Abstract
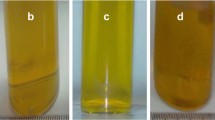
The synthesis of nanoparticles is usually carried out by chemical reduction, which is effective but uses many toxic substances, making the process potentially harmful to the environment. Hence, as part of the search for environmentally friendly or green synthetic methods, this study aimed to produce silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using only AgNO3, Milli-Q water, white light from a xenon lamp (Xe) and amino acids. Nanoparticles were synthetized using 21 amino acids, and the shapes and sizes of the resultant nanoparticles were evaluated. The products were characterized by UV–Vis, zeta potential measurements and transmission electron microscopy. The synthesis of silver nanoparticles with tryptophan and tyrosine, methionine, cystine and histidine was possible through photoreduction method. Spherical nanoparticles were produced, with sizes ranging from 15 to 30 nm. Tryptophan does not require illumination nor heating, and the solution color changes immediately after the mixing of reagents if sodium hydroxide is added to the solution (pH = 10). The Xe illumination acts as sodium hydroxide in the nanoparticles synthesis, releases H+ and allows the reduction of silver ions (Ag+) in metallic silver (Ag0).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow R, Blake JF (1989) Hill coefficients and the logistic equation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 10(11):440–441
Callegari A, Tonti D, Chergui M (2003) Photochemically grown silver nanoparticles with wavelength-controlled size and shape. Nano Lett 3(11):1565–1568
Choi S-H et al (2003) Interaction between the surface of the silver nanoparticles prepared by γ-irradiation and organic molecules containing thiol group. Radiat Phys Chem 67(3–4):517–521
Contino A, Maccarrone G, Zimbone M, Reitano R, Musumeci P, Calcagno L, Oliveri IP (2016) Tyrosine capped silver nanoparticles: a new fluorescent sensor for the quantitative determination of copper(II) and cobalt(II) ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 462:216–222
de Matos RA, Courrol LC (2014) Saliva and light as templates for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 441:539–543
Durán M, Silveira CP, Durán N (2015) Catalytic role of traditional enzymes for biosynthesis of biogenic metallic nanoparticles: a mini-review. IET Nanobiotechnol 9(5):314–323
Franci G, Falanga A, Galdiero S, Palomba L, Rai M, Morelli G, Galdiero M (2015) Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Molecules 20(5):8856–8874
G. Shustak,
 (2011) Biocompatible functionalized coatings on stainless steel medical implant devices, Jerusalem,
(2011) Biocompatible functionalized coatings on stainless steel medical implant devices, Jerusalem,  p 95
p 95Gottesman R, Shukla S, Perkas N, Solovyov LA, Nitzan Y, Gedanken A (2011) Sonochemical coating of paper by microbiocidal silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 27(2):720–726
Horikoshi S, Abe H, Torigoe K, Abe M, Serpone N (2010) Access to small size distributions of nanoparticles by microwave-assisted synthesis. Formation of Ag nanoparticles in aqueous carboxymethylcellulose solutions in batch and continuous-flow reactors. Nanoscale 2(8):1441–1447
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107(3):668–677
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim J-H, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park YK, Park YH, Hwang C-Y, Kim Y-K, Lee Y-S, Jeong DH, Cho M-H (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed-Nanotechnol Biol Med 3(1):95–101
Kshirsagar P, Sangaru SS, Brunetti V, Malvindi MA, Pompa PP (2014) Synthesis of fluorescent metal nanoparticles in aqueous solution by photochemical reduction. Nanotechnology 25(4):045601
Li ZP, Duan XR, Liu CH, Du BA (2006) Selective determination of cysteine by resonance light scattering technique based on self-assembly of gold nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 351(1):18–25
Makarov VV, Love AJ, Sinitsyna OV, Makarova SS, Yaminsky IV, Taliansky ME, Kalinina NO (2014) “Green” nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Naturae 6(1):35–44
Mandal S, Selvakannan P, Phadtare S, Pasricha R, Sastry M (2002) Synthesis of a stable gold hydrosol by the reduction of chloroaurate ions by the amino acid, aspartic acid. Proceed Indian Acad Sci-Chem Sci 114(5):513–520
McGilvray KL, Granger J, Correia M, Banks JT, Scaiano JC (2011) Opportunistic use of tetrachloroaurate photolysis in the generation of reductive species for the production of gold nanostructures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(25):11914–11918
Patronov A, Salamanova E, Dimitrov I, Flower DR, Doytchinova I (2014) Histidine hydrogen bonding in MHC at pH 5 and pH 7 modeled by molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 10(1):41–49
Pethig RR (1979) Dielectric and electronic properties of biological materials. Wiley
Ramezani F, Habibi M, Rafii-Tabar H, Amanlou M (2015) Effect of peptide length on the conjugation to the gold nanoparticle surface: a molecular dynamic study. Daru 23:9
Roni M, Murugan K, Panneerselvam C, Subramaniam J, Nicoletti M, Madhiyazhagan P, Dinesh D, Suresh U, Khater HF, Wei H, Canale A, Alarfaj AA, Munusamy MA, Higuchi A, Benelli G (2015) Characterization and biotoxicity of Hypnea musciformis-synthesized silver nanoparticles as potential eco-friendly control tool against Aedes aegypti and Plutella xylostella. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:31–38
Selvakannan PR, Swami A, Srisathiyanarayanan D, Shirude PS, Pasricha R, Mandale AB, Sastry M (2004) Synthesis of aqueous Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using tyrosine as a pH-dependent reducing agent and assembling phase-transferred silver nanoparticles at the air-water interface. Langmuir 20(18):7825–7836
Shankar S, Rhim JW (2015) Amino acid mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and preparation of antimicrobial agar/silver nanoparticles composite films. Carbohydr Polym 130:353–363
Sweet MJ, Chesser A, Singleton I (2012) Review: metal-Based Nanoparticles. Size Function Areas Adv Appl Microbiol Adv Appl Microbiol 80(80):113–142
Tomita RJ, de Matos RA, Vallim MA, Courrol LC (2014) A simple and effective method to synthesize fluorescent nanoparticles using tryptophan and light and their lethal effect against bacteria. J Photochem Photobiol B-Biol 140:157–162
Tung HT, Chen IG, Kempson IM, Song JM, Liu YF, Chen PW, Hwang WS, Hwu Y (2012) Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanocrystals by X-ray irradiation for inkjet printing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(11):5930–5935
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge ABC Federal University for zeta potential measurements and Fapesp 2014/06960-9 for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest to disclose.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: H. S. Sharma.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Matos, R.A., Courrol, L.C. Biocompatible silver nanoparticles prepared with amino acids and a green method. Amino Acids 49, 379–388 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2371-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2371-4




 (2011) Biocompatible functionalized coatings on stainless steel medical implant devices, Jerusalem,
(2011) Biocompatible functionalized coatings on stainless steel medical implant devices, Jerusalem,  p 95
p 95