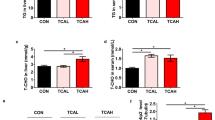
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of taurine (tau) supplementation to low fishmeal (FM) diets on growth performance, oxidative status, and immune response of European seabass juveniles. Four isoproteic (46% crude protein) and isolipidic (19% crude lipid) diets were formulated to contain either 25 or 12.5% FM and a mixture of plant feedstuffs, supplemented or not with 1% tau. Twelve groups of 20 fish (IBW = 9.4 g) were fed each diet for 9 weeks. Reduction of dietary FM from 25 to 12.5% impaired growth performance, feed efficiency, and protein efficiency ratio but had no effect on nitrogen retention (% N intake). Independently of FM level, dietary tau supplementation improved growth performance and nitrogen retention without affecting feed efficiency. Dietary FM level reduction increased liver G6PDH activity, but did not affect lipid peroxidation or activities of redox key enzymes. Contrarily, dietary tau supplementation decreased hepatic G6PDH and GPX activities and lipid peroxidation. Gene expression COX-2 was not affected either by FM or tau levels but TNF-α increased with the reduction of FM level but not with the tau level. Dietary tau supplementation decreased Casp3 and Casp9 expression regardless of dietary FM level. Overall, this study evidenced that dietary tau supplementation improved growth performance and antioxidant response and reduced intestine inflammatory and apoptosis processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 121–126
Baeverfjord G, Åsgård T, Shearer KD (1998) Development and detection of phosphorus deficiency in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., parr and post-smolts. Aquac Nutr 4:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.1998.00095.x
Bañuelos-Vargas I, López LM, Pérez-Jiménez A, Peres H (2014) Effect of fishmeal replacement by soy protein concentrate with taurine supplementation on hepatic intermediary metabolism and antioxidant status of totoaba juveniles (Totoaba macdonaldi). Fish Physiol Biochem Part B 170:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0058-5
Béné C, Barange M, Subasinghe R et al (2015) Feeding 9 billion by 2050—putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur 7:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-015-0427-z
Bergmeyer HU (1975) New values for the molar extinction coefficients of NADH and NADPH for the use in routine laboratories (author’s transl). Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem 13:507–508
Bhavsar TM, Patel SN, Lau-Cam CA (2010) Protective action of taurine, given as a pretreatment or as a posttreatment, against endotoxin-induced acute lung inflammation in hamsters. J Biomed Sci 17:S19
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brotons Martinez J, Chatzifotis S, Divanach P, Takeuchi T (2004) Effect of dietary taurine supplementation on growth performance and feed selection of sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax fry fed with demand-feeders. Fish Sci 70:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2003.00773.x
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) [30] Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(78)52032-6
Caminero A, Comabella M, Montalban X (2011) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), anti-TNF-α and demyelination revisited: an ongoing story. J Neuroimmunol 234:1–6
Chatzifotis S, Polemitou I, Divanach P, Antonopoulou E (2008) Effect of dietary taurine supplementation on growth performance and bile salt activated lipase activity of common dentex, Dentex dentex, fed a fish meal/soy protein concentrate-based diet. Aquaculture 275:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.12.013
Cheng CH, Guo ZX, Wang AL (2018) The protective effects of taurine on oxidative stress, cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ and apoptosis of pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus) under low temperature stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 77:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.022
Cohen S, Meys M, Tarvin T (1989) The Pico tag method: the method for amino acid analysis. Waters Chromatography Division, Millipore Corporation, Mildford
Coutinho F, Simões R, Oliva-Teles A et al (2017) Effects of dietary methionine and taurine supplementation to low-fish meal diets on growth performance and oxidative status of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquaculture 479:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.06.017
Couto A, Kortner TM, Penn M et al (2015) Saponins and phytosterols in diets for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles: effects on growth, intestinal morphology and physiology. Aquac Nutr 21:180–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12146
Couto A, Barroso C, Oliva-Teles A et al (2016) Carob seed germ meal in diets for meagre (Argyrosomus regius) juveniles: growth, digestive enzymes, intermediary metabolism, liver and gut histology. Aquaculture 451:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.10.007
De la Puerta C, Arrieta FJ, Balsa JA et al (2010) Taurine and glucose metabolism: a review. Nutr Hosp 25:910–919. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2010.25.6.4815
de Moura LB, Diógenes AF, Campelo DAV et al (2018) Taurine and methionine supplementation as a nutritional strategy for growth promotion of meagre (Argyrosomus regius) fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture 497:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.07.038
Dias J, Alvarez MJ, Arzel J et al (2005) Dietary protein source affects lipid metabolism in the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Comp Biochem Physiol Mol Integr Physiol 142:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2005.07.005
Divakaran S (2006) Taurine: an amino acid rich in fish meal. In: VIII Symp Int Nutr, pp 310–317
Espe M, Holen E (2013) Taurine attenuates apoptosis in primary liver cells isolated from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Br J Nutr 110:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512004679
Espe M, Lemme A, Petri A, El-Mowafi A (2006) Can Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) grow on diets devoid of fish meal? Aquaculture 255:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.12.030
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) [12] Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05015-1
Fournier V, Huelvan C, Desbruyeres E (2004) Incorporation of a mixture of plant feedstuffs as substitute for fish meal in diets of juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 236:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.035
Frederick CA, Coyle SD, Durborow RM et al (2016) Effect of taurine supplementation on growth response and body composition of largemouth bass. N Am J Aquac 78:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/15222055.2015.1084070
Geay F, Ferraresso S, Zambonino-Infante JL et al (2011) Effects of the total replacement of fish-based diet with plant-based diet on the hepatic transcriptome of two European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) half-sibfamilies showing different growth rates with the plant-based diet. BMC Genom 12:522. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-522
Gómez-Requeni P, Mingarro M, Calduch-Giner JA et al (2004) Protein growth performance, amino acid utilisation and somatotropic axis responsiveness to fish meal replacement by plant protein sources in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 232:493–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00532-5
Goto T, Ui T, Une M et al (1996) bile salt composition and distribution of the d-cysteinolic acid conjugated bile salts in fish. Fish Sci 62:606–609. https://doi.org/10.2331/fishsci.62.606
Gu M, Bai N, Zhang Y, Krogdahl Å (2016) Soybean meal induces enteritis in turbot Scophthalmus maximus at high supplementation levels. Aquaculture 464:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.035
Han Y, Han R, Koshio S et al (2014) Interactive effects of dietary valine and leucine on two sizes of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 432:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.05.004
Hansen AC, Hemre GI (2013) Effects of replacing fish meal and oil with plant resources in on-growing diets for Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. Aquac Nutr 19:641–650. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12078
Hardy RW (2010) Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquac Res 41:770–776. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02349.x
Henry MA, Gai F, Enes P et al (2018) Effect of partial dietary replacement of fishmeal by yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) larvae meal on the innate immune response and intestinal antioxidant enzymes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol 83:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.040
Hoseini SM, Hosseini SA, Eskandari S, Amirahmadi M (2018) Effect of dietary taurine and methionine supplementation on growth performance, body composition, taurine retention and lipid status of Persian sturgeon, Acipenser persicus (Borodin, 1897), fed with plant-based diet. Aquac Nutr 24:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12563
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of Taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Jirsa D, Davis DA, Salze GP et al (2014) Taurine requirement for juvenile white seabass (Atractoscion nobilis) fed soy-based diets. Aquaculture 422–423:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.11.029
Jong CJ, Azuma J, Schaffer S (2012) Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids 42:2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0962-7
Jong CJ, Ito T, Prentice H et al (2017) Role of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum in taurine-deficiency-mediated apoptosis. Nutrients 9:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080795
Kaushik SJ, Seiliez I (2010) Protein and amino acid nutrition and metabolism in fish: current knowledge and future needs. Aquacult Res 41:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02174.x
Kaushik SJ, Covès D, Dutto G, Blanc D (2004) Almost total replacement of fish meal by plant protein sources in the diet of a marine teleost, the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 230:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00422-8
Kim S-K, Matsunari H, Nomura K et al (2008a) Effect of dietary taurine and lipid contents on conjugated bile acid composition and growth performance of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Sci 74:875–881. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2008.01602.x
Kim S-K, Matsunari H, Takeuchi T et al (2008b) Comparison of taurine biosynthesis ability between juveniles of Japanese flounder and common carp. Amino Acids 35:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-007-0600-6
Konty E, Maslinski W, Marcinkiewicz J (2003) Anti-inflammatory activities of taurine chloramine. In: Lombardini et al (eds) Implication for immunoregulation and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 329–330
Krogdahl Å, Bakke-McKellep AM, Baeverfjord G (2003) Effects of graded levels of standard soybean meal on intestinal structure, mucosal enzyme activities, and pancreatic response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo solar L.). Aquac Nutr 9:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2003.00264.x
Lam NV, Chen W, Suruga K et al (2006) Enhancing effect of taurine on CYP7A1 mRNA expression in Hep G2 cells. Amino Acids 30:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-005-0244-3
Li M, Lai H, Li Q et al (2016) Effects of dietary taurine on growth, immunity and hyperammonemia in juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco fed all-plant protein diets. Aquaculture 450:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.08.013
López LM, Flores-Ibarra M, Bañuelos-Vargas I et al (2015) Effect of fishmeal replacement by soy protein concentrate with taurine supplementation on growth performance, hematological and biochemical status, and liver histology of totoaba juveniles (Totoaba macdonaldi). Fish Physiol Biochem 41:921–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0058-5
López-Bote CJ, Diez A, Corraze G et al (2001) Dietary protein source affects the susceptibility to lipid peroxidation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) muscle. Anim Sci 73:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1357729800058410
Lugrin J, Rosenblatt-Velin N, Parapanov R, Liaudet L (2014) The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes. Biol Chem 395:203–230
Lunger AN, McLean E, Gaylord TG et al (2007) Taurine supplementation to alternative dietary proteins used in fish meal replacement enhances growth of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture 271:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.07.006
Magalhães R, Sánchez-López A, Leal RS et al (2017) Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) pre-pupae meal as a fish meal replacement in diets for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 476:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.04.021
Martins N, Estevão-Rodrigues T, Diógenes AF et al (2018) Taurine requirement for growth and nitrogen accretion of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) juveniles. Aquaculture 494:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.05.007
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein. J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Médale F, Kaushik S, Sitjà-Bobadilla A et al (2005) Effect of fish meal replacement by plant protein sources on non-specific defence mechanisms and oxidative stress in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 249:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.03.031
Messina M, Piccolo G, Tulli F et al (2013) Lipid composition and metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) fed diets containing wheat gluten and legume meals as substitutes for fish meal. Aquaculture 376–379:6–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.11.005
Minghetti L (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/63.9.901
Morales AE, García-Rejón L, De La Higuera M (1990) Influence of handling and/or anaesthesia on stress response in rainbow trout. Effects on liver primary metabolism. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Physiol 95:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(90)90014-j
Morales AE, Pérez-Jiménez A, Carmen Hidalgo M et al (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses after prolonged starvation in Dentex dentex liver. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 139:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2004.10.008
Moutinho S, Peres H, Serra C et al (2017) Meat and bone meal as partial replacement of fishmeal in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) juveniles: diets digestibility, digestive function, and microbiota modulation. Aquaculture 479:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.07.021
Murakami S, Yamagishi I, Asami Y et al (1996) Hypolipidemic effect of taurine in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacology 52:303–313
Murakami S, Kondo Y, Toda Y et al (2002) Effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism in hamsters: up-regulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor by taurine. Life Sci 70:2355–2366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01507-2
Murakami S, Fujita M, Nakamura M et al (2016) Taurine ameliorates cholesterol metabolism by stimulating bile acid production in high-cholesterol-fed rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 43:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12534
Oliva-Teles A, Enes P, Peres H (2015) Replacing fishmeal and fish oil in industrial aquafeeds for carnivorous fish. Feed and feeding practices in aquaculture. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 203–233
Olsvik PAA, Torstensen BEE, Hemre G-II et al (2011) Hepatic oxidative stress in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) transferred from a diet based on marine feed ingredients to a diet based on plant ingredients. Aquac Nutr 17:e424–e436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2010.00778.x
Panserat S, Ducasse-Cabanot S, Plagnes-Juan E et al (2008) Dietary fat level modifies the expression of hepatic genes in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) as revealed by microarray analysis. Aquaculture 275:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.12.030
Park E, Jia J, Quinn MR, Schuller-Levis G (2002a) Taurine chloramine inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and decreases cytokine production in activated human leukocytes. Clin Immunol 102:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1006/clim.2001.5160
Park G-S, Takeuchi T, Yokoyama M, Seikai T (2002b) Optimal dietary taurine level for growth of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Sci 68:824–829. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1444-2906.2002.00498.x
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:45e-45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Plummer DT (1972) An introduction to practical biochemistry. Biochem Educ 1:14–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0307-4412(72)90021-0
Qi G, Ai Q, Mai K et al (2012) Effects of dietary taurine supplementation to a casein-based diet on growth performance and taurine distribution in two sizes of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 358–359:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.06.018
Richard N, Colen R, Aragão C (2017) Supplementing taurine to plant-based diets improves lipid digestive capacity and amino acid retention of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Aquaculture 468:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.09.050
Salze GP, Davis DA (2015) Taurine: a critical nutrient for future fish feeds. Aquaculture 437:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.12.006
Satriyo TB, Galaviz MA, Salze G, López LM (2017) Assessment of dietary taurine essentiality on the physiological state of juvenile Totoaba macdonaldi. Aquac Res 48:5677–5689. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13391
Sepulcre MP, Sarropoulou E, Kotoulas G et al (2007) Vibrio anguillarum evades the immune response of the bony fish sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) through the inhibition of leukocyte respiratory burst and down-regulation of apoptotic caspases. Mol Immunol 44:3751–3757. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLIMM.2007.03.021
Spitze AR, Wong DL, Rogers QR, Fascetti AJ (2003) Taurine concentrations in animal feed ingredients; cooking influences taurine content. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 87:251–262. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0396.2003.00434.x
Sunyer JO, Tort L (1995) Natural hemolytic and bactericidal activities of sea bream Sparus aurata serum are effected by the alternative complement pathway. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 45:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2427(94)05430-Z
Tacon AGJ, Hasan MR, Metian M (2011) Demand and supply of feed ingredients for farmed fish and crustaceans: trends and prospects. FAO fisheries and aquaculture technical paper, No. 564. FAO
Takagi S, Murata H, Goto T et al (2006a) Efficacy of taurine supplementation for preventing green liver syndrome and improving growth performance in yearling red sea bream Pagrus major fed low-fishmeal diet. Fish Sci 72:1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2006.01276.x
Takagi S, Murata H, Goto T et al (2006b) Hemolytic suppression roles of taurine in yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata fed non-fishmeal diet based on soybean protein. Fish Sci 72:546–555. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2006.01183.x
Takagi S, Murata H, Goto T et al (2011) Role of taurine deficiency in inducing green liver symptom and effect of dietary taurine supplementation in improving growth in juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major fed non-fishmeal diets based on soy protein concentrate. Fish Sci 77:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0322-2
Torrecillas S, Mompel D, Caballero MJ et al (2017) Effect of fishmeal and fish oil replacement by vegetable meals and oils on gut health of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 468:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.11.005
Tulli F, Tibaldi E, Comin A (1999) Dietary protein sources differently affect plasma lipid levels and body fat deposition in juvenile sea bass. In: Recent progress in animal production science. 1. Proceedings of the A.S.P.A. XIII Congress, Piacenza, Italy, 21–24 June, 1999. Tulli1999, pp 782–784
Urán PA, Gonçalves AA, Taverne-Thiele JJ et al (2008) Soybean meal induces intestinal inflammation in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:751–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.02.013
Wang L, Zhao N, Zhang F et al (2009) Effect of taurine on leucocyte function. Eur J Pharmacol 616:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.05.027
Wang X, He G, Mai K et al (2015) Ontogenetic taurine biosynthesis ability in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 185:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.03.003
Watson AM, Barrows FT, Place AR (2014) Effects of graded taurine levels on juvenile cobia. N Am J Aquac 76:190–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/15222055.2014.899531
Yokoyama M, Takeuchi T, Park GS, Nakazoe J (2001) Hepatic cysteinesulphinate decarboxylase activity in fish. Aquac Res 32:216–220. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1355-557x.2001.00017.x
Yun B, Ai Q, Mai K et al (2012) Synergistic effects of dietary cholesterol and taurine on growth performance and cholesterol metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture 324–325:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.10.012
Zhang Y, Wei Z, Liu G et al (2019) Synergistic effects of dietary carbohydrate and taurine on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and glucose metabolism in juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture 499:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.08.082
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Structured R&D&I Project INNOVMAR—Innovation and Sustainability in the Management and Exploitation of Marine Resources (ref. NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000035) within the research line “INSEAFOOD—Innovation and valorization of seafood products: meeting local challenges and opportunities”, founded by the Northern Regional Operational Programme (NORTE2020) through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). N. Martins was supported by INSEAFOOD Grant Inseafood/BI/L2/2017-026, R. Magalhães was supported by FCT Grant SFRH/BD/11570/2016, C. Castro was supported by FCT Grant SFRH/BPD/114942/2016, A. Couto was supported by National funds through FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors declare that they have contributed to the conception and design of the study or acquisition of data, and analysis including interpretation of data, drafting of the article, and final approval of the submitted version. All authors agree to authorship and submission of this manuscript for peer review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of informed consent and human/animal rights
The authors wish to declare that there were no conflicts, informed consent, and human or animal rights applicable. Fish were handled according to the Guidelines of the European Union (Directive 2010/63/UE) for the use of laboratory animals.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. W. Schaffer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, N., Magalhães, R., Castro, C. et al. Taurine modulates hepatic oxidative status and gut inflammatory markers of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed plant feedstuffs-based diets. Amino Acids 51, 1307–1321 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02769-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02769-4