Abstract
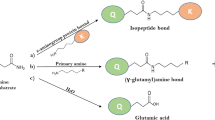
Microbial transglutaminase (TGase) has been successfully used to produce site-specific protein conjugates derivatized at the level of glutamine (Gln) or lysine (Lys) residues with diverse applications. Here, we study the drug human interferon β-1a (IFN) as a substrate of TGase. The derivatization reaction was performed using carbobenzoxy-l-glutaminyl-glycine to modify Lys residues and dansylcadaverine for Gln residues. The 166 amino acids polypeptide chain of IFN β-1a contains 11 Lys and 11 Gln residues potential sites of TGase derivatization. By means of mass spectrometry analyses, we demonstrate the highly selective derivatization of this protein by TGase at the level of Lys115 and as secondary site at the level of Lys33, while no reactive Gln residue was detected. Limited proteolysis experiments were performed on IFN to determine flexible regions of the protein under physiological conditions. Interestingly, primary and secondary sites of limited proteolysis and of TGase derivatization occur at the same regions of the polypeptide chain, indicating that the extraordinary selectivity of the TGase-mediated reaction is dictated by the conformational features of the protein substrate. We envisage that the TGase-mediated derivatization of IFN can be used to produce interesting derivatives of this important therapeutic protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- DC:
-
Dansylcadaverine
- E/S:
-
Enzyme to substrate ratio
- IFN:
-
Human interferon β-1a
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- TGase:
-
Transglutaminase
- TCEP:
-
Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine
- ZQG:
-
Carbobenzoxy-l-glutaminyl-glycine
References
Ando H, Adachi M, Umeda K et al (1989) Purification and characteristics of a novel transglutaminase derived from microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 53:2613–2617. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.53.2613
Baker DP, Lin EY, Lin K et al (2006) N-terminally PEGylated human interferon-β-1a with improved pharmacokinetic properties and in vivo efficacy in a melanoma angiogenesis model. Bioconjug Chem 17:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc050237q
Basu A, Yang K, Wang M et al (2006) Structure−function engineering of interferon-β-1b for improving stability, solubility, potency, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetic properties by site-selective mono-PEGylation. Bioconjug Chem 17:618–630. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc050322y
Cocco E, Marrosu MG (2015) Profile of PEGylated interferon beta in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:759–766. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S69123
Conradt HS, Egge H, Peter-Katalinic J et al (1987) Structure of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon-beta secreted by a recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. J Biol Chem 262:14600–14605
Dissing-Olesen L, Thaysen-Andersen M, Meldgaard M et al (2008) The function of the human interferon-1a glycan determined in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.138263
Folk JE (1983) Mechanism and basis for specificity of transglutaminase-catalyzed epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl) lysine bond formation. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 54:1–56
Fontana A, Spolaore B, Mero A, Veronese FM (2008) Site-specific modification and PEGylation of pharmaceutical proteins mediated by transglutaminase. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:13–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.06.015
Fontana A, Spolaore B, Mero A, Veronese FM (2009) The site-specific TGase-mediated PEGylation of proteins occurs at flexible sites. In: Veronese FM (ed) PEGylated protein drugs: basic science and clinical applications. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 89–112
Fontana A, de Laureto PP, Spolaore B, Frare E (2012) Identifying disordered regions in proteins by limited proteolysis. In: Uversky VN, Dunker AK (eds) Intrinsically disordered protein analysis, vol 2. Methods and Experimental Tools. Springer, New York, pp 297–318
Gershon PD (2014) Cleaved and missed sites for trypsin, Lys-C, and Lys-N can be predicted with high confidence on the basis of sequence context. J Proteome Res 13:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr400802z
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature’s biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20021234
Jeger S, Zimmermann K, Blanc A et al (2010) Site-specific and stoichiometric modification of antibodies by bacterial transglutaminase. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:9995–9997. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201004243
Karpusas M, Nolte M, Benton CB et al (1997) The crystal structure of human interferon β at 2.2 Å resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:11813–11818
Klaus W, Gsell B, Labhardt AM et al (1997) The three-dimensional high resolution structure of human interferon α-2a determined by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy in solution. J Mol Biol 274:661–675. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.1396
Lee JI, Eisenberg SP, Rosendahl MS et al (2013) Site-specific PEGylation enhances the pharmacokinetic properties and antitumor activity of interferon beta-1b. J Interferon Cytokine Res 33:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2012.0148
Mariniello L, Porta R, Sorrentino A et al (2014) Transglutaminase-mediated macromolecular assembly: production of conjugates for food and pharmaceutical applications. Amino Acids 46:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1561-6
Mark DF, Lu SD, Creasey AA et al (1984) Site-specific mutagenesis of the human fibroblast interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:5662–5666
Mastrangeli R, Rossi M, Mascia M et al (2015) In vitro biological characterization of IFN-β-1a major glycoforms. Glycobiology 25:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwu082
Mero A, Spolaore B, Veronese FM, Fontana A (2009) Transglutaminase-mediated PEGylation of proteins: direct identification of the sites of protein modification by mass spectrometry using a novel monodisperse PEG. Bioconjug Chem 20:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc800427n
Nairn NW, Shanebeck KD, Wang A et al (2012) Development of copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition for increased in vivo efficacy of interferon β-1b by site-specific PEGylation. Bioconjug Chem 23:2087–2097. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc300295x
Ohtsuka T, Ota M, Nio N, Motoki M (2000a) Comparison of substrate specificities of transglutaminases using synthetic peptides as acyl donors. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2608–2613. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.64.2608
Ohtsuka T, Sawa A, Kawabata R et al (2000b) Substrate specificities of microbial transglutaminase for primary amines. J Agric Food Chem 48:6230–6233. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000302k
Piehler J, Thomas C, Garcia KC, Schreiber G (2012) Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation. Immunol Rev 250:317–334. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12001
Radhakrishnan R, Walter LJ, Hruza A et al (1996) Zinc mediated dimer of human interferon-α2b revealed by X-ray crystallography. Structure 4:1453–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(96)00152-9
Runkel L, Meier W, Pepinsky RB et al (1998a) Structural and functional differences between glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms of human interferon-β (IFN-β). Pharm Res 15:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011974512425
Runkel L, Pfeffer L, Lewerenz M et al (1998b) Differences in activity between alpha and beta type I interferons explored by mutational analysis. J Biol Chem 273:8003–8008. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.14.8003
Runkel L, deDios C, Karpusas M et al (2000) Systematic mutational mapping of sites on human interferon-β-1a that are important for receptor binding and functional activity. Biochemistry 39:2538–2551. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi991631c
Sato H (2002) Enzymatic procedure for site-specific pegylation of proteins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:487–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00024-8
Shepard HM, Leung D, Stebbing N, Goeddel DV (1981) A single amino acid change in IFN-[beta]1 abolishes its antiviral activity. Nature 294:563–565. https://doi.org/10.1038/294563a0
Spolaore B, Raboni S, Ramos Molina A et al (2012) Local unfolding is required for the site-specific protein modification by transglutaminase. Biochemistry 51:8679–8689. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301005z
Spolaore B, Raboni S, Satwekar AA et al (2016) Site-specific transglutaminase-mediated conjugation of interferon α-2b at glutamine or lysine residues. Bioconjug Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00468
Strop P (2014) Versatility of microbial transglutaminase. Bioconjug Chem 25:855–862. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc500099v
Thom J, Anderson D, McGregor J, Cotton G (2011) Recombinant protein hydrazides: application to site-specific protein PEGylation. Bioconjug Chem 22:1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc2001374
Thomas C, Moraga I, Levin D et al (2011) Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons. Cell 146:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.048
Zhou Z, Zhang J, Sun L et al (2014) Comparison of site-specific PEGylations of the N-terminus of interferon beta-1b: selectivity, efficiency, and in vivo/vitro activity. Bioconjug Chem 25:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc400435u
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Silvia Gelio for conducting some experiments. This work was supported by the University of Padua (60A04-3887/12 and 60A04-8780/15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with regard to publication of this research work.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. Beninati.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spolaore, B., Forzato, G. & Fontana, A. Site-specific derivatization of human interferon β-1a at lysine residues using microbial transglutaminase. Amino Acids 50, 923–932 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2563-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2563-1