Summary.
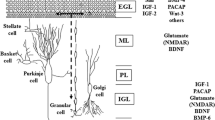
Excitatory amino acids which promote the survival of cerebellar granule cells in culture, also promote the expression of the survival of motor neuron (SMN) protein. Immunolocalization studies using SMN monoclonal antibody showed that SMN is decreased in cultures grown in low K+ or chemically defined medium with respect to cultures grown in high K+ medium and that an increase of SMN can be induced by treatment of low K+ cultures with glutamate or N-methyl-D-aspartate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received March 31, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreassi, C., Patrizi, A., Brahe, C. et al. Excitatory amino acid stimulation of the survival of rat cerebellar granule cells in culture is associated with an increase in SMN, the spinal muscular atrophy disease gene product. Amino Acids 18, 299–304 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260050026
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260050026