Abstract
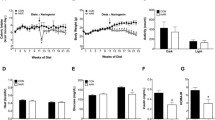
Low levels of estrogens are associated with obesity-related comorbidities. Mice with lower levels of estrogens are thereby more sensitive to the effects of a high-fat-diet (HFD) for the development of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Studies in vivo have demonstrated that taurine (TAU) supplementation prevents glucose and insulin resistance. Thus, we aimed to investigate the potential beneficial effects of TAU supplementation on glucose homeostasis of mice with low levels of estrogens fed with a HFD. 3-month-old female C57BL/6J mice underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX). After 1 week of recovery, mice were divided into 4 groups and either received: a standard chow diet (OVXC), chow diet plus drinking water enriched with 3% of TAU (OVXCT), HFD (OVXH), and HFD plus supplementation of TAU (OVXHT) for 14 weeks. Exposure to the HFD increased adiposity and plasma levels of glucose and insulin. Contrary to our prediction, the addition of TAU enhanced the deleterious effects of the HFD. Glucose and insulin tolerance tests (ipGTT and ipITT) indicated that mice maintained on the HFD + TAU had worse glucose intolerance and insulin resistance that was linked to lower insulin signaling in skeletal muscle and liver. Insulin secretion of isolated pancreatic islets of OVXH mice was higher than OVXC, and the addition of TAU associated with a HFD did not modulate insulin secretion, suggesting a failure of pancreatic β cells of OVXHT mice. These results suggest that despite the beneficial reports of TAU, it should be used cautiously in situations where the levels of estrogens are low.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abdel-Hakim SM, Ibrahim MY, Ibrahim HM et al (2014) The effect of ghrelin antagonist (D-Lys3) GHRP-6 on ovariectomy-induced obesity in adult female albino rats. Endocr Regul 48:126–134
Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, Amaral AG et al (2012) Taurine supplementation restores glucose and carbachol-induced insulin secretion in islets from low-protein diet rats: involvement of Ach-M3R, Synt 1 and SNAP-25 proteins. J Nutr Biochem 23:306–312
Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, da Silva PM et al (2013) Taurine supplementation improves liver glucose control in normal protein and malnourished mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:423–434
Bonfleur ML, Borck PC, Ribeiro RA et al (2015) Improvement in the expression of hepatic genes involved in fatty acid metabolism in obese rats supplemented with taurine. Life Sci 135:15–21
Borst SE, Conover CF (2005) High-fat diet induces increased tissue expression of TNF-alpha. Life Sci 77:2156–2165
Branco RC, Batista TM, Camargo RL et al (2015) Long-term taurine supplementation leads to enhanced hepatic steatosis, renal dysfunction and hyperglycemia in mice fed on a high-fat diet. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:339–351
Brand JS, van der Schouw YT, Onland-Moret NC et al (2013) Age at menopause, reproductive life span, and type 2 diabetes risk: results from the EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetes Care 36:1012–1019
Caetano LC, Bonfleur ML, Ribeiro RA et al (2015) Taurine supplementation regulates Iκ-Bα protein expression in adipose tissue and serum IL-4 and TNF-α concentrations in MSG obesity. Eur J Nutr 6:705–713
Camargo RL, Batista TM, Ribeiro RA et al (2015) Taurine supplementation preserves hypothalamic leptin action in normal and protein-restricted mice fed on a high-fat diet. Amino Acids 47:2419–2435
Camporez JP, Jornayvaz FR, Lee HY et al (2013) Cellular mechanism by which estradiol protects female ovariectomized mice from high-fat diet-induced hepatic and muscle insulin resistance. Endrocrinology 154:1021–1028
Cao PJ, Jin YJ, Li ME et al (2016) PGC-1α may associated with the anti-obesity effect of taurine on rats induced by arcuate nucleus lesion. Nutr Neurosci 19:86–93
Cappelli AP, Zoppi CC, Barbosa-Sampaio HC et al (2014) Taurine-induced insulin signalling improvement of obese malnourished mice is associated with redox balance and protein phosphatases activity modulation. Liver Int 34:771–783
Chatterjee A, Oh DJ, Kang MH et al (2013) Central corneal thickness does not correlate with ToneLab-measured IOP in several mouse strains with single transgenic mutations of matricellular proteins. Exp Eye Res 115:106–112
Chen W, Guo J, Zhang Y et al (2016) The beneficial effects of taurine in preventing metabolic syndrome. Food Funct 7:1849–1863
Chiang TI, Chang IC, Lee HH et al (2016) Amelioration of estrogen deficiency-induced obesity by collagen hydrolysate. Int J Med Sci. 13:853–857
Choi SB, Jang JS, Park S (2005) Estrogen and exercise may enhance β-cell function and mass via insulin receptor substrate 2 (ISR-2) induction in ovariectomized diabetic rats. Endocrinology 146:4786–4794
Cortez M, Carmo LS, Rogero MM et al (2013) A high-fat diet increases IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α production by increasing NF-κB and attenuating PPAR-γ expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Inflammation 36:379–386
da Silva RP, Zampieri TT, Pedroso JA et al (2014) Leptin resistance is not the primary cause of weight gain associated with reduced sex hormone levels in female mice. Endocrinology 155:4226–4236
de Souza Santos S, Batista TM, Camargo RL et al (2015) Taurine supplementation leads to a disruption in energy homeostasis in menopausal obese mice. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:735–748
Di Donato P, Giulini NA, Bacchi Modena A et al (2005) Risk factors for type 2 diabetes in women attending clinics in Italy: a cross-sectional study. Climacteric 8:287–293
Figueroa AL, Figueiredo H, Rebuffat SA et al (2016) Taurine treatment modulates circadian rhythms in mice fed a high fat diet. Sci Rep 6:36801
Filiputti E, Rafacho A, Araújo EP et al (2010) Augmentation of insulin secretion by leucine supplementation in malnourished rats: possible involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate kinase/mammalian target protein of rapamycin pathway. Metabolism 59:35–44
Hamilton DJ, Minze J, Kumar T et al (2016) Estrogen receptor alpha activation enhances mitochondrial function and systemic metabolism in high fat-diet OVX-mice. Physiol Rep 4:e12913
Hanley AJ, Williams K, Festa A et al (2005) Liver markers and development of the metabolic syndrome: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes 54:3140–3147
Heianza Y, Arase Y, Kodama S et al (2013) Effect of postmenopausal status and age at menopause on type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in Japanese individuals: toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 17 (TOPICS 17). Diabetes Care 36:4007–4014
Kim C (2012) Does menopause increase diabetes risk? Strategies for diabetes prevention in midlife women. Women’s Health 8:155–167
Kim KS, da Oh H, Kim JY et al (2012) Taurine ameliorates hyperglycemia ad dyslipidemia by reducing insulin resistance and leptin level in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) rats with long-term diabetes. Exp Mol Med 44:665–673
Lehnen AM, Leguisamo NM, Pinto GH et al (2010) The beneficial effects of exercise in rodents are preserved after detraining: a phenomenon unrelated to GLUT4 expression. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 28(9):67
Leite NC, de Paula F, Borck PC et al (2016) Protein malnutrition potentiates the amplifying pathway of insulin secretion in adult obese mice. Sci Rep 6:33464
Ma Q, Zhao J, Cao W et al (2015) Estradiol decreases taurine level by reducing cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase via the estrogen receptor-α in female mice liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308:G277–G286
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Clegg DJ, Hevener AL (2013) The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Endocr Rev 34:309–398
Merheb M, Daher RT, Nasrallah M et al (2007) Taurine intestinal absorption and renal excretion test in diabetic patients: a pilot study. Diabetes Care 30:2652–2654
Morin CL, Eckel RH, Marcel T et al (1997) High fat diets elevate adipose tissue-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha activity. Endocrinology 138:4665–4671
Nakhajavani M, Imani M, Larry M (2014) Metabolic syndrome in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with T2DM: loss of protective effects of premenopausal status. J Diabetes Metab Disord 13:102
Nardelli TR, Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL et al (2011) Taurine prevents fat deposition and ameliorates plasma lipid profile in monosodium glutamate-obese rats. Amino Acids 41:901–908
Neto NI, Rodrigues ME, Hachul AC et al (2015) a hyperlipidic diet combined with short-term ovariectomy increases adiposity and hyperleptinemia and decreases cytokine content in mesenteric adipose tissue. Mediat Inflamm 2015:923248
Otsuki M, Kasayama S, Morita S et al (2007) Menopause, but not age, is an independent risk factor for fasting plasma glucose levels in nondiabetic women. Menopause 14:404–407
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V et al (2001) Regulation of protein kinase B/Akt-serine 473 phosphorylation by integrin-linked kinase: critical roles for kinase activity and amino acids arginine 211 and serine 343. J Biol Chem 276:27462–27469
Qian S, Liu Y, Wang J et al (2016) BMP4 cross-talks with estrogen/ERα signaling to regulate adiposity and glucose metabolism in females. EBioMedicine 11:91–100
Raposo HF, Paiva AA, Kato LS et al (2015) Apolipoprotein CIII overexpression exacerbates diet-induced obesity due to adipose tissue higher exogenous lipid uptake and retention and lower lipolysis rates. Nutr Metab 12:61
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Rettberg JR, Yao J, Brinton RD (2014) Estrogen: a master regulator of bioenergetic systems in the brain and body. Front Neuroendocrinol 35:8–30
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Amaral AG et al (2009) Taurine supplementation enhances nutrient-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic mice islets. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25:370–379
Ribeiro RA, Vanzela EC, Oliveira CA et al (2010) Taurine supplementation: involvement of cholinergic/phospholipase C and protein kinase A pathways in potentiation of insulin secretion and Ca2 + handling in mouse pancreatic islets. Br J Nutr 104:1148–1155
Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC, Vettorazzi JF et al (2012) Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic β-cells. Amino Acids 43:1791–1801
Rogers NH, Perfiel JW, Strissel KJ et al (2009) Reduced energy expenditure and increased inflammation are early events in the development of ovariectomy-induced obesity. Endocrinology 150:2161–2168
Rosa FT, Freitas EC, Deminice R et al (2014) Oxidative stress and inflammation in obesity after taurine supplementation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Nutr 53:823–830
Santos RS, Batista TM, Camargo RL et al (2016) Lacking of estradiol reduces insulin exocytosis from pancreatic β-cells and increases hepatic insulin degradation. Steroids 114:16–24
Santos-Silva JC, Ribeiro RA, Vettorazzi JF et al (2015) Taurine supplementation ameliorates glucose homeostasis, prevents insulin and glucagon hypersecretion, and controls β, α and δ-cell masses in genetic obese mice. Amino Acids 47:1533–1548
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:1793–1801
Simental-Mendía LE, Rodríguez-Morán M, Gómez-Díaz R et al (2017) Insulin resistance is associated with elevated transaminases and low aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase ratio in young adults with normal weight. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:435–440
Straub RH (2007) The complex role of estrogens in inflammation. Endocr Rev 28:521–574
Suba Z (2012) Interplay between insulin resistance and estrogen deficiency as co-activators in carcinogenesis. Pathol Oncol Res 18:123–133
Tominaga K, Yamauchi A, Egawa T et al (2011) Vascular dysfunction and impaired insulin signaling in high-fat diet fed ovariectomized mice. Microvasc Res 82:171–176
Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Shozawa C, Sano K et al (2006) Taurine (2-amino-ethanesulfonic acid) deficiency creates a vicious circle promoting obesity. Endocrinol 147:3276–3284
Ueki I, Stipanuk MH (2007) Enzymes of the taurine biosynthetic pathway are expressed in rat mammary gland. J Nutr 137:1887–1894
Van Sinderen ML, Steinberg GR, Jørgensen SB et al (2015) Effects of estrogens on adipokines and glucose homeostasis in female aromatase knockout mice. PLoS One 10:e0136143
Vettorazzi JF, Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC et al (2014) Taurine supplementation increases K(ATP) channel protein content, improving Ca2 + handling and insulin secretion in islets from malnourished mice fed on a high-fat diet. Amino Acids 46:2123–2136
Wójcik OP, Koenig KL, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A et al (2013) Serum taurine and risk of coronary heart disease: a prospective, nested case-control study. Eur J Nutr 52:169–178
Wu F, Koenig KL, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A et al (2016) Serum taurine and stroke risk in women: a prospective, nested case-control study. PLoS One 11:e0149348
Xie P, Liu ML, Gu YP et al (2003) Oestrogen improves glucose metabolism and insulin signal transduction in HepG2 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:643–648
Yadav D, Choi E, Ahn SV et al (2016) Incremental predictive value of serum AST-to-ALT ratio for incident metabolic syndrome: the ARIRANG Study. PLoS One 11:e0161304
Yamato M, Shiba T, Ide T et al (2012) High-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance were ameliorated via enhanced fecal bile acid excretion in tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor knockout mice. Mol Cell Biochem 359:161–167
Yamori Y, Taguchi T, Mori H et al (2010) Low cardiovascular risks in the middle aged males and females excreting greater 24-hour urinary taurine and magnesium in 41 WHO-CARDIAC study populations in the world. J Biomed Sci 17:S21
Zhang M, Bi LF, Fang JH et al (2004) Beneficial effects of taurine on serum lipids in overweight or obese non-diabetic subjects. Amino Acids 26:267–271
Acknowledgements
This material was based upon work supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), under Grants 2012/50430-9 and 2013/07607-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OVX and subsequent post-operative care was performed by RSS. Experiments were designed by RSS, TMB, RLC, PNM and MGA. In vivo and ex vivo experiments were performed by RSS, RLC, TMB, PNM, NCL and JCR. Western blotting was performed by ECV and RLC. Statistics was performed by RSS. RSS, DJC and EMC prepared the manuscript. All authors discussed and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: P. R. Jungblut.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
726_2017_2533_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Suppl. Fig. 1. Imaging and computed reconstruction of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue through micro-CT scan. Representative images of transversal sections taken between L5 and L6 (A), and coronal plane (B). The less dense adipose tissue appears as darker gray than more dense organs such as muscle, bone and others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza Santos, R., Camargo, R.L., Vanzela, E.C. et al. Diet-induced glucose homeostasis dysregulation is enhanced by taurine supplementation in ovariectomized mice. Amino Acids 50, 469–477 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2533-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2533-z