Summary.
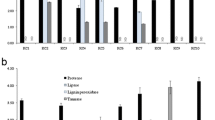
Thin layer chromatographical detection of tyrosine (Tyr) synthesized from l-[U-14C]phenylalanine (Phe) (1 mM) by rumen bacteria (B) and protozoa (P) collected from fistulated Japanese Goat was carried out. About 16 and 12% of the added Phe was converted to Tyr by B and P, respectively. Large amount of radioactivity in ether fractions indicated an abundant production of aromatic acids from Phe. Small amount of radioactivity found in CO2 fractions implied an occurrence of considerable decarboxylation reaction(s) by rumen bacteria and protozoa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received July 18, 2001 Accepted December 3, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R., Onodera, R. & Amin, M. Thin layer chromatographical detection of tyrosine produced from l-[U-14C]phenylalanine by ruminal microbes. Amino Acids 22, 427–432 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260200026
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260200026