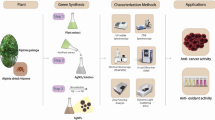
Abstract
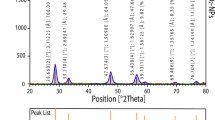
Synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles without any chemical reductant is always a challenging methodology for biological studies. In this study, sinapic acid, a phytochemical, is used for the synthesis of stable copper oxide nanoparticles. The as-synthesized nanoparticles were characterized thoroughly using UV–Visible, IR spectroscopy, Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Nanoparticles collected during different time intervals of synthesis (60,120 and 180 min) were subjected for analysis, where the occurrence of copper oxide nanoparticles with substantial morphology was seen at 180 min. Further, nanoparticles synthesized at 120 and 180 min were studied for their potential biological applications. These copper oxide nanoparticles evinced potential cytotoxic effects on breast cancer cells, MCF7 and MDA-MB231. Supplementarily, it also exhibited anti-angiogenic effect on endothelial cells (EA.hy926), thus confirming its potential to inhibit angiogenesis in cancer.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Aissa MA, Tremblay B, Andrieux-Ledier A, Maisonhaute E, Raouafi N, Courty A (2015) Copper nanoparticles of well-controlled size and shape: a new advance in synthesis and self-organization. Nanoscale 7(7):3189–3195
Alzahrani E, Ahmed RA (2016) synthesis of copper nanoparticles with various sizes and shapes: application as a superior non-enzymatic sensor and antibacterial agent. In J Electrochem Sci 11(6):4712–4723
Mott D, Galkowski J, Wang L, Luo J, Zhong CJ (2007) Synthesis of size-controlled and shaped copper nanoparticles. Langmuir 23(10):5740–5745
Pan K, Ming H, Yu H, Liu Y, Kang Z, Zhang H, Lee ST (2011) Different copper oxide nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and application for C-N cross-coupling catalysis. Crys Res Technol 46:1167–1174
Biswas A, Bayer IS, Biris AS, Wang T, Dervishi E, Faupel F (2012) Advances in top-down and bottom-up surface nanofabrication: techniques, applications & future prospects. Adv Coll Interface Sci 170(1–2):2–27
Dang TM, Le TT, Fribourg-Blanc E, Dang MC (2011) The influence of solvents and surfactants on the preparation of copper nanoparticles by a chemical reduction method. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 2(2):025004
Saikova SV, Vorob’ev SA, Nikolaeva RB, Mikhlin YL (2010) Conditions for the formation of copper nanoparticles by reduction of copper (II) ions with hydrazine hydrate solutions. Russ J Gen Chem 80(6):1122–1127
Jin-Cheng Yu, Zhao Fu-Gang, Shao Wei, Geb Cong-Wu, Li Wei-Shi (2015) Shape-controllable and versatile synthesis of copper nanocrystals with amino acids as capping agents. Nanoscale 7:8811–8818
Zhongying W, Von Annette Dem B, Kabadi KP, Agnes B, Robert HK (2013) Biological and environmental transformations of copper-based nanomaterials. ACS Nano 7(10):8715–8727
Jordan AJ, Lalic G, Sadighi JP (2016) coinage metal hydrides: synthesis, characterization, and reactivity. Chem Rev 116(15):8318–8372
Hokita Y, Kanzaki M, Sugiyama T, Arakawa R, Kawasaki H (2015) High-Concentration Synthesis of Sub-10-nm Copper Nanoparticles for Application to Conductive Nanoinks. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:19382–19389
Zhou M, Tian M, Li C (2016) Copper-based nanomaterials for cancer imaging and therapy. Bioconjug Chem 5:1188–1199
Sabbaghan M, Beheshtian J, Liarjdame RN (2015) Preparation of Cu2O nanostructures by changing reducing agent and their optical properties. Mater Lett 153:1–4
Gawande MB, Goswami A, Felpin FX, Asefa T, Huang X, Silva R, Zou X, Zboril R, Varma RS (2016) Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Chem Rev 116:3722–3811
Cioffi N, Torsi L, Ditaranto N, Tantillo G, Ghibelli L, Sabbatini L, Bleve-Zacheo T, D’Alessio M, Zambonin PG, Traversa E (2005) Copper nanoparticle/polymer composites with antifungal and bacteriostatic properties. Chem Mater 17(21):5255–5262
Solomon EI, Heppner DE, Johnston EM, Ginsbach JW, Cirera J, Qayyum M, Kieber-Emmons MT, Kjaergaard CH, Hadt RG, Tian L (2014) Copper active sites in biology. Chem Rev 114(7):3659–3853
Ingle AP, Duran N, Rai M (2014) Bioactivity, mechanism of action, and cytotoxicity of copper-based nanoparticles: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(3):1001–1009
Jaydeep B, Utpal C, Omprakash S, Prasenjit S, Anjan KD (2006) Interaction of hemoglobin and copper nanoparticles: implications in hemoglobinopathy. Nanomedicine 2(2):191–199
Gonçalves RV, Wojcieszak R, Wender H, Dias SBC, Vono LL, Eberhardt D, Teixeira SR, Rossi LM (2015) Easy access to metallic copper nanoparticles with high activity and stability for CO oxidation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(15):7987–7994
Mahmoud N, Mohammad S, Mehdi K (2014) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extract of the leaves of Euphorbia esula L and their catalytic activity for ligand-free Ullmann-coupling reaction and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 4:47313–47318
Jing X, Ye W, Qunji X, Xuedong W (2011) Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using l-ascorbic acid. Green Chem 13:900–904
Chen C (2016) sinapic acid and its derivatives as medicine in oxidative stress-induced diseases and aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:3571614
Zych M, Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak I, Wojnar W, Folwarczna J (2018) The effects of sinapic acid on the development of metabolic disorders induced by estrogen deficiency in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:9274246
Raish M, Ahmad A, Ansari MA, Ahad A, Al-Jenoobi FI, Al-Mohizea AM, Khan A, Ali N (2018) Sinapic acid ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 108:224–231
Silambarasan T, Manivannan J, Raja B, Chatterjee S (2016) Prevention of cardiac dysfunction, kidney fibrosis and lipid metabolic alterations in l-NAME hypertensive rats by sinapic acid–Role of HMG-CoA reductase. Eur J Pharmacol 777:113–123
Eroğlu C, Avcı E, Vural H, Kurar E (2018) Anticancer mechanism of Sinapic acid in PC-3 and LNCaP human prostate cancer cell lines. Gene S0378–1119(18):30539
Balaji C, Muthukumaran J, Nalini N (2014) Hemopreventive effect of sinapic acid on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced experimental rat coloncarcinogenesis. Hum Exp Toxicol 33(12):1253–1268
Caporarello N, Lupo G, Olivieri M, Cristaldi M, Cambria MT, Salmeri M, Anfuso CD (2017) Classical VEGF, notch and Ang signalling in cancer angiogenesis, alternative approaches and future directions. Mol Med Rep 16(4):4393–4402
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438(7070):932–936
Lupo G, Caporarello N, Olivieri M, Cristaldi M, Motta C, Bramanti V, Avola R, Salmeri M, Nicoletti F, Anfuso CD (2016) Anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer: downsides and new pivots for precision medicine. Front Pharmacol 7:519
Rajalakshmi S, Vimalraj S, Saravanan S, Preeth DR, Shairam M, Anuradha D (2018) Synthesis and characterization of silibinin/phenanthroline/neocuproine copper (II) complexes for augmenting bone tissue regeneration: an in vitro analysis. J Biol Inorg Chem 19:1
Barlow AJ, Jones RT, McDonald AJ, Pigram PJ (2018) XPSSurfA: an open collaborative XPS data repository using the CMSShub platform. Surf Interface Anal 50(5):527–540
Desnoyer AN, Bowes EG, Patrick BO, Love JA (2015) Synthesis of 2-Nickela (II) oxetanes from Nickel (0) and epoxides: structure, reactivity, and a new mechanism of formation. J Am Chem Soc 137(40):12748–12751
Nasrollahzadeh M, Maham M, Sajadi SM (2015) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Gundelia tournefortii and evaluation of their catalytic activity for the synthesis of N-monosubstituted ureas and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Coll Interface Sci 455:245–253
Sankar R, Maheswari R, Karthik S, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V (2014) Anticancer activity of Ficus religiosa engineered copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:234–239
Komori H, Hashizaki R, Osaka I, Hibi T, Katano H, Taira S (2015) Nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization using sinapic acid-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for mass spectrometry analysis. Analyst 140:8134–8137
Masarudin MJ, Cutts SM, Evison BJ, Phillips DR, Pigram PJ (2015) Factors determining the stability, size distribution, and cellular accumulation of small, monodisperse chitosan nanoparticles as candidate vectors for anticancer drug delivery: application to the passive encapsulation of [14C]-doxorubicin. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 8:67
Thakur NS, Bhaumik J, Kirar S, Banerjee UC (2017) Development of gold-based phototheranostic nanoagents through a bioinspired route and their applications in photodynamic therapy. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(9):7950–7960
Kozak DS, Sergiienko RA, Shibata E, Iizuka A, Nakamura T (2016) Non-electrolytic synthesis of copper oxide/carbon nanocomposite by surface plasma in super-dehydrated ethanol. Sci Rep 16(6):21178
Hua Q, Shi F, Chen K, Chang S, Ma Y, Jiang Z, Pan G, Huang W (2011) Cu2 O-Au nanocomposites with novel structures and remarkable chemisorption capacity and photocatalytic activity. Nano Res 4(10):948–962
Dutta B, Kar E, Bose N, Mukherjee S (2015) Significant enhancement of the electroactive β-phase of PVDF by incorporating hydrothermally synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5(127):105422–105434
Díaz-Visurraga J, Daza C, Pozo C, Becerra A, Plessing CV, García A (2012) Study on antibacterial alginate-stabilized copper nanoparticles by FT-IR and 2D-IR correlation spectroscopy. Int J Nanomed 7:3597
Gao D, Zhang J, Zhu J, Qi J, Zhang Z, Sui W, Shi H, Xue D (2010) Vacancy-mediated magnetism in pure copper oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:769–772
Zhu J, Chen H, Liu H, Yang X, Lu L, Wang X (2004) Needle-shaped nanocrystalline CuO prepared by liquid hydrolysis of Cu (OAc)2. Mater Sci Eng 384(1–2):172–176
Lin HH, Wang CY, Shih HC, Chen JM, Hsieh CT (2004) Characterizing well-ordered CuO nanofibrils synthesized through gas-solid reactions. J Appl Phys 95(10):5889–5895
Santini C, Pellei M, Gandin V, Porchia M, Tisato F, Marzano C (2013) Advances in copper complexes as anticancer agents. Chem Rev 114(1):815–862
Mendoza-Diaz G, Garcia-Nieto RM, Gracia-Mora I, Arias-Negrete S, Ruiz-Ramirez L, Cosenza IL, Ireta J, Moreno-Esparza R, Pannell KH, Cervantes-Lee F (1991) Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of some mixed complexes of Cu (II) and Zn (II) with antibiotics of the nalidixic acid family and N-N ligands. J Inorg Biochem 43:640
Teng H, Chen L (2018) Polyphenols and Bioavailability: an update. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1437023
Moses SL, Edwards VM, Brantley E (2016) Cytotoxicity in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, without harming MCF-10A healthy cells. Nanomed Nanotechnol 7:2
Levenson AS, Jordan VC (1997) MCF-7: the first hormone-responsive breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res 57:3071–3078
Meena R, Kumar S, Gaharwar US, Rajamani P (2017) PLGA-CTAB curcumin nanoparticles: fabrication, characterization and molecular basis of anticancer activity in triple negative breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 cells). Biomed Pharmacother 1(94):944–954
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massagué J (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3:537–549
Liu H, Zhang Y, Zheng S, Weng Z, Ma J, Li Y, Xie X, Zheng W (2016) Detention of copper by sulfur nanoparticles inhibits the proliferation of A375 malignant melanoma and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477(4):1031–1037
Laha D, Pramanik A, Maity J, Mukherjee A, Pramanik P, Laskar A, Karmakar P (2014) Interplay between autophagy and apoptosis mediated by copper oxide nanoparticles in human breast cancer cells MCF7. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(1):1–9
Liou GY, Storz P (2010) Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic Res 44(5):479–496
Wang J, Luo B, Li X, Lu W, Yang J, Hu Y, Huang P, Wen S (2017) Inhibition of cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by a novel ROS-modulating agent with ability to eliminate stem-like cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 8(6):e2887
Khanna P, Ong C, Bay BH, Baeg GH (2015) Nanotoxicity: an interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death. Nanomater (Basel) 5(3):1163–1180
Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Alhadlaq HA, Alshamsan A (2016) Copper ferrite nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Coll Surf B 142:46–54
Azizi M, Ghourchian H, Yazdian F, Dashtestani F, AlizadehZeinabad H (2017) Cytotoxic effect of albumin coated copper nanoparticle on human breast cancer cells of MDA-MB231. PLoS One 12(11):e0188639
Mukherjee S (2018) Recent progress toward antiangiogenesis application of nanomedicine in cancer therapy. Future Sci OA 4:FSO318
Mukherjee S, Nethi SK, Patra CR (2017) Green synthesized gold nanoparticles for future biomedical applications. In particulate technology for delivery of therapeutics. Springer, Singapore, pp 359–393
Setyawati MI, Leong DT (2017) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an antitumoral-angiogenesis strategy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(8):6690–6703
Gurunathan S, Lee KJ, Kalishwaralal K, Sheikpranbabu S, Vaidyanathan R, Eom SH (2009) Antiangiogenic properties of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 30(31):6341–6350
Song H, Wang W, Zhao P, Qi Z, Zhao S (2014) Cuprous oxide nanoparticles inhibit angiogenesis via downregulation of VEGFR2 expression. Nanoscale 6(6):3206–3216
Norton KA, Popel AS (2016) Effects of endothelial cell proliferation and migration rates in a computational model of sprouting angiogenesis. Sci Rep 6:36992
Trickler WJ, Lantz SM, Schrand AM, Robinson BL, Newport GD, Schlager JJ, Paule MG, Slikker W, Biris AS, Hussain SM, Ali SF (2012) Effects of copper nanoparticles on rat cerebral microvessel endothelial cells. Nanomedicine 7(6):835–846
Zheng W, Yang L, Liu Y, Qin X, Zhou Y, Zhou Y (2014) Liu J Mo polyoxometalate nanoparticles inhibit tumor growth and vascular endothelial growth factor induced angiogenesis. Sci Technol Adv Mater 15(3):035010
Acknowledgements
Dr. S. Rajalakshmi wishes to thank DST-Inspire Faculty (Grant No. DST/INSPIRE/04/2015/001945) program for the research grant. XPS spectra were acquired by Dr. Ken Wong from Advanced Materials and Process Engineering Lab (AMPEL) at University of British Columbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj Preeth, D., Shairam, M., Suganya, N. et al. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using sinapic acid: an underpinning step towards antiangiogenic therapy for breast cancer. J Biol Inorg Chem 24, 633–645 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-019-01676-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-019-01676-z