Summary.
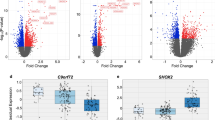
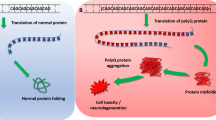
Down syndrome (DS) is the most common chromosomal abnormality associated with early mental retardation and neurological abnormalities followed by precocious age dependent Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration later in life. Knowledge of the pathological mechanisms involved in DS is far from complete, but overexpression of genes residing in chromosome 21 was considered to be the central point for the DS phenotype. In this regard, ßamyloid precursor protein (APP), CuZn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) and S100β have been implicated in causing apoptosis, a mechanism thought to be responsible for neuronal loss in DS, in one way or another. The gene dosage hypothesis has been challenged, however, and dysregulation of expression of genes located on other chromosomes has been described, which may well be secondary to chromosomal imbalance or a direct consequence of the disease process. The present review focuses on the protein expression profile in DS and we postulate that abnormalities in the coordinated expression, as well as interaction of proteins may be responsible for the neuropathology of DS. A series of candidate proteins are discussed that may be directly causing or reflecting the DS phenotype, in particular the brain abnormalities in DS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received July 6, 2001 Accepted October 1, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engidawork, E., Lubec, G. Protein expression in Down syndrome brain. Amino Acids 21, 331–361 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170001