Abstract
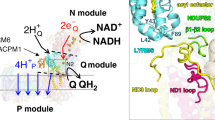
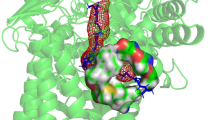
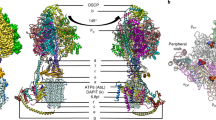
The eukaryotic F1FO-ATP synthase/hydrolase activity is coupled to H+ translocation through the inner mitochondrial membrane. According to a recent model, two asymmetric H+ half-channels in the a subunit translate a transmembrane vertical H+ flux into the rotor rotation required for ATP synthesis/hydrolysis. Along the H+ pathway, conserved aminoacid residues, mainly glutamate, address H+ both in the downhill and uphill transmembrane movements to synthesize or hydrolyze ATP, respectively. Point mutations responsible for these aminoacid changes affect H+ transfer through the membrane and, as a cascade, result in mitochondrial dysfunctions and related pathologies. The involvement of specific aminoacid residues in driving H+ along their transmembrane pathway within a subunit, sustained by the literature and calculated data, leads to depict a model consistent with some mitochondrial disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Δp :
-
Protonmotive force
- IMM:
-
Inner mitochondrial membrane
- MILS:
-
Maternally inherited Leigh syndrome
- MLASA:
-
Myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia
- NARP:
-
Neuropathy, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa
- PTP:
-
Permeability transition pore
References
Adachi K, Oiwa K, Nishizaka T et al (2007) Coupling of rotation and catalysis in F(1)-ATPase revealed by single-molecule imaging and manipulation. Cell 130:309–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.020
Allegretti M, Klusch N, Mills DJ et al (2015) Horizontal membrane-intrinsic α-helices in the stator a-subunit of an F-type ATP synthase. Nature 521:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14185
Baracca A, Sgarbi G, Mattiazzi M et al (2007) Biochemical phenotypes associated with the mitochondrial ATP6 gene mutations at nt8993. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:913–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2007.05.005
Burrage LC, Tang S, Wang J et al (2014) Mitochondrial myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) plus associated with a novel de novo mutation (m.8969G%3eA) in the mitochondrial encoded ATP6 gene. Mol Genet Metab 113:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.06.004
Dautant A, Meier T, Hahn A et al (2018) ATP synthase diseases of mitochondrial genetic origin. Front Physiol 9:329. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00329
Guo H, Bueler SA, Rubinstein JL (2017) Atomic model for the dimeric FO region of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Science 358:936–940. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao4815
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Li F et al (2018) The biochemical characterization of a missense mutation m.8914C%3eT in ATP6 gene associated with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Int J Dev Neurosci Off J Int Soc Dev Neurosci 71:172–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.09.007
Hahn A, Parey K, Bublitz M et al (2016) Structure of a complete ATP synthase dimer reveals the molecular basis of inner mitochondrial membrane morphology. Mol Cell 63:445–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.037
Hahn A, Vonck J, Mills DJ et al (2018) Structure, mechanism, and regulation of the chloroplast ATP synthase. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat4318
Hansen SH, Andersen ML, Cornett C et al (2010) A role for taurine in mitochondrial function. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S23
Jonckheere AI, Smeitink JAM, Rodenburg RJT (2012) Mitochondrial ATP synthase: architecture, function and pathology. J Inherit Metab Dis 35:211–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9382-9
Jong CJ, Ito T, Mozaffari M et al (2010) Effect of beta-alanine treatment on mitochondrial taurine level and 5-taurinomethyluridine content. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S25
Junge W, Nelson N (2015) ATP synthase. Annu Rev Biochem 84:631–657. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-034124
Junge W, Lill H, Engelbrecht S (1997) ATP synthase: an electrochemical transducer with rotatory mechanics. Trends Biochem Sci 22:420–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(97)01129-8
N Klusch, Murphy BJ, Mills DJ et al (2017) Structural basis of proton translocation and force generation in mitochondrial ATP synthase. eLife 6:e33274. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33274
Kucharczyk R, Rak M, di Rago J-P (2009) Biochemical consequences in yeast of the human mitochondrial DNA 8993T%3eC mutation in the ATPase6 gene found in NARP/MILS patients. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:817–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.02.011
Kucharczyk R, Dautant A, Godard F et al (2019) Functional investigation of an universally conserved leucine residue in subunit a of ATP synthase targeted by the pathogenic m.9176 T%3eG mutation. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1860:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.11.005
Kühlbrandt W, Davies KM (2016) Rotary ATPases: a new twist to an ancient machine. Trends Biochem Sci 41:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2015.10.006
Mitchell P, Moyle J (1967) Respiration-driven proton translocation in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J 105:1147–1162
Mitome N, Ono S, Sato H et al (2010) Essential arginine residue of the F(o)-a subunit in F(o)F(1)-ATP synthase has a role to prevent the proton shortcut without c-ring rotation in the F(o) proton channel. Biochem J 430:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20100621
Nesci S (2018) A lethal channel between the ATP synthase monomers. Trends Biochem Sci 43:311–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.02.013
Nesci S, Ventrella V, Trombetti F et al (2013) Mussel and mammalian ATP synthase share the same bioenergetic cost of ATP. J Bioenerg Biomembr 45:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-013-9504-1
Nesci S, Trombetti F, Ventrella V, Pagliarani A (2015) Opposite rotation directions in the synthesis and hydrolysis of ATP by the ATP synthase: hints from a subunit asymmetry. J Membr Biol 248:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9760-y
Nesci S, Trombetti F, Ventrella V, Pagliarani A (2016) The c-ring of the F1FO-ATP synthase: facts and perspectives. J Membr Biol 249:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9860-3
Nesci S, Trombetti F, Ventrella V, Pagliarani A (2018) From the Ca2+-activated F1FO-ATPase to the mitochondrial permeability transition pore: an overview. Biochimie 152:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.06.022
Niedzwiecka K, Tisi R, Penna S et al (2018) Two mutations in mitochondrial ATP6 gene of ATP synthase, related to human cancer, affect ROS, calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial permeability transition in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1865:117–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.10.003
Pagliarani A, Nesci S, Ventrella V (2016) Novel drugs targeting the c-ring of the F1FO-ATP synthase. Mini Rev Med Chem 16:815–824
Pogoryelov D, Yildiz O, Faraldo-Gómez JD, Meier T (2009) High-resolution structure of the rotor ring of a proton-dependent ATP synthase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:1068–1073. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1678
Pogoryelov D, Krah A, Langer JD et al (2010) Microscopic rotary mechanism of ion translocation in the F(o) complex of ATP synthases. Nat Chem Biol 6:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.457
Santo-Domingo J, Demaurex N (2012) The renaissance of mitochondrial pH. J Gen Physiol 139:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201110767
Schmidt T, Situ AJ, Ulmer TS (2016) Structural and thermodynamic basis of proline-induced transmembrane complex stabilization. Sci Rep 6:29809. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29809
Schon EA (2015) Chapter 22—The mitochondrial genome. In: Rosenberg RN, Pascual JM (eds) Rosenberg’s molecular and genetic basis of neurological and psychiatric disease, 5th edn. Academic Press, Boston, pp 259–269
Sgarbi G, Baracca A, Lenaz G et al (2006) Inefficient coupling between proton transport and ATP synthesis may be the pathogenic mechanism for NARP and Leigh syndrome resulting from the T8993G mutation in mtDNA. Biochem J 395:493–500. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20051748
Skoczeń N, Dautant A, Binko K et al (2018) Molecular basis of diseases caused by the mtDNA mutation m.8969G%3eA in the subunit a of ATP synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859:602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.05.009
Solaini G, Harris DA, Lenaz G et al (2008) The study of the pathogenic mechanism of mitochondrial diseases provides information on basic bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1777:941–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.04.034
Srivastava AP, Luo M, Zhou W et al (2018) High-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the yeast ATP synthase in a lipid membrane. Science 360:eaas9699. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aas9699
Symersky J, Pagadala V, Osowski D et al (2012) Structure of the c(10) ring of the yeast mitochondrial ATP synthase in the open conformation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2284 (S1)
Trounce I, Neill S, Wallace DC (1994) Cytoplasmic transfer of the mtDNA nt 8993 T–%3eG (ATP6) point mutation associated with Leigh syndrome into mtDNA-less cells demonstrates cosegregation with a decrease in state III respiration and ADP/O ratio. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8334–8338
Uziel G, Moroni I, Lamantea E et al (1997) Mitochondrial disease associated with the T8993G mutation of the mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene: a clinical, biochemical, and molecular study in six families. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:16–22
von Ballmoos C, Cook GM, Dimroth P (2008) Unique rotary ATP synthase and its biological diversity. Annu Rev Biophys 37:43–64. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.130018
Watt IN, Montgomery MG, Runswick MJ et al (2010) Bioenergetic cost of making an adenosine triphosphate molecule in animal mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:16823–16827. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1011099107
Xu T, Pagadala V, Mueller DM (2015) Understanding structure, function, and mutations in the mitochondrial ATP synthase. Microb Cell Graz Austria 2:105–125. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2015.04.197
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the University of Bologna, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable for the journal and the research does not involve data regarding humans or animals.
Additional information
Handaling Editor: S. W. Schaffer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trombetti, F., Pagliarani, A., Ventrella, V. et al. Crucial aminoacids in the FO sector of the F1FO-ATP synthase address H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane: molecular implications in mitochondrial dysfunctions. Amino Acids 51, 579–587 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02710-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02710-9