Abstract
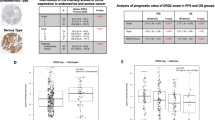
In our prior study we identified N w-hydroxy-l-arginine (NOHA) as a simple, yet sensitive indicator for estrogen negative (ER−) breast cancer early-prognosis, but not estrogen positive (ER+), and to offer ethnic selectivity for ER− detection. However, the ability of NOHA to assess ER− breast tumor based on disease progression, and tumor severity needs further delineation. Also, the overall NOHA storage stability needs to be validated. To assess the NOHA predictive capability based on disease progression, ER−/ER+ 3D-spheroids (from breast tumor cell lines of human origin) were cultured for 10 weeks. We found only ER− 3D-spheroid cultured for 10 weeks to show a gradual reduction in NOHA (both in culture medium and 3D-spheroid lysates) that correlated with a progressive increase in cellular NOS2 expression and NOS2 activity (measured as total nitrites). We additionally identified the NOHA-NOS2 correlation to be ethnically selective between ER− African American versus ER− Caucasian groups. Interestingly, such NOHA reduction was observed earlier in ER− culture medium (viz., after week 1) than from ER− 3D-spheroids lysates (viz., at the end of 3 weeks). When categorized based on 3D-spheroid grade, we found a ≥ 68% NOHA reduction in ER− spheroids that were ≤ 3 weeks old, that was categorized as “low-grade” (based on tumor size ≤ 250 µm, and with cellular characteristics identical to healthy cells). A substantial reduction in NOHA of ≥ 87% occurred with ER− 3D-spheroids grown for 6 weeks, which were categorized as “intermediate-grade” (with tumor size of ≥ 400 µm, and with less characteristic similarity to control spheroids). These in vitro findings thus suggest a distinct correlation between NOHA reduction and ER− tumor grade. Such distinctive correlation between NOHA and ER− tumor grade was additionally observed in de-identified clinical samples where a onefold higher reduction in NOHA occurred in grade-2 than with grade-1 de-identified patient plasma (when compared with control), and such correlation offered ethnic selectivity between ER− African American and ER− Caucasian groups. Of additional interest, when NOHA overall storage stability was assessed by incubating patient plasma and culture medium spiked with 75 pg/ml NOHA at multiple incubation temperatures and time-points, we found NOHA to maintain its stability for up to 6 weeks in culture medium and for 7 days in plasma at 4 °C and below. These results thus provide the first evidence of NOHA as a stable indicator to monitor ER− disease progression and tumor severity in ethnically distinctive populations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders CK, Carey LA (2009) Biology, metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 9(Suppl 2):S73–S81. https://doi.org/10.3816/CBC.2009.s.008
Bentzon N, During M, Rasmussen BB, Mouridsen H, Kroman N (2008) Prognostic effect of estrogen receptor status across age in primary breast cancer. Int J Cancer 122(5):1089–1094. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22892
Boucher JL, Moali C, Tenu JP (1999) Nitric oxide biosynthesis, nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and arginase competition for l-arginine utilization. Cell Mol Life Sci 55(8–9):1015–1028
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC (2006) Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA 295(21):2492–2502. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.21.2492
Chavez KJ, Garimella SV, Lipkowitz S (2010) Triple negative breast cancer cell lines: one tool in the search for better treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis 32(1–2):35–48. https://doi.org/10.3233/BD-2010-0307
Closs EI, Scheld JS, Sharafi M, Forstermann U (2000) Substrate supply for nitric-oxide synthase in macrophages and endothelial cells: role of cationic amino acid transporters. Mol Pharmacol 57(1):68–74
Closs EI, Simon A, Vekony N, Rotmann A (2004) Plasma membrane transporters for arginine. J Nutr 134(10 Suppl):2752S–2759S (discussion 2765S-2767S)
Dawood S, Merajver SD, Viens P, Vermeulen PB, Swain SM, Buchholz TA, Dirix LY, Levine PH, Lucci A, Krishnamurthy S, Robertson FM, Woodward WA, Yang WT, Ueno NT, Cristofanilli M (2011) International expert panel on inflammatory breast cancer: consensus statement for standardized diagnosis and treatment. Ann Oncol 22(3):515–523. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq345
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P, Narod SA (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 13(15 Pt 1):4429–4434. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3045
Dos Anjos Pultz B, da Luz FA, de Faria PR, Oliveira AP, de Araujo RA, Silva MJ (2014) Far beyond the usual biomarkers in breast cancer: a review. J Cancer 5(7):559–571. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.8925
Duffy MJ (2006) Serum tumor markers in breast cancer: are they of clinical value? Clin Chem 52(3):345–351. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.059832
Dunnwald LK, Rossing MA, Li CI (2007) Hormone receptor status, tumor characteristics, and prognosis: a prospective cohort of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res 9(1):R6. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr1639
Durante W, Johnson FK, Johnson RA (2007) Arginase: a critical regulator of nitric oxide synthesis and vascular function. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34(9):906–911. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04638.x
Ekert JE, Johnson K, Strake B, Pardinas J, Jarantow S, Perkinson R, Colter DC (2014) Three-dimensional lung tumor microenvironment modulates therapeutic compound responsiveness in vitro—implication for drug development. PLoS One 9(3):e92248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092248
Febbo PG, Ladanyi M, Aldape KD, De Marzo AM, Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Iafrate AJ, Kelley RK, Marcucci G, Ogino S, Pao W, Sgroi DC, Birkeland ML (2011) NCCN Task Force report: evaluating the clinical utility of tumor markers in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 9(Suppl 5):S1–S32
Food and Drug Administration (2001) Guidance for industry: bioanalytical method validation. US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Rockville
Garcia M, Jemal A, Ward EM (2007) Global cancer facts and figures. Am Cancer Soc. https://doi.org/10.3233/BD-2010-0307
Garlichs CD, Beyer J, Zhang H, Schmeisser A, Plotze K, Mugge A, Schellong S, Daniel WG (2000) Decreased plasma concentrations of l-hydroxy-arginine as a marker of reduced NO formation in patients with combined cardiovascular risk factors. J Lab Clin Med 135(5):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1067/mlc.2000.105975
Geng B, Liang MM, Ye XB, Zhao WY (2015) Association of CA 15-3 and CEA with clinicopathological parameters in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 3(1):232–236. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2014.419
Glynn SA, Boersma BJ, Dorsey TH, Yi M, Yfantis HG, Ridnour LA, Martin DN, Switzer CH, Hudson RS, Wink DA, Lee DH, Stephens RM, Ambs S (2010) Increased NOS2 predicts poor survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer patients. J Clin Invest 120(11):3843–3854. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI42059
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W, Toppmeyer D (2006) Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 24(36):5652–5657. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.5664
Hecker M, Schott C, Bucher B, Busse R, Stoclet JC (1995) Increase in serum N G-hydroxy-l-arginine in rats treated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Pharmacol 275(1):R1–R3
Holowatz LA, Thompson CS, Kenney WL (2006) l-Arginine supplementation or arginase inhibition augments reflex cutaneous vasodilatation in aged human skin. J Physiol 574(Pt 2):573–581. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108993
Huang HL, Stasyk T, Morandell S, Dieplinger H, Falkensammer G, Griesmacher A, Mogg M, Schreiber M, Feuerstein I, Huck CW, Stecher G, Bonn GK, Huber LA (2006) Biomarker discovery in breast cancer serum using 2-D differential gel electrophoresis/MALDI-TOF/TOF and data validation by routine clinical assays. Electrophoresis 27(8):1641–1650. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500857
Kelm M (1999) Nitric oxide metabolism and breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta 1411(2–3):273–289
Klatt P, Schmidt K, Uray G, Mayer B (1993) Multiple catalytic functions of brain nitric oxide synthase. Biochemical characterization, cofactor-requirement, and the role of N omega-hydroxy-l-arginine as an intermediate. J Biol Chem 268(20):14781–14787
Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Bode-Boger SM (2006) Fast and efficient determination of arginine, symmetric dimethylarginine, and asymmetric dimethylarginine in biological fluids by hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 52(3):488–493. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.060152
Mohan S, Moua N, Harding L (2016) N w-hydroxy-l-arginine as a novel ethnic specific indicator of estrogen-negative breast cancer. Amino Acids. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2301-5
Oakman C, Viale G, Di Leo A (2010) Management of triple negative breast cancer. Breast 19(5):312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2010.03.026
Penault-Llorca F, Viale G (2012) Pathological and molecular diagnosis of triple-negative breast cancer: a clinical perspective. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi19–vi22. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds190
Pervin S, Singh R, Chaudhuri G (2008) Nitric oxide, N omega-hydroxy-l-arginine and breast cancer. Nitric Oxide 19(2):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.016
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Lee AH, Elston CW, Grainge MJ, Hodi Z, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2008) Prognostic significance of Nottingham histologic grade in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(19):3153–3158. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.15.5986
Schade D, Kotthaus J, Clement B (2010) Modulating the NO generating system from a medicinal chemistry perspective: current trends and therapeutic options in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther 126(3):279–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.02.005
Stuehr DJ, Kwon NS, Nathan CF, Griffith OW, Feldman PL, Wiseman J (1991) N omega-hydroxy-l-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from l-arginine. J Biol Chem 266(10):6259–6263
Uematsu T, Kasami M, Yuen S (2009) Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology 250(3):638–647. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2503081054
Vinci M, Gowan S, Boxall F, Patterson L, Zimmermann M, Court W, Lomas C, Mendiola M, Hardisson D, Eccles SA (2012) Advances in establishment and analysis of three-dimensional tumor spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. BMC Biol 10:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-10-29
Yerushalmi R, Tyldesley S, Kennecke H, Speers C, Woods R, Knight B, Gelmon KA (2012) Tumor markers in metastatic breast cancer subtypes: frequency of elevation and correlation with outcome. Ann Oncol 23(2):338–345. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdr154
Zharikov SI, Block ER (1998) Characterization of l-arginine uptake by plasma membrane vesicles isolated from cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1369(1):173–183
Zhou L, Li K, Luo Y, Tian L, Wang M, Li C, Huang Q (2013) Novel prognostic markers for patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol 44(10):2180–2187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2013.03.021
Acknowledgements
The University of New England Office of Research and Scholarship, and the College of Pharmacy provided funding support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
As authors of this manuscript, we declare no conflict of interest, either financial or otherwise.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
No human participants were directly involved with this project. All clinical samples used in this study came from bio-banks.
Informed consent
Only de-identified patient samples from bio-banks were used for this study, thus exempting informed consent requirement.
Additional information
Handling Editor: G. J. Peters.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, S., Greenstein, I., Ng, C. et al. Assessing N w-hydroxy-l-arginine applicability as a novel ethnic specific estrogen-negative breast cancer marker. Amino Acids 50, 373–382 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2523-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2523-1