Abstract
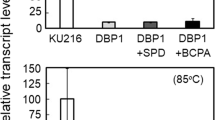
Branched-chain polyamines (BCPAs) are unique polycations found in (hyper)thermophiles. Thermococcus kodakarensis grows optimally at 85 °C and produces the BCPA N4-bis(aminopropyl)spermidine by sequential addition of decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine (dcSAM) aminopropyl groups to spermidine (SPD) by BCPA synthase A (BpsA). The T. kodakarensis bpsA deletion mutant (DBP1) did not grow at temperatures at or above 93 °C, and grew at 90 °C only after a long lag period following accumulation of excess cytoplasmic SPD. This suggests that BCPA plays an essential role in cell growth at higher temperatures and raises the possibility that BCPA is involved in controlling gene expression. To examine the effects of BCPA on transcription, the RNA polymerase (RNAP) core fraction was extracted from another bpsA deletion mutant, DBP4 (RNAPDBP4), which carried a His-tagged rpoL, and its enzymatic properties were compared with those of RNAP from wild-type (WT) cells (RNAPWT). LC–MS analysis revealed that nine ribosomal proteins were detected from RNAPWT but only one form RNAPDBP4. These results suggest that BCPA increases the linkage between RNAP and ribosomes to achieve efficient coupling of transcription and translation. Both RNAPs exhibited highest transcription activity in vitro at 80 °C, but the specific activity of RNAPDBP4 was lower than that of RNAPWT. Upon addition of SPD and BCPA, both increased the transcriptional activity of RNAPDBP4; however, elevation by BCPA was achieved at a tenfold lower concentration. Addition of BCPA also protected RNAPDBP4 against thermal inactivation at 90 °C. These results suggest that BCPA increases transcriptional activity in T. kodakarensis by stabilizing the RNAP complex at high temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acids
- ASW:
-
Artificial seawater
- BCPA:
-
Branched-chain polyamine
- BpsA:
-
Branched-chain polyamine synthase A
- Ca(OAc)2 :
-
Calcium acetate
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- EtBr:
-
Ethidium bromide
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- KOAc:
-
Potassium acetate
- LC–MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
- LCPA:
-
Long-chain polyamine
- Mg(OAc)2 :
-
Magnesium acetate
- PA:
-
Polyamine
- PAGE:
-
Poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis
- RNAP:
-
RNA polymerase
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SPD:
-
Spermidine
- TBP:
-
TATA-box binding protein
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TFB:
-
Transcription factor B
- Tris:
-
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
References
Atomi H, Fukui T, Kanai T, Morikawa M, Imanaka T (2004) Description of Thermococcus kodakaraensis sp. nov., a well studied hyperthermophilic archaeon previously reported as Pyrococcus sp KOD1. Archaea 1:263–267
Casero RA, Pegg AE (2009) Polyamine catabolism and disease. Biochem J 421:323–338. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20090598
Cohen SS, McCormick FP (1979) Polyamines and virus multiplication. Adv Virus Res 24:331–387
Demo G, Rasouly A, Vasilyev N, Svetlov V, Loveland AB, Diaz-Avalos R, Grigorieff N, Nudler E, Korostelev AA (2017) Struvture of RNA polymerase bound to ribosomal S30 subunit. Elife 6:e28560. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLIFE.28560
French SL, Santangelo TJ, Beyer AL, Reeve JN (2007) Transcription and translation are coupled in Archaea. Mol Biol Evol 24:893–895. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm007
Frugier M, Florentz C, Hosseini MW, Lehn JM, Giege R (1994) Synthetic polyamines stimulate in vitro transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 22:2784–2790
Fujiwara S, Aki R, Yoshida M, Higashibata H, Imanaka T, Fukuda W (2008) Expression profiles and physiological roles of two types of molecular chaperonins from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7306–7312. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01245-08
Fukuda W, Yamori Y, Hamakawa M, Hidese R, Kanesaki Y, Kainuma (Okamoto) A, Kato S, Fujiwara S (2019) Genes regulated by branched-chain polyamine in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. Submitted to Amino Acids
Fukui T, Atomi H, Kanai T, Matsumi R, Fujiwara S, Imanaka T (2005) Complete genome sequence of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1 and comparison with Pyrococcus genomes. Genome Res 15:352–363
Gao L, Danno A, Fujii S, Fukuda W, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2012) Indole-3-glycerol-phosphate synthase is recognized by a cold-inducible group II chaperonin in Thermococcus kodakarensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:3806–3815. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.07996-11
Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2008) Polyamines and abiotic stress: recent advances. Amino Acids 34:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-007-0501-8
Hamana K, Niitsu M, Samejima K, Matsuzaki S (1991) Polyamine distributions in thermophilic eubacteria belonging to Thermus and Acidothermus. J Biochem 109:444–449
Hamana K, Niitsu M, Matsuzaki S, Samejima K, Igarashi Y, Kodama T (1992) Novel linear and branched polyamines in the extremely thermophilic eubacteria Thermoleophilum, Bacillus and Hydrogenobacter. Biochem J 284:741–747
Hamana K, Hamana H, Niitsu M, Samejima K, Sakane T, Yokota A (1993) Tertiary and quaternary branched polyamines distributed in thermophilic Saccharococcus and Bacillus. Microbios 75:23–32
Hamana K, Hamana H, Niitsu M, Samejima K, Sakane T, Yokota A (1994) Occurrence of tertiary and quaternary branched polyamines in thermophilic archaebacteria. Microbios 79:109–119
Hamana K, Niitsu M, Samejima K, Itoh T (2001) Polyamines of the thermophilic eubacteria belonging to the genera Thermosipho, Thermaerobacter and Caldicellulosiruptor. Microbios 104:177–185
Hamana K, Tanaka T, Hosoya R, Niitsu M, Itoh T (2003) Cellular polyamines of the acidophilic, thermophilic and thermoacidophilic archaebacteria, Acidilobus, Ferroplasma, Pyrobaculum, Pyrococcus, Staphylothermus, Thermococcus, Thermodiscus and Vulcanisaeta. J Gen Appl Microbiol 49:287–293
Hamana K, Hosoya R, Itoh T (2007) Polyamine analysis of methanogens, thermophiles and extreme halophiles belonging to the domain Archaea. J Jpn Soc Extremophiles 6:25–31. https://doi.org/10.3118/jjse.6.25
Hidese R, Nishikawa R, Gao L, Katano M, Imai T, Kato S, Kanai T, Atomi H, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2014) Different roles of two transcription factor B proteins in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. Extremophiles 18:573–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0638-9
Hidese R, Tse KM, Kimura S, Mizohata E, Fujita J, Horai Y, Umezawa N, Higuchi T, Niitsu M, Oshima T, Imanaka T, Inoue T, Fujiwara S (2017) Active site geometry of a novel aminopropyltransferase for biosynthesis of hyperthermophile-specific branched-chain polyamine. FEBS J 284:3684–3701. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14262
Hirata A, Kanai T, Santangelo TJ, Tajiri M, Manabe K, Reeve JN, Imanaka T, Murakami KS (2008) Archaeal RNA polymerase subunits E and F are not required for transcription in vitro, but a Thermococcus kodakarensis mutant lacking subunit F is temperature-sensitive. Mol Microbiol 70:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06430.x
Hosoya R, Hamana K, Niitsu M, Itoh T (2004) Polyamine analysis for chemotaxonomy of thermophilic eubacteria: Polyamine distribution profiles within the orders Aquificales, Thermotogales, Thermodesulfobacteriales, Thermales, Thermoanaerobacteriales, Clostridiales and Bacillales. J Gen Appl Microbiol 50:271–287
Iwata M, Izawa M, Sasaki N, Nagumo Y, Sasabe H, Hayashizaki Y (2000) T7 RNA polymerase activation and improvement of the transcriptional sequencing by polyamines. Bioorg Med Chem 8:2185–2194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(00)00156-5
Jun SH, Hirata A, Kanai T, Santangelo TJ, Imanaka T, Murakami KS (2014) The X-ray crystal structure of the euryarchaeal RNA polymerase in an open-clamp configuration. Nat Commun 5:5132. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6132
Kohler R, Mooney RA, Mills DJ, Landick R, Cramer P (2017) Architecture of a transcribing–translating expressome. Science 14(356):194–197. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal3059
Miller-Fleming L, Olin-Sandoval V, Campbell K, Ralser M (2015) Remaining mysteries of molecular biology: the role of polyamines in the cell. J Mol Biol 427:3389–3406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.06.020
Minocha R, Majumdar R, Minocha SC (2014) Polyamines and abiotic stress in plants: a complex relationship. Front Plant Sci 5:175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00175
Morikawa M, Izawa Y, Rashid N, Hoaki T, Imanaka T (1994) Purification and characterization of a thermostable thiol protease from a newly isolated hyperthermophilic Pyrococcus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4559–4566
Morimoto N, Fukuda W, Nakajima N, Masuda T, Terui Y, Kanai T, Oshima T, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2010) Dual biosynthesis pathway for longer-chain polyamines in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. J Bacteriol 192:4991–5001. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00279-10
Muramatsu A, Shimizu Y, Yoshikawa Y, Fukuda W, Umezawa N, Horai Y, Higuchi T, Fujiwara S, Imanaka T, Yoshikawa K (2016) Naturally occurring branched-chain polyamines induce a crosslinked meshwork structure in a giant DNA. J Chem Phys 145:235103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972066
Nishio T, Yoshikawa Y, Fukuda W, Umezawa N, Higuchi T, Fujiwara S, Imanaka T, Yoshikawa K (2018) Branched-chain polyamine found in hyperthermophiles induces unique temperature-dependent structural changes in genome-size DNA. Chem Phys Chem 19:2299–2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201800396
Okada K, Hidese R, Fukuda W, Niitsu M, Takao K, Horai Y, Umezawa N, Higuchi T, Oshima T, Yoshikawa Y, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2014) Identification of a novel aminopropyltransferase involved in the synthesis of branched-chain polyamines in hyperthermophiles. J Bacteriol 196:1866–1876. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01515-14
Oshima T (2007) Unique polyamines produced by an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus. Amino Acids 33:367–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-007-0526-z
Oshima T, Kawahata S (1983) Homocaldpentamine: a new naturally occurring penta-amine. J Biochem 93:1455–1456
Oshima T, Hamasaki N, Senshu M, Kakinuma K, Kuwajima I (1987) A new naturally occurring polyamine containing a quaternary ammonium nitrogen. J Biol Chem 262:11979–11981
Santangelo TJ, Reeve JN (2006) Archaeal RNA polymerase is sensitive to intrinsic termination directed by transcribed and remote sequences. J Mol Biol 355:196–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.10.062
Santangelo TJ, Cubonova L, James CL, Reeve JN (2007) TFB1 or TFB2 is sufficient for Thermococcus kodakaraensis viability and for basal transcription in vitro. J Mol Biol 367:344–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.069
Sato T, Fukui T, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2003) Targeted gene disruption by homologous recombination in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1. J Bacteriol 185:210–220
Sato T, Fukui T, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2005) Improved and versatile transformation system allowing multiple genetic manipulations of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3889–3899. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.7.3889-3899.2005
Sato T, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2007) Archaeal type III RuBisCOs function in a pathway for AMP metabolism. Science 16:1003–1006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1135999
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1976) 1,4-Diaminobutane (putrescine), spermidine, and spermine. Annu Rev Biochem 45:285–306. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001441
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1984) Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem 53:749–790. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533
Terui Y, Ohnuma M, Hiraga K, Kawashima E, Oshima T (2005) Stabilization of nucleic acids by unusual polyamines produced by an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus. Biochem J 388:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20041778
Acknowledgements
This study was mainly supported by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (18K19191). Bioinformatic analysis was supported by a Grant for Individual Special Research, provided by Kwansei-Gakuin University.
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (18K19191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to study design. YY, MH, RH, MF, and SF performed the experiments. YY, FW, HA, and SF wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. Agostinelli.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamori, Y., Hamakawa, M., Hidese, R. et al. Branched-chain polyamine stabilizes RNA polymerase at elevated temperatures in hyperthermophiles. Amino Acids 52, 275–285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02745-y