Abstract
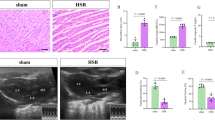
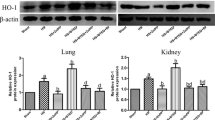
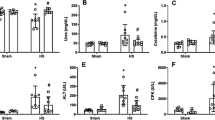
Oxidative stress induced by hemorrhagic shock (HS) initiates a systemic inflammatory response, which leads to subsequent kidney injury. This study assessed the efficacy of c-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) in attenuating kidney injury in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation (HS/R). Sodium pentobarbital-anesthetized adult male Wistar rats underwent HS induced by the withdrawal of blood to a mean arterial pressure of 30–35 mmHg for 50 min. Then, the animals received CNP (25 μg/kg) or vehicle (saline) intravenously, followed byresuscitation with 1.5 times the shed blood volume in the form of normal saline. Mean arterial pressure was measured throughout the experiment, and acid–base status, oxidative stress, inflammation, tissue injury and kidney function were evaluated after resuscitation. CNP infusion reduced the malondialdehyde content, lowered the myeloperoxidase activity and decreased the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in the kidney. The histologic injury score and the plasma creatinine concentration were also significantly decreased after CNP treatment compared to the vehicle group. CNP treatment ameliorates oxidative stress, the inflammatory response, and consequently acute kidney injury after HS/R. Thus, CNP may represent a promising strategy to improve resuscitation for the treatment of HS and deserves further investigation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benns M, Carr B, Kallan MJ, Sims CA (2013) Benchmarking the incidence of organ failure after injury at trauma centers and nontrauma centers in the United States. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 75:426–431
Bonventre JV, Zuk A (2004) Ischemic acute renal failure: An inflammatory disease? Kidney Int 66:480–485
Brown J, Zuo Z (1992) Renal receptors for atrial and C-type natriuretic peptides in the rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 263:F89–F96
Chen G, You G, Wang Y, Lu M, Cheng W, Yang J et al (2013) Effects of synthetic colloids on oxidative stress and inflammatory response in hemorrhagic shock: comparison of hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4, hydroxyethyl starch 200/0.5, and succinylated gelatin. Crit Care 17:R141
Chen G, Zhao J, Yin Y, Wang B, Liu Q, Li P et al (2014) C-type natriuretic peptide attenuates LPS-induced endothelial activation: involvement of p38, Akt, and NF-kappaB pathways. Amino Acids 46:2653–2663
Chima RS, Hake PW, Piraino G, Mangeshkar P, Denenberg A, Zingarelli B (2008) Ciglitazone ameliorates lung inflammation by modulating the inhibitor kappaB protein kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway after hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med 36:2849–2857
Dean AD, Vehaskari VM, Greenwald JE (1994) Synthesis and localization of C-type natriuretic peptide in mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 266:F491–F496
Gülberg V, Møller S, Henriksen JH, Gerbes AL (2000) Increased renal production of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) in patients with cirrhosis and functional renal failure. Gut 47:852–857
Hama N, Itoh H, Shirakami G, Suga S, Komatsu Y, Yoshimasa T et al (1994) Detection of C-Type natriuretic peptide in human circulation and marked increase of plasma CNP level in septic shock patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198:1177–1182
Harris DG, Koo G, McCrone MP, Weltz AS, Chiu WC, Sarkar R et al (2015) Acute kidney injury in critically ill vascular surgery patients is common and associated with increased mortality. Front Surg 2:8
Jin X, Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang J, Xu D (2014) C-type natriuretic peptide ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats. Life Sci 117:40–45
Kimura T, Nojiri T, Hosoda H, Ishikane S, Shintani Y, Inoue M, Miyazato M, Okumura M, Kangawa K (2015a) Protective effects of C-type natriuretic peptide on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75:1057–1063
Kimura T, Nojiri T, Hosoda H, Ishikane S, Shintani Y, Inoue M et al (2015b) C-type natriuretic peptide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Surg Res 194:631–637
Lee JH, Jo YH, Kim K, Lee JH, Rim KP, Kwon WY et al (2013) Effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on acute lung injury and acute kidney injury in hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation 84:121–127
Luo X, Yin Y, You G, Chen G, Wang Y, Zhao J et al (2015) Gradually increased oxygen administration improved oxygenation and mitigated oxidative stress after resuscitation from severe hemorrhagic shock. Anesthesiology 123:1122–1132
Luo X, Chen G, You G, Wang B, Lu M, Zhao J et al (2016) Gradually increased oxygen administration promoted survival after hemorrhagicshock. Exp Biol Med 241:1603–1610
Moyes AJ, Khambata RS, Villar I, Bubb KJ, Baliga RS, Lumsden NG et al (2014) Endothelial C-type natriuretic peptide maintains vascular homeostasis. J Clin Invest 124:4039–4051
Obata H, Yanagawa B, Tanaka K, Ohnishi S, Kataoka M, Miyahara Y et al (2007) CNP infusion attenuates cardiac dysfunction and inflammation in myocarditis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:60–66
Qian JY, Haruno A, Asada Y, Nishida T, Saito Y, Matsuda T et al (2002) Local expression of C-type natriuretic peptide suppresses inflammation, eliminates shear stress-induced thrombosis, and prevents neointima formation through enhanced nitric oxide production in rabbit injured carotid arteries. Circ Res 91:1063–1069
Rabb H, O’Meara YM, Maderna P, Coleman P, Brady HR (1997) Leukocytes, cell adhesion molecules and ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int 51:1463–1468
Soeki T, Kishimoto I, Okumura H, Tokudome T, Horio T, Mori K et al (2005) C-type natriuretic peptide, a novel antifibrotic and antihypertrophic agent, prevents cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:608–616
Suwa T, Hogg J, Klut M, Hards J, vanEeden S (2001) Interleukin-6 changes deformability of neutrophils and induces their sequestration in the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:970–976
Totsune K, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Satoh F, Sone M, Mouri T (1994) Elevated plasma C-type natriuretic peptide concentrations in patients with chronic renal failure. Clin Sci 87:319–322
Wang Y, Yan J, Xi L, Qian Z, Wang Z, Yang L (2012) Protective effect of crocetin on hemorrhagic shock-induced acute renal failure in rats. Shock 38:63–67
Wang H, Guan Y, Karamercan MA, Ye L, Bhatti T, Becker LB et al (2015) Resveratrol rescues kidney mitochondrial function following hemorrhagic shock. Shock 44:173–180
Wohlauer MV, Sauaia A, Moore EE, Burlew CC, Banerjee A, Johnson J (2012) Acute kidney injury and posttrauma multiple organ failure: the canary in the coal mine. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 72:373–378 (discussion 9–80)
Zhao ZG, Niu CY, Zhang LL, Zhang J, Han R, Zhang Y-P et al (2013) Exogenous normal lymph alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Ren Fail 35:806–811
Zhao JX, Wang B, You GX, Wang Y, Chen G, Wang Q et al (2015) Hypertonic saline dextran ameliorates organ damage in beagle hemorrhagic shock. PLoS One 10:e0136012
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the Youth Science Fund of AMMS (No. 2015CXJJ22) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81300751 and 81600148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. D. Wade.
G. Chen, X. Song and Y. Yin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Song, X., Yin, Y. et al. C-type natriuretic peptide prevents kidney injury and attenuates oxidative and inflammatory responses in hemorrhagic shock. Amino Acids 49, 347–354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2367-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2367-0