Abstract
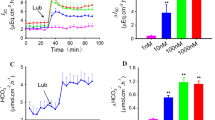
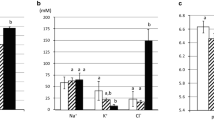
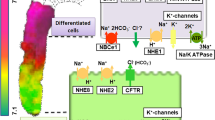
Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE)-3 is important for intestinal absorption of nutrients and minerals, including calcium. The previous investigations have shown that the intestinal calcium absorption is also dependent on luminal nutrients, but whether aliphatic amino acids and glucose, which are abundant in the luminal fluid during a meal, similarly enhance calcium transport remains elusive. Herein, we used the in vitro Ussing chamber technique to determine epithelial electrical parameters, i.e., potential difference (PD), short-circuit current (Isc), and transepithelial resistance, as well as 45Ca flux in the rat duodenum directly exposed on the mucosal side to glucose or various amino acids. We found that mucosal glucose exposure led to the enhanced calcium transport, PD, and Isc, all of which were insensitive to NHE3 inhibitor (100 nM tenapanor). In the absence of mucosal glucose, several amino acids (12 mM in the mucosal side), i.e., alanine, isoleucine, leucine, proline, and hydroxyproline, markedly increased the duodenal calcium transport. An inhibitor for NHE3 exposure on the mucosal side completely abolished proline- and leucine-enhanced calcium transport, but not transepithelial transport of both amino acids themselves. In conclusion, glucose and certain amino acids in the mucosal side were potent stimulators of the duodenal calcium absorption, but only amino-acid-enhanced calcium transport was NHE3-dependent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bröer S (2008) Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev 88:249–286. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2006
Charoenphandhu N, Krishnamra N (2007) Prolactin is an important regulator of intestinal calcium transport. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 85:569–581. doi:10.1139/y07-041
Charoenphandhu N, Tudpor K, Pulsook N, Krishnamra N (2006) Chronic metabolic acidosis stimulated transcellular and solvent drag-induced calcium transport in the duodenum of female rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G446–G455. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00108.2006
Charoenphandhu N, Nakkrasae LI, Kraidith K, Teerapornpuntakit J, Thongchote K, Thongon N, Krishnamra N (2009) Two-step stimulation of intestinal Ca2+ absorption during lactation by long-term prolactin exposure and suckling-induced prolactin surge. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E609–E619. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00347.2009
Chen MM, Singh A, Xiao F, Dringenberg U, Wang J, Engelhardt R, Yeruva S, Rubio-Aliaga I, Nässl AM, Kottra G, Daniel H, Seidler U (2010) Gene ablation for PEPT1 in mice abolishes the effects of dipeptides on small intestinal fluid absorption, short-circuit current, and intracellular pH. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G265–G274. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00055.2010
Comar CL, Nold MM, Wasserman RH (1956) The influence of amino acids and other organic compounds on the gastrointestinal absorption of calcium45 and strontium89 in the rat. J Nutr 59:371–383
Donowitz M, Ming Tse C, Fuster D (2013) SLC9/NHE gene family, a plasma membrane and organellar family of Na+/H+ exchangers. Mol Aspects Med 34:236–251. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2012.05.001
Dorkkam N, Wongdee K, Suntornsaratoon P, Krishnamra N, Charoenphandhu N (2013) Prolactin stimulates the L-type calcium channel-mediated transepithelial calcium transport in the duodenum of male rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 430:711–716. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.11.085
Freeman TC, Bentsen BS, Thwaites DT, Simmons NL (1995) H+/di-tripeptide transporter (PepT1) expression in the rabbit intestine. Pflugers Arch 430:394–400
Gerritsen KG, Boer WH, Joles JA (2015) The importance of intake: a gut feeling. Ann Transl Med 3:49. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.03.21
Hoenderop JG, Nilius B, Bindels RJ (2005) Calcium absorption across epithelia. Physiol Rev 85:373–422. doi:10.1152/physrev.00003.2004
Hoogerwerf WA, Tsao SC, Devuyst O, Levine SA, Yun CH, Yip JW, Cohen ME, Wilson PD, Lazenby AJ, Tse CM, Donowitz M (1996) NHE2 and NHE3 are human and rabbit intestinal brush-border proteins. Am J Physiol 270:G29–G41
Kellett GL (2011) Alternative perspective on intestinal calcium absorption: proposed complementary actions of Cav1.3 and TRPV6. Nutr Rev 69:347–370. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00395.x
Kesvatera T, Jonsson B, Telling A, Tougu V, Vija H, Thulin E, Linse S (2001) Calbindin D9k: a protein optimized for calcium binding at neutral pH. Biochemistry 40:15334–15340. doi:10.1021/bi0114022
Kulaksiz H, Bektas H, Cetin Y (2001) Expression and cell-specific and membrane-specific localization of NHE-3 in the human and guinea pig upper gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 303:337–343. doi:10.1007/s004410000329
Larsen EH, Nedergaard S, Ussing HH (2000) Role of lateral intercellular space and sodium recirculation for isotonic transport in leaky epithelia. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 141:153–212
Larsen EH, Sorensen JB, Sorensen JN (2002) Analysis of the sodium recirculation theory of solute-coupled water transport in small intestine. J Physiol 542:33–50. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013248
Li C, Naren AP (2010) CFTR chloride channel in the apical compartments: spatiotemporal coupling to its interacting partners. Integr Biol (Camb) 2:161–177. doi:10.1039/b924455g
Lu Z, Yao L, Jiang Z, Aschenbach JR, Martens H, Shen Z (2016) Acidic pH and short-chain fatty acids activate Na+ transport but differentially modulate expression of Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms 1, 2, and 3 in omasal epithelium. J Dairy Sci 99:733–745. doi:10.3168/jds.2015-9605
Mackenzie B, Erickson JD (2004) Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid (System N/A) transporters of the SLC38 gene family. Pflugers Arch 447:784–795. doi:10.1007/s00424-003-1117-9
Mineo H, Hara H, Shigematsu N, Okuhara Y, Tomita F (2002) Melibiose, difructose anhydride III and difructose anhydride IV enhance net calcium absorption in rat small and large intestinal epithelium by increasing the passage of tight junctions in vitro. J Nutr 132:3394–3399
Morgan EL, Mace OJ, Affleck J, Kellett GL (2007) Apical GLUT2 and Cav1.3: regulation of rat intestinal glucose and calcium absorption. J Physiol 580:593–604. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124768
Nakkrasae LI, Thongon N, Thongbunchoo J, Krishnamra N, Charoenphandhu N (2010) Transepithelial calcium transport in prolactin-exposed intestine-like Caco-2 monolayer after combinatorial knockdown of TRPV5, TRPV6 and Cav1.3. J Physiol Sci 60:9–17. doi:10.1007/s12576-009-0068-0
Pan W, Borovac J, Spicer Z, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ, Shull GE, Doschak MR, Cordat E, Alexander RT (2012) The epithelial sodium/proton exchanger, NHE3, is necessary for renal and intestinal calcium (re)absorption. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302:F943–F956. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00504.2010
Pramod AB, Foster J, Carvelli L, Henry LK (2013) SLC6 transporters: structure, function, regulation, disease association and therapeutics. Mol Aspects Med 34:197–219. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.002
Reyes-Fernandez PC, Fleet JC (2015) Luminal glucose does not enhance active intestinal calcium absorption in mice: evidence against a role for Cav1.3 as a mediator of calcium uptake during absorption. Nutr Res 35:1009–1015. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2015.08.004
Rievaj J, Pan W, Cordat E, Alexander RT (2013) The Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 is required for active paracellular and transcellular Ca2+ transport across murine cecum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 305:G303–G313. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00490.2012
Romeo E, Dave MH, Bacic D, Ristic Z, Camargo SM, Loffing J, Wagner CA, Verrey F (2006) Luminal kidney and intestine SLC6 amino acid transporters of B0AT-cluster and their tissue distribution in Mus musculus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F376–F383. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00286.2005
Tanrattana C, Charoenphandhu N, Limlomwongse L, Krishnamra N (2004) Prolactin directly stimulated the solvent drag-induced calcium transport in the duodenum of female rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 1665:81–91. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.06.017
Thwaites DT, Ford D, Glanville M, Simmons NL (1999) H+/solute-induced intracellular acidification leads to selective activation of apical Na+/H+ exchange in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 104:629–635. doi:10.1172/JCI7192
Thwaites DT, Kennedy DJ, Raldua D, Anderson CM, Mendoza ME, Bladen CL, Simmons NL (2002) H+/dipeptide absorption across the human intestinal epithelium is controlled indirectly via a functional Na+/H+ exchanger. Gastroenterology 122:1322–1333. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.32992
Turner JR, Rill BK, Carlson SL, Carnes D, Kerner R, Mrsny RJ, Madara JL (1997) Physiological regulation of epithelial tight junctions is associated with myosin light-chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol 273:C1378–C1385
Watanabe C, Kato Y, Ito S, Kubo Y, Sai Y, Tsuji A (2005) Na+/H+ exchanger 3 affects transport property of H+/oligopeptide transporter 1. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20:443–451. doi:10.2133/dmpk.20.443
Wongdee K, Charoenphandhu N (2015) Vitamin D-enhanced duodenal calcium transport. Vitam Horm 98:407–440. doi:10.1016/bs.vh.2014.12.010
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Thailand Research Fund (TRF)–Mahidol University through Distinguished Research Professor Grant (DPG5780004 to N. Krishnamra), the TRF–Mahidol University through the TRF Senior Research Scholar Grant (RTA5780001 to N. Charoenphandhu), the Faculty of Science, Mahidol University (to N. Charoenphandhu and J. Thongbunchoo), the Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Burapha University and TRF through TRF Research Scholar Award (RSA5780041 to K. Wongdee), the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission (185100 to K. Wongdee), and TRF International Research Network Program (IRN59W0002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. I. Closs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thammayon, N., Wongdee, K., Lertsuwan, K. et al. Na+/H+ exchanger 3 inhibitor diminishes the amino-acid-enhanced transepithelial calcium transport across the rat duodenum. Amino Acids 49, 725–734 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2374-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2374-1