Abstract
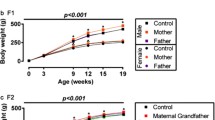
Obesity in fathers leads to DNA damage and epigenetic changes in sperm that may carry potential risk factors for metabolic diseases to the next generation. Taurine (TAU) supplementation has demonstrated benefits against testicular dysfunction and pancreatic islet impairments induced by obesity, but it is not known if these protective actions prevent the propagation of metabolic disruptions to the next generation; as such, we hypothesized that paternal obesity may increase the probability of endocrine pancreatic dysfunction in offspring, and that this could be prevented by TAU supplementation in male progenitors. To test this, male C57Bl/6 mice were fed on a control diet (CTL) or a high-fat diet (HFD) without or with 5% TAU in their drinking water (CTAU and HTAU) for 4 months. Subsequently, all groups of mice were mated with CTL females, and the F1 offspring were identified as: CTL-F1, CTAU-F1, HFD-F1, and HTAU-F1. HFD-fed mice were normoglycemic, but glucose intolerant and their islets hypersecreted insulin. However, at 90 days of age, HFD-F1 offspring displayed normal glucose homeostasis and adiposity, but reduced glucose-induced insulin release. HFD-F1 islets also exhibited β- and α-cell hypotrophy, and lower δ-cell number per islet. Paternal TAU supplementation prevented the decrease in glucose-induced insulin secretion and normalized β-cell size and δ-cell number, and increased α-cell size/islet in HTAU-F1 mice. In conclusion, HFD consumption by male founders decreases β-cell secretion and islet-cell distribution in their offspring. TAU attenuates the deleterious effects of paternal obesity on insulin secretion and islet-cell morphology in F1 offspring.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arany E, Strutt B, Romanus P, Remacle C, Reusens B, Hill DJ (2004) Taurine supplement in early life altered islet morphology, decreased insulitis and delayed the onset of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetologia 47(10):1831–1837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-004-1535-z
Bae CR, Hino J, Hosoda H, Arai Y, Son C, Makino H, Tokudome T, Tomita T, Kimura T, Nojiri T, Hosoda K, Miyazato M, Kangawa K (2017) Overexpression of C-type natriuretic peptide in endothelial cells protects against insulin resistance and inflammation during diet-induced obesity. Sci Rep 7(1):9807. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10240-1
Bakos HW, Mitchell M, Setchell BP, Lane M (2011) The effect of paternal diet-induced obesity on sperm function and fertilization in a mouse model. Int J Androl 34(5 Pt 1):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01092.x
Barbosa TC, Ingerslev LR, Alm PS, Versteyhe S, Massart J, Rasmussen M, Donkin I, Sjögren R, Mudry JM, Vetterli L, Gupta S, Krook K, Zierath JR, Barrès R (2016) High-fat diet reprograms the epigenome of rat spermatozoa and transgenerationally affects metabolism of the offspring. Mol Metab 5:184–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.12.002
Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, da Silva PM, Camargo RL, Lollo PC, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2013) Taurine supplementation improves liver glucose control in normal protein and malnourished mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(3):423–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200345
Bonfleur ML, Borck PC, Ribeiro RA, Caetano LC, Soares GM, Carneiro EM, Balbo SL (2015) Improvement in the expression of hepatic genes involved in fatty acid metabolism in obese rats supplemented with taurine. Life Sci 135:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.019
Borck PC, Vettorazzi JF, Branco RCS, Batista TM, Santos-Silva JC, Nakanishi VY, Boschero AC, Ribeiro RA, Carneiro EM (2018) Taurine supplementation induces long-term beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis in ob/ob mice. Amino Acids 50(6):765–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2553-3
Boujendar S, Reusens B, Merezak S, Ahn MT, Arany E, Hill D, Remacle C (2002) Taurine supplementation to a low protein diet during foetal and early postnatal life restores a normal proliferation and apoptosis of rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 45(6):856–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-002-0833-6
Boujendar S, Arany E, Hill D, Remacle C, Reusens B (2003) Taurine supplementation of a low protein diet fed to rat dams normalizes the vascularization of the fetal endocrine pancreas. J Nutr 133(9):2820–2825
Branco RC, Batista TM, Camargo RL, Borck PC, Ribeiro RA, Zoppi CC, Lollo PC, Morato PN, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2015) Long-term taurine supplementation leads to enhanced hepatic steatosis, renal dysfunction and hyperglycemia in mice fed on a high-fat diet. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15126-7_26
Bridgewater LC, Zhang C, Wu Y, Hu W, Zhang Q, Wang J, Li S, Zhao L (2017) Gender-based differences in host behavior and gut microbiota composition in response to high fat diet and stress in a mouse model. Sci Rep 7(1):10776. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11069-4
Busquets O, Ettcheto M, Pallas M, Beas-Zarate C, Verdaguer E, Auladell C, Folch J, Camins A (2017) Long-term exposition to a high fat diet favors the appearance of beta-amyloid depositions in the brain of C57BL/6 J mice. A potential model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 162:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.11.002
Bustamante J, Lobo MV, Alonso FJ, Mukala NT, Gine E, Solis JM, Tamarit-Rodriguez J, Martin Del Rio R (2001) An osmotic-sensitive taurine pool is localized in rat pancreatic islet cells containing glucagon and somatostatin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281(6):E1275–E1285
Caicedo A (2013) Paracrine and autocrine interactions in the human islet: more than meets the eye. Semin Cell Dev Biol 24(1):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.09.007
Cavan D, Fernandes JR, Makaroff L, Ogurtsova K, Webber S (2015) Diabetes Atlas. International Diabetes Federation, Karakas print, pp 1–144
Chung MC, Malatesta P, Bosquesi PL, Yamasaki PR, Santos JL, Vizioli EO (2012) Advances in drug design based on the amino Acid approach: taurine analogues for the treatment of CNS diseases. Pharmaceuticals 5(10):1128–1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5101128
Collaborators GBDO, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, Lee A, Marczak L, Mokdad AH, Moradi-Lakeh M, Naghavi M, Salama JS, Vos T, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Ahmed MB, Al-Aly Z, Alkerwi A, Al-Raddadi R, Amare AT, Amberbir A, Amegah AK, Amini E, Amrock SM, Anjana RM, Arnlov J, Asayesh H, Banerjee A, Barac A, Baye E, Bennett DA, Beyene AS, Biadgilign S, Biryukov S, Bjertness E, Boneya DJ, Campos-Nonato I, Carrero JJ, Cecilio P, Cercy K, Ciobanu LG, Cornaby L, Damtew SA, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dharmaratne SD, Duncan BB, Eshrati B, Esteghamati A, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Furst T, Gebrehiwot TT, Gold A, Gona PN, Goto A, Habtewold TD, Hadush KT, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hay SI, Horino M, Islami F, Kamal R, Kasaeian A, Katikireddi SV, Kengne AP, Kesavachandran CN, Khader YS, Khang YH, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kim YJ, Kinfu Y, Kosen S, Ku T, Defo BK, Kumar GA, Larson HJ, Leinsalu M, Liang X, Lim SS, Liu P, Lopez AD, Lozano R, Majeed A, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Mazidi M, McAlinden C, McGarvey ST, Mengistu DT, Mensah GA, Mensink GBM, Mezgebe HB, Mirrakhimov EM, Mueller UO, Noubiap JJ, Obermeyer CM, Ogbo FA, Owolabi MO, Patton GC, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Rafay A, Rai RK, Ranabhat CL, Reinig N, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Santos IS, Sartorius B, Sawhney M, Schmidhuber J, Schutte AE, Schmidt MI, Sepanlou SG, Shamsizadeh M, Sheikhbahaei S, Shin MJ, Shiri R, Shiue I, Roba HS, Silva DAS, Silverberg JI, Singh JA, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tegegne BS, Terkawi AS, Thakur JS, Tonelli M, Topor-Madry R, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vaezghasemi M, Vasankari T, Vlassov VV, Vollset SE, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Wesana J, Westerman R, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Yonga G, Zaidi Z, Zenebe ZM, Zipkin B, Murray CJL (2017) Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377(1):13–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
de Fatima Leao V, Raimundo JM, Ferreira LL, Santos-Silva JC, Vettorazzi JF, Bonfleur ML, Carneiro EM, Ribeiro RA (2015) Effects of paternal hypothalamic obesity and taurine supplementation on adiposity and vascular reactivity in rat offspring. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:749–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15126-7_60
Duivenvoorden I, Teusink B, Rensen PC, Romijn JA, Havekes LM, Voshol PJ (2005) Apolipoprotein C3 deficiency results in diet-induced obesity and aggravated insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 54(3):664–671
Ferguson-Smith AC, Patti ME (2011) You are what your dad ate. Cell Metab 13(2):115–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.01.011
Fullston T, Palmer NO, Owens JA, Mitchell M, Bakos HW, Lane M (2012) Diet-induced paternal obesity in the absence of diabetes diminishes the reproductive health of two subsequent generations of mice. Hum Reprod 27(5):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/des030
Hauge-Evans AC, King AJ, Carmignac D, Richardson CC, Robinson IC, Low MJ, Christie MR, Persaud SJ, Jones PM (2009) Somatostatin secreted by islet delta-cells fulfills multiple roles as a paracrine regulator of islet function. Diabetes 58(2):403–411. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-0792
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72(1):101–163
Lecomte V, Maloney CA, Wang KW, Morris MJ (2017) Effects of paternal obesity on growth and adiposity of male rat offspring. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 312(2):E117–E125. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00262.2016
Lee MO (1929) Determination of the surface area of the white rat with its application to the expression of metabolic results. Am J Physiol 89:24–33
Mao Z, Xia W, Chang H, Huo W, Li Y, Xu S (2015) Paternal BPA exposure in early life alters Igf2 epigenetic status in sperm and induces pancreatic impairment in rat offspring. Toxicol Lett 238(3):30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.08.009
Mosser RE, Maulis MF, Moulle VS, Dunn JC, Carboneau BA, Arasi K, Pappan K, Poitout V, Gannon M (2015) High-fat diet-induced beta-cell proliferation occurs prior to insulin resistance in C57Bl/6 J male mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308(7):E573–E582. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00460.2014
Ng SF, Lin RC, Laybutt DR, Barres R, Owens JA, Morris MJ (2010) Chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs beta-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring. Nature 467(7318):963–966. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09491
Ng SF, Lin RC, Maloney CA, Youngson NA, Owens JA, Morris MJ (2014) Paternal high-fat diet consumption induces common changes in the transcriptomes of retroperitoneal adipose and pancreatic islet tissues in female rat offspring. FASEB J 28(4):1830–1841. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-244046
Ornellas F, Bringhenti I, Mattos BANF, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2018) Father’s obesity programs the adipose tissue in the offspring via the local renin-angiotensin system and MAPKs pathways, especially in adult male mice. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1473-4
Palmer NO, Fullston T, Mitchell M, Setchell BP, Lane M (2011) SIRT6 in mouse spermatogenesis is modulated by diet-induced obesity. Reprod Fertil Dev 23(7):929–939. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD10326
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123(11):1939–1951
Ribeiro RA, Vanzela EC, Oliveira CA, Bonfleur ML, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2010) Taurine supplementation: involvement of cholinergic/phospholipase C and protein kinase A pathways in potentiation of insulin secretion and Ca2 + handling in mouse pancreatic islets. Br J Nutr 104(8):1148–1155. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510001820
Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC, Vettorazzi JF, Cotrim BB, Mobiolli DD, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2012) Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic beta-cells. Amino Acids 43(4):1791–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1263-5
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Batista TM, Borck PC, Carneiro EM (2018) Regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism by the pancreatic and extra-pancreatic actions of taurine. Amino Acids 50(11):1511–1524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2650-3
Santos-Silva JC, Ribeiro RA, Vettorazzi JF, Irles E, Rickli S, Borck PC, Porciuncula PM, Quesada I, Nadal A, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2015) Taurine supplementation ameliorates glucose homeostasis, prevents insulin and glucagon hypersecretion, and controls beta, alpha, and delta-cell masses in genetic obese mice. Amino Acids 47(8):1533–1548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1988-z
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Mozaffari M (2009) Role of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 87(2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1139/Y08-110
Sharma RB, Alonso LC (2014) Lipotoxicity in the pancreatic beta cell: not just survival and function, but proliferation as well? Curr DiabRep 14(6):492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-014-0492-2
Soubry A (2015) Epigenetic inheritance and evolution: a paternal perspective on dietary influences. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 118(1–2):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.02.008
Soubry A, Murphy SK, Wang F, Huang Z, Vidal AC, Fuemmeler BF, Kurtzberg J, Murtha A, Jirtle RL, Schildkraut JM, Hoyo C (2015) Newborns of obese parents have altered DNA methylation patterns at imprinted genes. Int J Obes 39(4):650–657. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.193
Stamateris RE, Sharma RB, Hollern DA, Alonso LC (2013) Adaptive beta-cell proliferation increases early in high-fat feeding in mice, concurrent with metabolic changes, with induction of islet cyclin D2 expression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305(1):E149–159. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00040.2013
Tellechea ML, Mensegue MF, Pirola CJ (2017) the association between high fat diet around gestation and metabolic syndrome-related phenotypes in rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 7(1):5086. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05344-7
Tsatsoulis A, Mantzaris MD, Bellou S, Andrikoula M (2013) Insulin resistance: an adaptive mechanism becomes maladaptive in the current environment—an evolutionary perspective. Metabolism 62(5):622–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2012.11.004
Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Shozawa C, Sano K, Kamei Y, Kasaoka S, Hosokawa Y, Ezaki O (2006) Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) deficiency creates a vicious circle promoting obesity. Endocrinology 147(7):3276–3284. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-1007
Yang J, Wu G, Feng Y, Lv Q, Lin S, Hu J (2010) Effects of taurine on male reproduction in rats of different ages. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S9
Acknowledgements
This study forms part of the M.Sc. thesis of Israelle Netto Freitas and was supported by grants from Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ n.: E-26/203.632/2015) and Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). We are grateful to Professor Thiago Alvares (Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Campus UFRJ-Macaé) for help with statistical analyses and Nicola Conran for English edition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ribeiro RA, Freitas IN and Araujo TR: conception and experimental design, execution of all experiments, analyses, data interpretation, and manuscript writing; Vettorazzi JF and Magalhães EA: insulin secretion measurement and endocrine pancreatic morphology; Carneiro EC and Bonfleur ML: intellectual contribution during work development and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All contributing authors report that there are no conflicts of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Ethical approval
This study used experimental animals. The use of mice in this study was approved by the local Ethics Animal Care and Use Committee (CEUA UFRJ-Macaé Campus, license nº.: MAC31).
Additional information
Handling Editor: P. R. Jungblut.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas, I.N., dos Reis Araujo, T., Vettorazzi, J.F. et al. Taurine supplementation in high-fat diet fed male mice attenuates endocrine pancreatic dysfunction in their male offspring. Amino Acids 51, 727–738 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02712-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02712-7