Abstract
Objective
This integrative review aimed to report the toxic effect of submicron and nano-scale commercially pure titanium (cp Ti) debris on cells of peri-implant tissues.
Materials and methods
A systematic search was carried out on the PubMed electronic platform using the following key terms: Ti “OR” titanium “AND” dental implants “AND” nanoparticles “OR” nano-scale debris “OR” nanometric debris “AND” osteoblasts “OR “cytotoxicity” OR “macrophage” OR “mutagenic” OR “peri-implantitis”. The inclusion criteria involved articles published in the English language, until December 26, 2020, reporting the effect of nano-scale titanium particles as released from dental implants on the toxicity and damage of osteoblasts.
Results
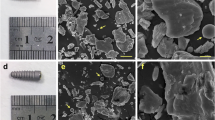
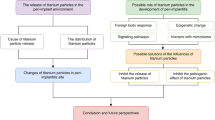
Of 258 articles identified, 14 articles were selected for this integrative review. Submicron and nano-scale cp Ti particles altered the behavior of cells in culture medium. An inflammatory response was triggered by macrophages, fibroblasts, osteoblasts, mesenchymal cells, and odontoblasts as indicated by the detection of several inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and PGE2. The formation of a bioactive complex composed of calcium and phosphorus on titanium nanoparticles allowed their binding to proteins leading to the cell internalization phenomenon. The nanoparticles induced mutagenic and carcinogenic effects into the cells.
Conclusions
The cytotoxic effect of debris released from dental implants depends on the size, concentration, and chemical composition of the particles. A high concentration of particles on nanometric scale intensifies the inflammatory responses with mutagenic potential of the surrounding cells.
Clinical relevance
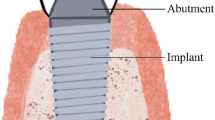
Titanium ions and debris have been detected in peri-implant tissues with different size, concentration, and forms. The presence of metallic debris at peri-implant tissues also stimulates the migration of immune cells and inflammatory reactions. Cp Ti and TiO2 micro- and nano-scale particles can reach the bloodstream, accumulating in lungs, liver, spleen, and bone marrow.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moraschini V, Poubel LADC, Ferreira VF, Barboza EDSP (2015) Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental implants reported in longitudinal studies with a follow-up period of at least 10 years: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2014.10.023
Albrektsson T, Buser D, Chen ST, Cochran D, DeBruyn H, Jemt T, Koka S, Nevins M, Sennerby L, Simion M, Taylor TD, Wennerberg A (2012) Statements from the Estepona consensus meeting on peri-implantitis, February 2–4, 2012. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:781–782
Derks J, Tomasi C (2015) Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin Periodontol 42:S158–S171. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12334
Kordbacheh Changi K, Finkelstein J, Papapanou PN (2019) Peri-implantitis prevalence, incidence rate, and risk factors: a study of electronic health records at a U.S. dental school. Clin Oral Implants Res 30:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13416
Lee CT, Huang YW, Zhu L, Weltman R (2017) Prevalences of peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent 62:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2017.04.011
Rakic M, Galindo-Moreno P, Monje A, Radovanovic S, Wang HL, Cochran D, Sculean A, Canullo L (2018) How frequent does peri-implantitis occur? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig 22:1805–1816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2276-y
Patel K, Mardas N, Donos N (2013) Radiographic and clinical outcomes of implants placed in ridge preserved sites: a 12-month post-loading follow-up. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:599–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02500.x
Zhou W, Tangl S, Reich KM, Kirchweger F, Liu Z, Zechner W, Christian Ulm, Rausch-Fan X (2019) The influence of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the osseointegration of titanium implants with different surface modifications—a histomorphometric study in high-fat diet/low-dose streptozotocin-treated rats. Implant Dent 28:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000836
Fretwurst T, Nelson K, Tarnow DP, Wang HL, Giannobile WV (2018) Is metal particle release associated with peri-implant bone destruction? An emerging concept. J Dent Res 97:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517740560
Noronha Oliveira M, Schunemann WVH, Mathew MT, Henriques B, Magini RS, Teughels W, Souza JCM (2018) Can degradation products released from dental implants affect peri-implant tissues? J Periodontal Res 53:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12479
Apaza-Bedoya K, Tarce M, Benfatti CAMAM et al (2017) Synergistic interactions between corrosion and wear at titanium-based dental implant connections: a scoping review. J Periodontal Res 52:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12469
Souza JCM, Apaza-Bedoya K, Benfatti CAM et al (2020) A comprehensive review on the corrosion pathways of titanium dental implants and their biological adverse effects. Met. 10(9):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091272
Bressan E, Ferroni L, Gardin C, Bellin G, Sbricoli L, Sivolella S, Brunello G, Schwartz-Arad D, Mijiritsky E, Penarrocha M, Penarrocha D, Taccioli C, Tatullo M, Piattelli A, Zavan B (2019) Metal nanoparticles released from dental implant surfaces: potential contribution to chronic inflammation and peri-implant bone loss. Materials (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12122036
Berryman Z, Bridger L, Hussaini HM, Rich AM, Atieh M, Tawse-Smith A (2019) Titanium particles: an emerging risk factor for peri-implant bone loss. Saudi Dent J 32:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sdentj.2019.09.008
Wilson TG, Valderrama P, Burbano M et al (2015) Foreign bodies associated with peri-implantitis human biopsies. J Periodontol 86:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2014.140363
Michalakis KX, Lino P, Muftu S et al (2014) The effect of different implant–abutment connections on screw joint stability. J Oral Implantol 40:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-11-00032
Prado AM, Pereira J, Silva FS, Henriques B, Nascimento RM, Benfatti CAM, López-López J, Souza JCM (2017) Wear of Morse taper and external hexagon implant joints after abutment removal. J Mater Sci Mater Med 28:65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-017-5879-6
Suárez-López Del Amo F, Garaicoa-Pazmiño C, Fretwurst T et al (2018) Dental implants-associated release of titanium particles: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 29:1085–1100. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13372
Happe A, Sielker S, Hanisch M, Jung S (2019) The biologic effect of particulate titanium contaminants of dental implants on human osteoblasts and gingival fibroblasts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 34:673–680. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6929
Yang F, Tang J, Dai K, Huang Y (2019) Metallic wear debris collected from patients induces apoptosis in rat primary osteoblasts via reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Med Rep 19:1629–1637. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9825
Suárez-López Del Amo F, Rudek I, Wagner VP et al Titanium activates the DNA damage response pathway in oral epithelial cells: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:1413–1420. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6077
Dodo CG, Meirelles L, Aviles-Reyes A, Ruiz KGS, Abranches J, Cury AADB (2017) Pro-inflammatory analysis of macrophages in contact with titanium particles and porphyromonas gingivalis. Braz Dent J 28:428–434. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201701382
Pettersson M, Kelk P, Belibasakis GN, Bylund D, Molin Thorén M, Johansson A (2017) Titanium ions form particles that activate and execute interleukin-1$β$ release from lipopolysaccharide-primed macrophages. J Periodontal Res 52:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12364
He X, Hartlieb E, Rothmund L, Waschke J, Wu X, van Landuyt KL, Milz S, Michalke B, Hickel R, Reichl FX, Högg C (2015) Intracellular uptake and toxicity of three different titanium particles. Dent Mater 31:734–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2015.03.017
Rutkunas V, Bukelskiene V, Sabaliauskas V, Balciunas E, Malinauskas M, Baltriukiene D (2015) Assessment of human gingival fibroblast interaction with dental implant abutment materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5481-8
Vallès G, González-Melendi P, Saldaña L et al (2008) Rutile and titanium particles differentially affect the production of osteoblastic local factors. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A 84:324–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.31315
Valles G, Gonzalez-Melendi P, Gonzalez-Carrasco JL et al (2006) Differential inflammatory macrophage response to rutile and titanium particles. Biomaterials 27:5199–5211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.05.045
Wang ML, Tuli R, Manner PA, Sharkey PF, Hall DJ, Tuan RS (2003) Direct and indirect induction of apoptosis in human mesenchymal stem cells in response to titanium particles. J Orthop Res 21:697–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00241-3
Kraft CN, Diedrich O, Burian B, Schmitt O, Wimmer MA (2003) Microvascular response of striated muscle to metal debris. A comparative in vivo study with titanium and stainless steel. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 85:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.85B1.12749
Goiato MC, Pellizzer EP, da Silva EVF, Bonatto LR, dos Santos DM (2015) Is the internal connection more efficient than external connection in mechanical, biological, and esthetical point of views? A systematic review. Oral Maxillofac Surg 19:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-015-0494-5
Saidin S, Abdul Kadir MR, Sulaiman E, Abu Kasim NH (2012) Effects of different implant-abutment connections on micromotion and stress distribution: prediction of microgap formation. J Dent 40:467–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2012.02.009
Macedo JP, Pereira J, Vahey BR et al (2016) Morse taper dental implants and platform switching: the new paradigm in oral implantology. Eur J Dent 10:148–154. https://doi.org/10.4103/1305-7456.175677
Souza JCM, Henriques M, Teughels W, Ponthiaux P, Celis JP, Rocha LA (2015) Wear and corrosion interactions on titanium in oral environment: literature review. J Bio- Tribo-Corrosion 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-015-0013-0
Niinomi M (1998) Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 243:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00806-X
Shah FA, Trobos M, Thomsen P, Palmquist A (2016) Commercially pure titanium (cp-Ti) versus titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) materials as bone anchored implants – is one truly better than the other? Mater Sci Eng C 62:960–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.01.032
Kuromoto NK, Simão RA, Soares GA (2007) Titanium oxide films produced on commercially pure titanium by anodic oxidation with different voltages. Mater Charact 58:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2006.03.020
Lara Rodriguez L, Sundaram PA, Rosim-Fachini E, Padovani AM, Diffoot-Carlo N (2014) Plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on γtiAl alloy for potential biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res - Part B Appl Biomater 102:988–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33079
Noumbissi S, Scarano A, Gupta S (2019) A literature review study on atomic ions dissolution of titanium and its alloys in implant dentistry. Mater (Basel, Switzerland) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030368
Addison O, Davenport AJ, Newport RJ, Kalra S, Monir M, Mosselmans JFW, Proops D, Martin RA (2012) Do “passive” medical titanium surfaces deteriorate in service in the absence of wear? J R Soc Interface 9:3161–3164. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2012.0438
Souza JCM, Barbosa SL, Ariza EA, Henriques M, Teughels W, Ponthiaux P, Celis JP, Rocha LA (2015) How do titanium and Ti6Al4V corrode in fluoridated medium as found in the oral cavity? An in vitro study. Mater Sci Eng C 47:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.11.055
Nuevo-Ordóñez Y, Montes-Bayón M, Blanco-González E, Paz-Aparicio J, Raimundez JD, Tejerina JM, Peña MA, Sanz-Medel A (2011) Titanium release in serum of patients with different bone fixation implants and its interaction with serum biomolecules at physiological levels. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:2747–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5232-8
Ribeiro AR, Gemini-Piperni S, Travassos R, Lemgruber L, C. Silva R, Rossi AL, Farina M, Anselme K, Shokuhfar T, Shahbazian-Yassar R, Borojevic R, Rocha LA, Werckmann J, Granjeiro JM (2016) Trojan-like internalization of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles by human osteoblast cells. Sci Rep 6:23615. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23615
Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, el Ghissassi F, Cogliano V (2006) Carcinogenicity of carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. Lancet Oncol 7:295–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70651-9
Girardello F, Custódio Leite C, Vianna Villela I, da Silva Machado M, Luiz Mendes Juchem A, Roesch-Ely M, Neves Fernandes A, Salvador M, Antonio Pêgas Henriques J (2016) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce genotoxicity but not mutagenicity in golden mussel Limnoperna fortunei. Aquat Toxicol 170:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.030
Jain AK, Senapati VA, Singh D, Dubey K, Maurya R, Pandey AK (2017) Impact of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mutagenic and genotoxic response in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells (V-79): the role of cellular uptake. Food Chem Toxicol 105:127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.04.005
Boisen AMZ, Shipley T, Jackson P et al (2012) NanoTIO2 (UV-titan) does not induce ESTR mutations in the germline of prenatally exposed female mice. Part Fibre Toxicol 9(19). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-9-19
Zdravković TP, Zdravković B, Lunder M, Ferk P (2019) The effect of micro-sized titanium dioxide on WM-266-4 metastatic melanoma cell line. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 19:60–66. https://doi.org/10.17305/BJBMS.2018.3674
Bhatavadekar NB (2012) Squamous cell carcinoma in association with dental implants: an assessment of previously hypothesized carcinogenic mechanisms and a case report. J Oral Implantol 38:792–798
Wheelis SE, Wilson TG, Valderrama P, Rodrigues DC (2018) Surface characterization of titanium implant healing abutments before and after placement. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 20:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12566
Sato S, Kishida M, Ito K (2004) The comparative effect of ultrasonic scalers on titanium surfaces: an in vitro study. J Periodontol 75:1269–1273. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2004.75.9.1269
Khraisat A, Abu-hammad O, Al-kayed AM (2004) Stability of the implant/abutment joint in a single-tooth external-hexagon implant system: clinical and mechanical review. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 6:222–229
Zembic A, Kim S, Zwahlen M, Kelly JR (2014) Systematic review of the survival rate and incidence of biologic, technical, and esthetic complications of single implant abutments supporting fixed prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 29:99–116. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.2014suppl.g2.2
Schwarz MS (2000) Mechanical complications of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 11(Suppl 1):156–158. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.2000.011S1156.x
Noronha Oliveira M, Schunemann WVH, Mathew MT et al (2018) Can degradation products released from dental implants affect peri-implant tissues? J Periodontal Res 53. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12479
Bolzoni L, Esteban PG, Ruiz-Navas EM, Gordo E (2012) Mechanical behaviour of pressed and sintered titanium alloys obtained from master alloy addition powders. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 15:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.05.019
Souza JCM, Henriques M, Oliveira R, Teughels W, Celis JP, Rocha LA (2010) Do oral biofilms influence the wear and corrosion behavior of titanium? Biofouling 26:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927011003767985
Souza JCM, Barbosa SL, Ariza E, Celis JP, Rocha LA (2012) Simultaneous degradation by corrosion and wear of titanium in artificial saliva containing fluorides. Wear 292–293:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.05.030
Manaranche C, Hornberger H (2007) A proposal for the classification of dental alloys according to their resistance to corrosion. Dent Mater 23:1428–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2006.11.030
Kirmanidou Y, Sidira M, Drosou ME et al (2016) New Ti-alloys and surface modifications to improve the mechanical properties and the biological response to orthopedic and dental implants: a review. Biomed Res Int 2908570. 10.1155/2016/2908570
Flatebø RS, Johannessen AC, Grønningsæter AG, Bøe OE, Gjerdet NR, Grung B, Leknes KN (2006) Host response to titanium dental implant placement evaluated in a human oral model. J Periodontol 77:1201–1210. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2006.050406
Souza JCM, Ponthiaux P, Henriques M, Oliveira R, Teughels W, Celis JP, Rocha LA (2013) Corrosion behaviour of titanium in the presence of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent 41:528–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2013.03.008
Huang GY, Jiang HB, Cha JY, Kim KM, Hwang CJ (2017) The effect of fluoride-containing oral rinses on the corrosion resistance of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V). Korean J Orthod 47:306–312. https://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2017.47.5.306
Vieira AC, Ribeiro AR, Rocha LA, Celis JP. (2006) Influence of pH and corrosion inhibitors on the tribocorrosion of titanium in artificial saliva. Wear 261(9):994-1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.03.031
Messias A, Rocha S, Calha N, Neto MA, Nicolau P, Guerra F (2017) Effect of intentional abutment disconnection on the micro-movements of the implant–abutment assembly: a 3D digital image correlation analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 28:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12607
Matusiewicz H (2014) Potential release of in vivo trace metals from metallic medical implants in the human body: from ions to nanoparticles – a systematic analytical review. Acta Biomater 10:2379–2403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2014.02.027
Delgado-Ruiz R, Romanos G (2018) Potential causes of titanium particle and ion release in implant dentistry: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci 19
Flatebø RS, Høl PJ, Leknes KN, Kosler J, Lie SA, Gjerdet NR (2011) Mapping of titanium particles in peri-implant oral mucosa by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and high-resolution optical darkfield microscopy. J Oral Pathol Med 40:412–420. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00958.x
Geurtsen W (2002) Biocompatibility of dental casting alloys. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 13:71–84
Souza W, Piperni SG, Laviola P, Rossi AL, Rossi MID, Archanjo BS, Leite PE, Fernandes MH, Rocha LA, Granjeiro JM, Ribeiro AR (2019) The two faces of titanium dioxide nanoparticles bio-camouflage in 3D bone spheroids. Sci Rep 9:9309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45797-6
Tawse-Smith A, Payne AGT, Kumara R, Thomson WM (2002) Early loading of unsplinted implants supporting mandibular overdentures using a one-stage operative procedure with two different implant systems: a 2-year report. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 4:33–42
Takahashi K, Takashiba S, Nagai A, Takigawa M, Myoukai F, Kurihara H, Murayama Y (1994) Assessment of Interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J Periodontol 65:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1994.65.2.147
Kumazawa R, Watari F, Takashi N, Tanimura Y, Uo M, Totsuka Y (2002) Effects of Ti ions and particles on neutrophil function and morphology. Biomaterials 23:3757–3764. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00115-1
Shanbhag AS, Jacobs JJ, Black J, Galante JO, Glant TT (1994) Macrophage/particle interactions: effect of size, composition and surface area. J Biomed Mater Res 28:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820280111
Zhang Y, Yu W, Jiang X, Lv K, Sun S, Zhang F (2011) Analysis of the cytotoxicity of differentially sized titanium dioxide nanoparticles in murine MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. J Mater Sci Mater Med 22:1933–1945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4375-7
Sund J, Palomäki J, Ahonen N, Savolainen K, Alenius H, Puustinen A (2014) Phagocytosis of nano-sized titanium dioxide triggers changes in protein acetylation. J Proteome 108:469–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2014.06.011
Souza PPC, Lerner UH (2013) The role of cytokines in inflammatory bone loss. Immunol Investig 42:555–622. https://doi.org/10.3109/08820139.2013.822766
Darowish M, Rahman R, Li P et al (2009) Reduction of particle-induced osteolysis by interleukin-6 involves anti-inflammatory effect and inhibition of early osteoclast precursor differentiation. Bone 45:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.06.004
Steeve KT, Marc P, Sandrine T, Dominique H, Yannick F (2004) IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2003.10.005
Goodman SB, Ma T, Chiu R, Ramachandran R, Lane Smith R (2006) Effects of orthopaedic wear particles on osteoprogenitor cells. Biomaterials 27:6096–6101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.023
Gill SE, Parks WC (2008) Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors: regulators of wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1334–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.10.024
Zhang X, Morham SG, Langenbach R, Young DA, Xing L, Boyce BF, Puzas EJ, Rosier RN, O'Keefe RJ, Schwarz EM (2001) Evidence for a direct role of cyclo-oxygenase 2 in implant wear debris-induced osteolysis. J Bone Miner Res 16:660–670. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.4.660
Perry MJ, Ponsford FM, Mortuza FY et al (1996) Osteolytic properties of the synovial-like tissue from aseptically failed joint prostheses. Br J Rheumatol 35:943–950. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.943
Theoleyre S, Wittrant Y, Tat SK, Fortun Y, Redini F, Heymann D (2004) The molecular triad OPG/RANK/RANKL: involvement in the orchestration of pathophysiological bone remodeling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:457–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.06.004
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by the following FCT-Portugal projects: UID/EEA/04436/2013, NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000018—HAMaBICo, and POCI-01-0145-FEDER-031035. The authors thank the financial support by the project IMPLDEBRIS-PL-3RL-IINFACTS-2019 at CESPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messous, R., Henriques, B., Bousbaa, H. et al. Cytotoxic effects of submicron- and nano-scale titanium debris released from dental implants: an integrative review. Clin Oral Invest 25, 1627–1640 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03785-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03785-z