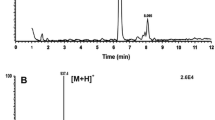
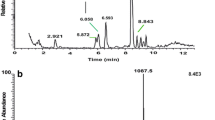
Abstract
Eight beetle species of the superfamily Scarabaeoidea were investigated with respect to peptides belonging to the adipokinetic hormone (AKH) family in their neurohemal organs, the corpora cardiaca (CC). The following beetle families are represented: Scarabaeidae, Lucanidae, and Geotrupidae. AKH peptides were identified through a heterospecific trehalose-mobilizing bioassay and by sequence analyses, using liquid chromatography coupled to positive electrospray mass spectrometry (LC–ESI–MS) and analysis of the tandem MS2 spectra obtained by collision-induced dissociation. All the beetle species have octapeptide AKHs; some have two AKHs, while others have only one. Novel AKH members were found in Euoniticellus intermedius and Circellium bacchus (family Scarabaeidae), as well as in Dorcus parallelipipedus (family Lucanidae). Two species of the family Geotrupidae and two species of the Scarabaeidae subfamily Cetoniinae contain one known AKH peptide, Melme-CC, while E. intermedius produces a novel peptide code named Euoin-AKH: pEINFTTGWamide. Two AKH peptides were each identified in CC of C. bacchus and D. parallelipipedus: the novel Cirba-AKH: pEFNFSAGWamide and the known peptide, Scade-CC-I in the former, and the novel Dorpa-AKH: pEVNYSPVW amide and the known peptide, Melme-CC in the latter. Kheper bonelli (subfamily Scarabaeinae) also has two AKHs, the known Scade-CC-I and Scade-CC-II. All the novel peptides were synthesized and the amino acid sequence assignments were unequivocally confirmed by co-elution of the synthetic peptides with their natural equivalent, and identical MS parameters of the two forms. The novel synthetic peptides are all active in inducing hypertrehalosemia in cockroaches.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens D, Fabrizzi S, Šipek P et al (2013) Integrative analysis of DNA phylogeography and morphology of the European rose chafer (Cetonia aurata) to infer species taxonomy and patterns of postglacial colonisation in Europe. Mol Phylogen Evol 69:83–94
Ajaykumar AP, Gokuldas M (2011) Primary structure of an adipokinetic neuropeptide from the rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros L (Coleoptera: Dynastidae). Ann Neurosci 18:100–104
Bartholomew GA, Heinrich B (1978) Endothermy in African dung beetles during flight, ball making, and ball rolling. J Exp Biol 73:65–83
Bouchard P, Bousquet Y, Davies AE et al (2011) Family-group names in Coleoptera (Insecta). ZooKeys 88:1–972
Browne J, Scholtz CH (1999) A phylogeny of the families of Scarabaeoidea (Coleoptera). Syst Entomol 24:51–84
Christie AE (2014) Peptide discovery in the ectoparasitic crustacean Argulus siamensis. Identification of the first neuropeptides from a member of the Branchiura. Gen Comp Endocrinol 201:74–86
Christie AE, Cashman CR, Brennan HR et al (2008) Identification of putative crustacean neuropeptides using in silico analyses of publicly accessible expressed sequence tags. Gen Comp Endocrinol 156:246–264
Davis ALV, Frolov AV, Scholtz CH (2008) The African Dung Beetle Genera. Protea Book House, Pretoria
Dircksen H, Neupert S, Predel R et al (2011) Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of Daphnia pulex neuropeptides and protein hormones. J Proteome Res 10:4478–4504
Duncan FD (2002) The role of the subelytral cavity in water loss in the flightless dung beetle, Circellium bacchus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeinae). Eur J Entomol 99:253–258
Duncan FD, Byrne MJ (2005) The role of the mesothoracic spiracles in respiration in flighted and flightless dung beetles. J Exp Biol 208:907–914
Duncan FD, Förster TD, Hetz SK (2010) Pump out the volume—the effect of tracheal and subelytral pressure pulses on convective gas exchange in a dung beetle, Circellium bacchus (Fabricius). J Insect Physiol 56:551–558
Fernlund P, Josefsson L (1972) Crustacean color-change hormone: amino acid sequence and chemical synthesis. Science 177:173–175
Gäde G (1980) Further characteristics of adipokinetic and hyperglycaemic factor(s) of stick insects. J Insect Physiol 26:351–360
Gäde G (1986) Relative hypertrehalosaemic activities of naturally occurring neuropeptides from the AKH/RPCH family. Z Naturforsch 41c:315–320
Gäde G (1991) A unique charged tyrosine-containing member of the adipokinetic hormone/red-pigment-concentrating hormone peptide family isolated and sequenced from two beetle species. Biochem J 275:671–677
Gäde G (1992) Structure–activity relationships for the carbohydrate-mobilizing action of further bioanalogues of the adipokinetic hormone/red pigment-concentrating hormone family of peptides. J Insect Physiol 38:259–266
Gäde G (1997a) The explosion of structural information on insect neuropeptides. In: Herz W, Kirby GW, Moore RE, Steglich W, Tamm CH (eds) Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products, vol 71. Springer, New York, pp 1–128
Gäde G (1997b) Distinct sequences of AKH/RPCH family members in beetle (Scarabaeus-species) corpus cardiacum contain three aromatic amino acid residues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:16–21
Gäde G (1997c) Hyperprolinaemia caused by novel members of the adipokinetic hormone/red pigment-concentrating hormone family of peptides isolated from corpora cardiac of onitine beetles. Biochem J 321:201–206
Gäde G (2009) Peptides of the adipokinetic hormone/red pigment-concentrating hormone family. A new take on biodiversity. Ann NY Acad Sci 1163:125–136
Gäde G, Auerswald L (2002) Beetles’ choice—proline for energy output: control by AKHs. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 132:117–129
Gäde G, Marco HG (2005) The adipokinetic hormones of Odonata: a phylogenetic approach. J Insect Physiol 51:333–341
Gäde G, Marco HG (2006) Structure, function and mode of action of select arthropod neuropeptides. In: Rahman AU (ed) Studies in natural products chemistry. Bioactive natural products (Part M), vol 33. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 69–139
Gäde G, Marco HG (2015) The decapeptide red pigment-concentrating hormone (Panbo-RPCH) is the first identified neuropeptide of the order Plecoptera and is interpreted as homoplastic character state. Gen Comp Endocrinol 221:228–235
Gäde G, Goldsworthy GJ, Kegel G et al (1984) Single step purification of locust adipokinetic hormones I and II by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography and the amino-acid composition of the hormone II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 365:393–398
Gäde G, Šimek P, Clark KD et al (2006) Unique translational modification of an invertebrate neuropeptide: a phosphorylated member of the adipokinetic hormone peptide family. Biochem J 393:705–713
Gäde G, Šimek P, Marco HG (2011) An invertebrate [hydroxyproline]-modified neuropeptide: further evidence for a close evolutionary relationship between insect adipokinetic hormone and mammalian gonadotropin hormone family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414:592–597
Gäde G, Šimek P, Marco HG (2015a) Two novel tyrosine-containing peptides (Tyr4) of the adipokinetic hormone family in beetles of the families Coccinellidae and Silphidae. Amino Acids 47:2323–2333
Gäde G, Šimek P, Marco HG (2015b) A novel adipokinetic peptide from the corpus cardiacum of the primitive caeliferan pygmy grasshopper Tetrix subulata (Caelifera, Tetrigidae). Peptides 68:43–49
Goldsworthy G, Opoku-Ware K, Mullen L (2002) Adipokinetic hormone enhances laminarin and bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of the prophenoloxidase cascade in the African migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol 48:601–608
Grebennikov VV, Scholtz CH (2004) The basal phylogeny of Scarabaeoidea (Insecta: Coleoptera) inferred from larval morphology. Invert Syst 18:321–348
Hauser F, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2014) Evolution of the AKH/corazonin/ACP/GnRH receptor superfamily and their ligands in the Protostomia. Gen Comp Endocrinol 209:35–49
Hull R, Alaouna M, Khanyile L et al (2013) Lifestyle and host defense mechanisms of the dung beetle, Euoniticellus intermedius: the Toll signalling pathway. J Insect Science 13:108
Johnson JI, Kavanaugh SI, Nguyen C et al (2014) Localization and functional characterization of a novel adipokinetic hormone in the mollusc, Aplysia californica. PloS One 9:e106014
Kodrik D, Marco HG, Šimek P et al (2010) The adipokinetic hormones of Heteroptera: a comparative study. Physiol Entomol 35:117–127
Lindemans M, Liu F, Janssen T et al (2009) Adipokinetic hormone signaling through the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor modulates egg-laying in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1642–1647
Marco HG, Gäde G (2010) Biological activity of the predicted red pigment-concentrating hormone of Daphnia pulex in a crustacean and an insect. Gen Comp Endocrinol 166:104–110
Mlambo S, Sole CL, Scholtz CH (2015) A molecular phylogeny of the African Scarabaeinae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Arthropod Syst Phylogen 73:303–321
Monaghan MT, Inward DJG, Hunt T et al (2007) A molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Scarabaeinae (dung beetles). Mol Phylogen Evol 45:674–692
Ohta Y, Kobayashi N, Suzuki S et al (2009) Evolution of flight-muscle polymorphism in the dung beetle Phelotrupes laevistriatus (Coleoptera: Geotrupidae): a phylogeographic analysis. Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:826–834
Pomfret JC, Knell RJ (2006) Immunity and the expression of a secondary sexual trait in a horned beetle. Behav Ecol 17:466–472
Reaney LT, Knell RJ (2015) Building a beetle: how larval environment leads to adult performance in a horned beetle. PLoS One 10:e0134399
Roch GJ, Busby ER, Sherwood NM (2011) Evolution of GnRH: diving deeper. Gen Comp Endocrinol 171:1–16
Roch GJ, Busby ER, Sherwood NM (2014) GnRH receptors and peptides: skating backwards. Gen Comp Endocrinol 209:118–134
Tarasov S, Genier F (2015) Innovative Bayesian and parsimony phylogeny of dung beetles (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae, Scarabaeinae) enhanced by ontology-based portioning of morphological characters. PLoS One 10:e016671
Wood LA, Kaufman PE (2008) Euoniticellus intermedius (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae: Tribe Coprini): its presence and relative abundance in cattle pastures in Northcentral Florida. Fla Entomol 91:128–130
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by funds from the National Research Foundation (Pretoria, South Africa; Grant No. 85768 (IFR13020116790 to GG) and IFR2011033100049 to HGM), and by staff awards from the Research Council of the University of Cape Town (to GG and HGM). Financial support of the Czech Science Foundation for PS, project No. 13-18509S, is acknowledged. The authors thank Frank Wolf (Schwaan, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany) for his help with collecting the lesser stag beetle and the two Geotrupidae species; Dr Marcus Byrne (School of Animal, Plant and Environmental Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa) for the gift of some specimens of E. intermedius; National Parks Board for allowing the collection of C. bacchus; Ms Alukhanyo Xonti (University of Cape Town) for assisting with the biological assays and Mrs Pavla Kruzberska for the LC–MS analyses (Ceske Budejovice).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: M. S. Palma.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gäde, G., Šimek, P. & Marco, H.G. Novel members of the adipokinetic hormone family in beetles of the superfamily Scarabaeoidea. Amino Acids 48, 2785–2798 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2314-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2314-0