Abstract
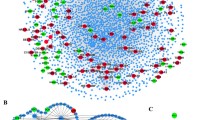
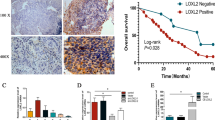
Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4), a member of the LOX family proteins, catalyzes oxidative deamination of lysine residues in collagen and elastin, which are responsible for maintaining extracellular matrix homeostasis. In this study, the mRNA expression of LOXL4 in seven esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines and 15 ESCC pairs of clinical samples were examined. Furthermore, LOXL4 protein levels in the ESCC cell lines were determined using western blotting. With the use of immunofluorescence, LOXL4 was observed to be localized primarily in the cytoplasm, but was also present in the nucleus. In addition, the results indicated that the upregulated expression of LOXL4 was associated with poor survival in patients with ESCC even following curative resection (P = 0.010). Similar Kaplan–Meier estimator curves for proteins that interact with LOXL4, SUV39H1 (P = 0.014) and COL2A1 (P = 0.011), were plotted. The analyses based on the protein–protein interaction network depicted the expression of LOXL4 and its associated proteins as well as their functions, suggesting that LOXL4 and its associated proteins may serve a significant role in the development and progression of ESCC. In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that LOXL4 is a potential biomarker for patients with ESCC, as well as SUV39H1 and COL2A1, and high expression levels of these genes are associated with poor prognosis in patients with ESCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LOX:
-
Lysyl oxidase
- LOXL4:
-
Lysyl oxidase-like 4
- SUV39H1:
-
Suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1
- COL2A1:
-
Collagen type II alpha 1 chain
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction network
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
References
Bird AP (1986) CpG island and the function of DNA methylation. Nature 321:209–213
Camp RL, Dolled Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259
Chiba T, Saito T, Yuki K, Zen Y, Koide S, Kanogawa N, Motoyama T, Ogasawara S, Suzuki E, Ooka Y, Tawada A, Otsuka M, Miyazaki M, Iwama A, Yokosuka O (2015) Histone lysine methyltransferase SUV39H1 is a potent target for epigenetic therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 136(2):289–298
Choi SK, Kim HS, Jin TF, Moon WK (2017) LOXL4 knockdown enhances tumor growth and lung metastasis through collagen-dependent extracellular matrix changes in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 8(7):11977–11989
Deng H, Lv L, Li Y, Zhang C, Meng F, Pu Y, Xiao J, Qian L, Zhao W, Liu Q, Zhang D, Wang Y, Zhang H, He Y, Zhu J (2014) miR-193a-3p regulates the multi-drug resistance of bladder cancer by targeting the LOXL4 gene and the oxidative stress pathway. Mol Cancer 13:234. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-234
Dong C, Wu Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Kang T, Rychahou PG, Chi YI, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2013) Interaction with Suv39H1 is critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in breast cancer. Oncogene 32(11):1351–1362
Fan DN, Tsang FH, Tam AH, Au SL, Wong CC, Wei L, Lee JM, He X, Ng IO, Wong CM (2013) Histone lysine methyltransferase, suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and is negatively regulated by microRNA-125b. Hepatology 57(2):637–647
Fritschy JM (2001) Immunofluorescence. https://doi.org/10.1038/npg.els.0001174
Gama-Sosa MA, Slagel VA, Trewyn RW, Oxenhandler R, Kuo KC, Gehrke CW, Ehrlich M (1983) The 5-methylcytosine content of DNA from human tumors. Nucleic Acids Res 11(19):6883–6894
Ganapathi MK, Jones WD, Sehouli J, Michener CM, Braicu IE, Norris EJ, Biscotti CV, Vaziri SA, Ganapathi RN (2016) Expression profile of COL2A1 and the pseudogene SLC6A10P predicts tumor recurrence in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 138(3):679–688
Görögh T, Weise JB, Holtmeier C, Rudolph P, Hedderich J, Gottschlich S, Hoffmann M, Ambrosch P, Csiszar K (2007) Selective upregulation and amplification of the lysyl oxidase like-4 (LOXL4) gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 212(1):74–82
Görögh T, Quabius ES, Nagy A, Muffels T, Ambrosch P, Hoffmann M (2016) Lysyl oxidase like-4 monoclonal antibody demonstrates therapeutic effect against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells and xenografts. Int J Cancer 138(10):2529–2538
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–457
Ito H, Akiyama H, Iguchi H, Iyama K, Miyamoto M, Ohsawa K, Nakamura T (2001) Molecular cloning and biological activity of a novel lysyl oxidase-related gene expressed in cartilage. J Biol Chem 276(26):24023–24029
Jiang WP, Sima ZH, Wang HC, Zhang JY, Sun LS, Chen F, Li TJ (2014) Identification of the involvement of LOXL4 in generation of keratocystic odontogenic tumors by RNA-Seq analysis. Int J Oral Sci 6(1):31–38
Jones S, Thornton JM (1996) Principles of protein–protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93(1):13–20
Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B (2011) Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Methods Mol Biol 696:291–303
Li RK, Zhao WY, Fang F, Zhuang C, Zhang XX, Yang XM, Jiang SH, Kong FZ, Tu L, Zhang WM, Yang SL, Cao H, Zhang ZG (2015) Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via FAK/Src pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141(2):269–281
Li CQ, Huang GW, Wu ZY, Xu YJ, Li XC, Xue YJ, Zhu Y, Zhao JM, Li M, Zhang J, Wu JY, Lei F, Wang QY, Li S, Zheng CP, Ai B, Tang ZD, Feng CC, Liao LD, Wang SH, Shen JH, Liu YJ, Bai XF, He JZ, Cao HH, Wu BL, Wang MR, Lin DC, Koeffler HP, Wang LD, Li X, Li EM, Xu LY (2017) Integrative analyses of transcriptome sequencing identify novel functional lncRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 6:297
Li TY, Li EM (2012) Reduced nuclear and ectopic cytoplasmic expression of lysyl oxidase–like 2 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 43:1068–1076
Mäki JM, Tikkanen H, Kivirikko KI (2001) Cloning and characterization of a fifth human lysyl oxidase isoenzyme: the third member of the lysyl oxidase-related subfamily with four scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains. Matrix Biol 20(7):493–496
Mandrell RE, Griffiss JM, Macher BA (1988) Lipooligosaccharides (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis have components that are immunochemically similar to precursors of human blood group antigens carbohydrate sequence specificity of the mouse monoclonal antibodies that recognize crossreacting antigens on LOS and human erythrocytes. J Exp Med 168(1):107–126
Rivas JDL, Fontanillo C (2010) Protein–protein interactions essentials: key concepts to building and analyzing interactome networks. PLoS Comput Biol. 6(6):1000807
Scola N, Görögh T (2010) LOXL4 as a selective molecular marker in primary and metastatic head/neck carcinoma. Anticancer Res 30(11):4567–4571
Shen Z, Cen S, Shen J, Cai W, Xu J, Teng Z, Hu Z, Zeng Y (2000) Study of immortalization and malignant transformation of human embryonic esophageal epithelial cells induced by HPV18 E6E7. J Cancer Res Clin Onco 126:589–594
Tian MX, Liu WR, Jin L, Jiang XF, Yang LX, Ding ZB, Shen YH, Peng YF, Gao DN, Li LX, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Dai Z, Fan J, Shi YH (2015) LOXL4 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma with a favorable prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(4):3892–3900
Wang SX, Mure M, Medzihradszky KF, Burlingame AL, Brown DE, Dooley M, Smith AJ, Kagan HM, Klinman JP (1996) A crosslinked cofactor in lysyl oxidase: redox function for amino acid side chains. Science 273:1078–1084
Weise JB, Rudolph P, Heiser A, Kruse ML, Hedderich J, Cordes C, Hoffmann M, Brant O, Ambrosch P, Csiszar K, Görögh T (2008) LOXL4 is a selectively expressed candidate diagnostic antigen in head and neck cancer. Eur J Cancer 44(9):1323–1331
Wu G, Guo Z, Chang X, Kim MS, Nagpal JK, Liu J, Trink B, Sidransky D (2007) LOXL1 and LOXL4 are epigenetically silenced and can inhibit Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in human bladder cancer Cancer Res 67 9 4123 4129
Wu BL, Xie JJ, Wu JY, Zhang PX, Li EM (2013) Comprehensive bioinformation analysis of the mRNA profile of fascin knockdown in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(12):7221–7227
Wu BL, Zou HY, Lv GQ, Du ZP, Wu JY, Zhang PX, Xu LY, Li EM (2014) Protein–protein interaction network analyses for elucidating the roles of LOXL2-delta72 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(5):2345–2351
Wu YH, Chang TH, Huang YF, Huang HD, Chou CY (2014) COL11A1 promotes tumor progression and predicts poor clinical outcome in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 33:3432–3440
Yilmaz M, Cansiz H (2016) Differential expression of LOXL4 in normal and tumour tissue samples of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol 41(3):206–210
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81472613 and 81360331), the Natural Science Foundation of China-GuangDong Joint Fund (Nos. U1301227 and U1601229), the Science & Technology Planning Project of GuangDong Province (No. 2014A020212286), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2018A030313664).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. Beninati.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, W., Huang, P., Wu, B. et al. Clinical significance of LOXL4 expression and features of LOXL4-associated protein–protein interaction network in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Amino Acids 51, 813–828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02723-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02723-4