianguo Z (2016) The effect of surface functionality of carbon nanotubes on mechanical and tribological behaviours of carbon fibre-filled styrene–butadiene rubber composite. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 29(9):1167–1175
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional University for providing the computation facility and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chawla, R., Sharma, S. A molecular dynamics study on Young’s modulus and tribology of carbon nanotube reinforced styrene-butadiene rubber. J Mol Model 24, 96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3636-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3636-5