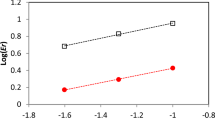
Abstract
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a meshfree method and has been widely used in the field of fluid dynamics. However, there is still a lack of robust approach to implement the far-field boundary condition in the simulation of free stream flow past the rigid body. To solve this problem, on the basis of Lastiwka et al.’s work, an improved non-reflecting boundary condition, called mixed characteristic boundary condition is proposed in this paper. The mixed characteristic boundary condition is tested by two-dimensional incompressible flows with a perturbation at the initial moment. The numerical results show that the mixed characteristic boundary condition can effectively suppress the reflection of waves on far-field boundaries. Finally, flows past a hydrofoil are simulated within the framework of the kernel gradient free SPH in two kinds of non-reflecting boundary condition. The results indicate that the present boundary condition is more robust and suitable for SPH than the one adopted by Lastiwka et al.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu MB, Liu GR (2010) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): an overview and recent developments. Arch Comput Methods Eng 17(1):25–76
Liu M-B, Li S-m (2016) On the modeling of viscous incompressible flows with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J Hydrodyn 28(5):731–745
Violeau D (2012) Fluid mechanics and the SPH method: theory and applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Monaghan JJ (2005) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Rep Prog Phys 68(8):1703–1759
Monaghan JJ (2012) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its diverse applications. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 44:323–346
Liu MB, Shao JR, Li HQ (2014) An SPH model for free surface flows with moving rigid objects. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 74(9):684–697
Sun PN, Ming FR, Zhang AM (2015) Numerical simulation of interactions between free surface and rigid body using a robust SPH method. Ocean Eng 98:32–49
Violeau D, Rogers BD (2016) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) for free-surface flows: past, present and future. J Hydraul Res 54(1):1–26
Liu MB, Liu GR, Lam KY, Zong Z (2003) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics for numerical simulation of underwater explosion. Comput Mech 30(2):106–118
Liu MB, Liu GR, Zong Z, Lam KY (2003) Computer simulation of high explosive explosion using smoothed particle hydrodynamics methodology. Comput Fluids 32(3):305–322
Ming F-r, Sun P-n, Zhang Am (2014) Investigation on charge parameters of underwater contact explosion based on axisymmetric SPH method. Appl Math Mech Engl Ed 35(4):453–468
Sun PN, Colagrossi A, Marrone S, Antuono M, Zhang AM (2017) Targeting viscous flows around solid body at high Reynolds numbers with the delta-plus-SPH model. In: Proceedings of 12th international SPHERIC workshop, pp 13–15
Le Touze D, Colagrossi A, Colicchio G, Greco M (2013) A critical investigation of smoothed particle hydrodynamics applied to problems with free-surfaces. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 73(7):660–691
Bouscasse B, Antuono M, Colagrossi A, Lugni C (2013) Numerical and experimental investigation of nonlinear shallow water sloshing. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14(2):123–138
Bouscasse B, Colagrossi A, Souto-Iglesias A, Cercos-Pita JL (2014) Mechanical energy dissipation induced by sloshing and wave breaking in a fully coupled angular motion system. I. Theoretical formulation and numerical investigation. Phys Fluids 26(3):033103-1–033103-21
Bouscasse B, Colagrossi A, Souto-Iglesias A, Cercos-Pita L (2014) Mechanical energy dissipation induced by sloshing and wave breaking in a fully coupled angular motion system. II. Experimental investigation. Phys Fluids 26(3):033104-1–033104-22
Marrone S, Colagrossi A, Park JS, Campana EF (2017) Challenges on the numerical prediction of slamming loads on LNG tank insulation panels. Ocean Eng 141:512–530
Marrone S, Colagrossi A, Antuono M, Colicchio G, Graziani G (2013) An accurate SPH modeling of viscous flows around bodies at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. J Comput Phys 245:456–475
Giles MB (1990) Nonreflecting boundary conditions for Euler equation calculations. AIAA J 28(12):2050–2058
Thompson KW (1990) Time-dependent boundary conditions for hyperbolic systems, II. J Comput Phys 89(2):439–461
Hu FQ (1996) On absorbing boundary conditions for linearized Euler equations by a perfectly matched layer. J Comput Phys 129(1):201–219
Colonius T, Lele SK, Moin P (1993) Boundary conditions for direct computation of aerodynamic sound generation. AIAA J 31(9):1574–1582
Lastiwka M, Basa M, Quinlan NJ (2009) Permeable and non-reflecting boundary conditions in SPH. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 61:709–724
Thompson KW (1987) Time dependent boundary conditions for hyperbolic systems. J Comput Phys 68(1):1–24
Huang C, Lei JM, Liu MB, Peng XY (2016) An improved KGF-SPH with a novel discrete scheme of Laplacian operator for viscous incompressible fluid flows. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 81(6):377–396
Liu GR, Liu MB (2003) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: a meshfree particle method. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore
Huang C, Lei JM, Liu MB, Peng XY (2016) An improved KGF-SPH with a novel discrete scheme of Laplacian operator for viscous incompressible fluid flows. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 81:377–396
Morris JP, Fox PJ, Zhu Y (1997) Modeling low Reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. J Comput Phys 136:214–226
Colagrossi A, Rossi E, Marrone S, Le Touze D (2016) Particle methods for viscous flows: analogies and differences between the SPH and DVH methods. Commun Comput Phys 20(3):660–688
Marrone S, Antuono M, Colagrossi A, Colicchio G, Le Touze D, Graziani G (2011) delta-SPH model for simulating violent impact flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(13–16):1526–1542
Huang C, Lei JM, Liu MB, Peng XY (2015) A kernel gradient free (KGF) SPH method. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 78(11):691–707
Poinsot TJ, Lele SK (1992) Boundary conditions for direct simulations of compressible viscous flows. J Comput Phys 101(1):104–129
Yoo CS, Wang Y, Trouve A, Im HG (2005) Characteristic boundary conditions for direct simulations of turbulent counterflow flames. Combust Theor Model 9(4):617–646
Yoo CS, Im HG (2007) Characteristic boundary conditions for simulations of compressible reacting flows with multi-dimensional, viscous and reaction effects. Combust Theor Model 11(2):259–286
Shadloo MS, Zainali A, Sadek SH, Yildiz M (2011) Improved incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for simulating flow around bluff bodies. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200:1008–1020
Shadloo MS, Zainali A, Yildiz M, Suleman A (2012) A robust weakly compressible SPH method and its comparison with an incompressible SPH. Int J Numer Methods Eng 89:939–956
Lei J-M, Huang C (2014) An improved pre-processing method for smooth particle hydrodynamics. Acta Phys Sin 63(14):215–225
Colagrossi A, Bouscasse B, Antuono M, Marrone S (2012) Particle packing algorithm for SPH schemes. Comput Phys Commun 183:1641–1653
Antuono M, Bouscasse B, Colagrossi A, Marrone S (2014) A measure of spatial disorder in particle methods. Comput Phys Commun 185(10):2609–2621
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 51579222, 51120195001 and 51521064), the international collaboration and exchange program from the NSFC-RCUK/EPSRC (Grant no. 51761135011), Youth Funds of the State Key Laboratory of Fluid Power and Mechatronic Systems (Zhejiang University) (no. KLoFP_QN_1604) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (+2017XZZX001-02A). The authors are grateful to Prof. Mou Bin Liu, Dr. Peng Nan Sun, Xue Ying Peng and Dr. Qing Yang Liu who provided valuable guidance and useful suggestions for this work. The authors are also grateful to referees whose suggestions make this article better.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D.H., Shi, Y.X., Huang, C. et al. A mixed characteristic boundary condition for simulating viscous incompressible fluid flows around a hydrofoil. J Mar Sci Technol 24, 73–85 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00773-018-0532-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00773-018-0532-8