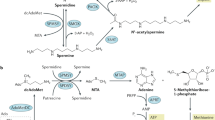
Abstract
The unique amino acid hypusine is present in only two proteins in eukaryotic cells, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 (eIF5A1), and eIF5A2, where it is covalently linked to the lysine-50 residue of these proteins via a post-translational modification coined hypusination. This unique modification is directed by two highly conserved and essential enzymes, deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS), and deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), which selectively use the polyamine spermidine as a substrate to generate hypusinated eIF5A. Notably, elevated levels of polyamines are a hallmark of most tumor types, and increased levels of polyamines can also be detected in the urine and blood of cancer patients. Further, in-clinic agents that block the function of key biosynthetic enzymes in the polyamine pathway markedly impair tumor progression and maintenance of the malignant state. Thus, the polyamine pathway is attractive as a prognostic, prevention and therapeutic target. As we review, recent advances in our understanding of the specific functions of hypusinated eIF5A and its role in tumorigenesis suggest that the polyamine-hypusine circuit is a high priority target for cancer therapeutics.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- eIF5A:
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A
- DHPS:
-
Deoxyhypusine synthase
- DOHH:
-
Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase
- GC7:
-
N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineheptane
- CPX:
-
Ciclopirox
- DEF:
-
Deferiprone
References
Abbruzzese A, Hanauske-Abel HM, Park MH, Henke S, Folk JE (1991) The active site of deoxyhypusyl hydroxylase: use of catecholpeptides and their component chelator and peptide moieties as molecular probes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1077:159–166
Balabanov S, Gontarewicz A, Ziegler P, Hartmann U, Kammer W, Copland M, Brassat U, Priemer M, Hauber I, Wilhelm T et al (2007) Hypusination of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A): a novel therapeutic target in BCR-ABL-positive leukemias identified by a proteomics approach. Blood 109:1701–1711
Bandino A, Geerts D, Koster J, Bachmann AS (2014) Deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) inhibitor GC7 induces p21/Rb-mediated inhibition of tumor cell growth and DHPS expression correlates with poor prognosis in neuroblastoma patients. Cell Oncol 37:387–398
Benne R, Brown-Luedi ML, Hershey JW (1978) Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation factors eIF-1, eIF-4C, eIF-4D, and eIF-5 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem 253:3070–3077
Bullwinkle TJ, Zou SB, Rajkovic A, Hersch SJ, Elgamal S, Robinson N, Smil D, Bolshan Y, Navarre WW, Ibba M (2013) (R)-beta-lysine-modified elongation factor P functions in translation elongation. J Biol Chem 288:4416–4423
Clement PM, Hanauske-Abel HM, Wolff EC, Kleinman HK, Park MH (2002) The antifungal drug ciclopirox inhibits deoxyhypusine and proline hydroxylation, endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis in vitro. Int J Cancer 100:491–498
Cracchiolo BM, Heller DS, Clement PM, Wolff EC, Park MH, Hanauske-Abel HM (2004) Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A-1 (eIF5A-1) as a diagnostic marker for aberrant proliferation in intraepithelial neoplasia of the vulva. Gynecol Oncol 94:217–222
Doerfel LK, Wohlgemuth I, Kothe C, Peske F, Urlaub H, Rodnina MV (2013) EF-P is essential for rapid synthesis of proteins containing consecutive proline residues. Science 339:85–88
Durie BG, Salmon SE, Russell DH (1977) Polyamines as markers of response and disease activity in cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res 37:214–221
Eberhard Y, McDermott SP, Wang X, Gronda M, Venugopal A, Wood TE, Hurren R, Datti A, Batey RA, Wrana J et al (2009) Chelation of intracellular iron with the antifungal agent ciclopirox olamine induces cell death in leukemia and myeloma cells. Blood 114:3064–3073
Eisenberg T, Knauer H, Schauer A, Buttner S, Ruckenstuhl C, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Ring J, Schroeder S, Magnes C, Antonacci L et al (2009) Induction of autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity. Nature Cell Biol 11:1305–1314
Epis MR, Giles KM, Barker A, Kendrick TS, Leedman PJ (2009) miR-331-3p regulates ERBB-2 expression and androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem 284:24696–24704
Epis MR, Giles KM, Kalinowski FC, Barker A, Cohen RJ, Leedman PJ (2012) Regulation of expression of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), the enzyme that catalyzes the activation of eIF5A, by miR-331-3p and miR-642-5p in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 287:35251–35259
Francis SM, Taylor CA, Tang T, Liu Z, Zheng Q, Dondero R, Thompson JE (2014) SNS01-T modulation of eIF5A inhibits B-cell cancer progression and synergizes with bortezomib and lenalidomide. J Am Soc Gene Ther 22:1643–1652
Frey AG, Nandal A, Park JH, Smith PM, Yabe T, Ryu MS, Ghosh MC, Lee J, Rouault TA, Park MH et al (2014) Iron chaperones PCBP1 and PCBP2 mediate the metallation of the dinuclear iron enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:8031–8036
Fujimura K, Wright T, Strnadel J, Kaushal S, Metildi C, Lowy AM, Bouvet M, Kelber JA, Klemke RL (2014) A hypusine-eIF5A-PEAK1 switch regulates the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 74:6671–6681
Fujimura K, Choi S, Wyse M, Strnadel J, Wright T, Klemke R (2015) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (EIF5A) regulates pancreatic cancer metastasis by modulating RhoA and Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) protein expression levels. J Biol Chem 290:29907–29919
Guan XY, Fung JM, Ma NF, Lau SH, Tai LS, Xie D, Zhang Y, Hu L, Wu QL, Fang Y et al (2004) Oncogenic role of eIF-5A2 in the development of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 64:4197–4200
Gutierrez E, Shin BS, Woolstenhulme CJ, Kim JR, Saini P, Buskirk AR, Dever TE (2013) eIF5A promotes translation of polyproline motifs. Mol Cell 51:35–45
He LR, Zhao HY, Li BK, Liu YH, Liu MZ, Guan XY, Bian XW, Zeng YX, Xie D (2011) Overexpression of eIF5A-2 is an adverse prognostic marker of survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer 129:143–150
Imam S, Mirmira RG, Jaume JC (2014) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A inhibition alters physiopathology and immune responses in a "humanized" transgenic mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E791–E798
Ingolia NT, Ghaemmaghami S, Newman JR, Weissman JS (2009) Genome-wide analysis in vivo of translation with nucleotide resolution using ribosome profiling. Science 324:218–223
Kang HA, Hershey JW (1994) Effect of initiation factor eIF-5A depletion on protein synthesis and proliferation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 269:3934–3940
Kim Y, Schmidt M, Endo T, Lu D, Carson D, Schmidt-Wolf IG (2011) Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway with the antifungal agent ciclopirox olamine in a murine myeloma model. In Vivo 25:887–893
Lasry A, Zinger A, Ben-Neriah Y (2016) Inflammatory networks underlying colorectal cancer. Nat Immunol 17:230–240
Lee NP, Tsang FH, Shek FH, Mao M, Dai H, Zhang C, Dong S, Guan XY, Poon RT, Luk JM (2010) Prognostic significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 127:968–976
Li Y, Fu L, Li JB, Qin Y, Zeng TT, Zhou J, Zeng ZL, Chen J, Cao TT, Ban X et al (2014) Increased expression of EIF5A2, via hypoxia or gene amplification, contributes to metastasis and angiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 146(1701–1713):e1709
Liu TA, Chang HK, Shieh RC (2012) Revisiting inward rectification: K ions permeate through Kir2.1 channels during high-affinity block by spermidine. J Gen Physiol 139:245–259
Luo Y, Zhou H, Liu L, Shen T, Chen W, Xu B, Han X, Zhang F, Scott RS, Alexander JS et al (2011) The fungicide ciclopirox inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell tube formation by suppressing VEGFR-3-mediated ERK signaling pathway. Oncogene 30:2098–2107
Maier B, Ogihara T, Trace AP, Tersey SA, Robbins RD, Chakrabarti SK, Nunemaker CS, Stull ND, Taylor CA, Thompson JE et al (2010) The unique hypusine modification of eIF5A promotes islet beta cell inflammation and dysfunction in mice. J Clin Invest 120:2156–2170
Mandal A, Mandal S, Park MH (2014) Genome-wide analyses and functional classification of proline repeat-rich proteins: potential role of eIF5A in eukaryotic evolution. PLoS One 9:e111800
Memin E, Hoque M, Jain MR, Heller DS, Li H, Cracchiolo B, Hanauske-Abel HM, Pe’ery T, Mathews MB (2014) Blocking eIF5A modification in cervical cancer cells alters the expression of cancer-related genes and suppresses cell proliferation. Cancer Res 74:552–562
Meng QB, Kang WM, Yu JC, Liu YQ, Ma ZQ, Zhou L, Cui QC, Zhou WX (2015) Overexpression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) correlates with cell aggressiveness and poor survival in gastric cancer. PLoS One 10:e0119229
Miller-Fleming L, Olin-Sandoval V, Campbell K, Ralser M (2015) Remaining mysteries of molecular biology: the role of polyamines in the cell. J Mol Biol 427:3389–3406
Minden MD, Hogge DE, Weir SJ, Kasper J, Webster DA, Patton L, Jitkova Y, Hurren R, Gronda M, Goard CA et al (2014) Oral ciclopirox olamine displays biological activity in a phase I study in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Am J Hematol 89:363–368
Moore CC, Martin EN, Lee G, Taylor C, Dondero R, Reznikov LL, Dinarello C, Thompson J, Scheld WM (2008) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A small interference RNA-liposome complexes reduce inflammation and increase survival in murine models of severe sepsis and acute lung injury. J Infect Dis 198:1407–1414
Neufeld EJ (2010) Update on iron chelators in thalassemia. Hematology/the Education Program of the American Society of Hematology American Society of Hematology Education Program 2010, pp 451–455
Nishimura K, Lee SB, Park JH, Park MH (2012) Essential role of eIF5A-1 and deoxyhypusine synthase in mouse embryonic development. Amino Acids 42:703–710
Oliverio S, Corazzari M, Sestito C, Piredda L, Ippolito G, Piacentini M (2014) The spermidine analogue GC7 (N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineoheptane) induces autophagy through a mechanism not involving the hypusination of eIF5A. Amino Acids 46:2767–2776
Pallmann N, Braig M, Sievert H, Preukschas M, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Schweizer M, Nagel CH, Neumann M, Wild P, Haralambieva E et al (2015) Biological relevance and therapeutic potential of the hypusine modification system. J Biol Chem 290:18343–18360
Park MH, Wolff EC, Folk JE (1993a) Hypusine: its post-translational formation in eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and its potential role in cellular regulation. BioFactors 4:95–104
Park MH, Wolff EC, Folk JE (1993b) Is hypusine essential for eukaryotic cell proliferation? TIBS 18:475–479
Park MH, Nishimura K, Zanelli CF, Valentini SR (2010) Functional significance of eIF5A and its hypusine modification in eukaryotes. Amino Acids 38:491–500
Park JH, Johansson HE, Aoki H, Huang BX, Kim HY, Ganoza MC, Park MH (2012) Post-translational modification by beta-lysylation is required for activity of Escherichia coli elongation factor P (EF-P). J Biol Chem 287:2579–2590
Pegg AE (2008) Spermidine/spermine-N(1)-acetyltransferase: a key metabolic regulator. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:995–1010
Preukschas M, Hagel C, Schulte A, Weber K, Lamszus K, Sievert H, Pallmann N, Bokemeyer C, Hauber J, Braig M (2012) Expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and hypusine forming enzymes in glioblastoma patient samples: implications for new targeted therapies. PloS one 7:e43468
Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES, Golub TR (2003) A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors. Nat Gen 33:49–54
Robbins RD, Tersey SA, Ogihara T, Gupta D, Farb TB, Ficorilli J, Bokvist K, Maier B, Mirmira RG (2010) Inhibition of deoxyhypusine synthase enhances islet beta cell function and survival in the setting of endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. J Biol Chem 285:39943–39952
Russell DH (1971) Increased polyamine concentrations in the urine of human cancer patients. Nat New Biol 233:144–145
Schmidt C, Becker T, Heuer A, Braunger K, Shanmuganathan V, Pech M, Berninghausen O, Wilson DN, Beckmann R (2016) Structure of the hypusinylated eukaryotic translation factor eIF-5A bound to the ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res 44:1944–1951
Scuoppo C, Miething C, Lindqvist L, Reyes J, Ruse C, Appelmann I, Yoon S, Krasnitz A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Pappin D et al (2012) A tumour suppressor network relying on the polyamine-hypusine axis. Nature 487:244–248
Sievert H, Pallmann N, Miller KK, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Venz S, Sendoel A, Preukschas M, Schweizer M, Boettcher S, Janiesch PC et al (2014) A novel mouse model for inhibition of DOHH-mediated hypusine modification reveals a crucial function in embryonic development, proliferation and oncogenic transformation. Dis Models Mech 7:963–976
Song S, Christova T, Perusini S, Alizadeh S, Bao RY, Miller BW, Hurren R, Jitkova Y, Gronda M, Isaac M et al (2011) Wnt inhibitor screen reveals iron dependence of beta-catenin signaling in cancers. Cancer Res 71:7628–7639
Subissi A, Monti D, Togni G, Mailland F (2010) Ciclopirox: recent nonclinical and clinical data relevant to its use as a topical antimycotic agent. Drugs 70:2133–2152
Sun Z, Cheng Z, Taylor CA, McConkey BJ, Thompson JE (2010) Apoptosis induction by eIF5A1 involves activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. J Cell Physiol 223:798–809
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, Xie D, Chen L, Fu L, Lau SH, Li Y, Li Y, Guan XY (2010) Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51:1255–1263
Taylor CA, Sun Z, Cliche DO, Ming H, Eshaque B, Jin S, Hopkins MT, Thai B, Thompson JE (2007) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells and associates with the nucleus in response to tumour necrosis factor alpha signalling. Exp Cell Res 313:437–449
Taylor CA, Liu Z, Tang TC, Zheng Q, Francis S, Wang TW, Ye B, Lust JA, Dondero R, Thompson JE (2012) Modulation of eIF5A expression using SNS01 nanoparticles inhibits NF-kappaB activity and tumor growth in murine models of multiple myeloma. J Am Soc Gene Ther 20:1305–1314
Taylor CA, Zheng Q, Liu Z, Thompson JE (2013) Role of p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways and tumor suppressor p53 on induction of apoptosis in response to Ad-eIF5A1 in A549 lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer 12:35
Templin AT, Maier B, Nishiki Y, Tersey SA, Mirmira RG (2011) Deoxyhypusine synthase haploinsufficiency attenuates acute cytokine signaling. Cell Cycle 10:1043–1049
Tunca B, Tezcan G, Cecener G, Egeli U, Zorluoglu A, Yilmazlar T, Ak S, Yerci O, Ozturk E, Umut G et al (2013) Overexpression of CK20, MAP3K8 and EIF5A correlates with poor prognosis in early-onset colorectal cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139:691–702
Ude S, Lassak J, Starosta AL, Kraxenberger T, Wilson DN, Jung K (2013) Translation elongation factor EF-P alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches. Science 339:82–85
Umland TC, Wolff EC, Park MH, Davies DR (2004) A new crystal structure of deoxyhypusine synthase reveals the configuration of the active enzyme and of an enzyme·NAD·inhibitor ternary complex. J Biol Chem 279:28697–28705
Wei JH, Cao JZ, Zhang D, Liao B, Zhong WM, Lu J, Zhao HW, Zhang JX, Tong ZT, Fan S et al (2014) EIF5A2 predicts outcome in localised invasive bladder cancer and promotes bladder cancer cell aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 110:1767–1777
Woolstenhulme CJ, Guydosh NR, Green R, Buskirk AR (2015) High-precision analysis of translational pausing by ribosome profiling in bacteria lacking EFP. Cell Rep 11:13–21
Xu G, Yu H, Shi X, Sun L, Zhou Q, Zheng D, Shi H, Li N, Zhang X, Shao G (2014) Cisplatin sensitivity is enhanced in non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2. BMC Pulm Med 14:174
Yang GF, Xie D, Liu JH, Luo JH, Li LJ, Hua WF, Wu HM, Kung HF, Zeng YX, Guan XY (2009) Expression and amplification of eIF-5A2 in human epithelial ovarian tumors and overexpression of EIF-5A2 is a new independent predictor of outcome in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 112:314–318
Zhou H, Shen T, Luo Y, Liu L, Chen W, Xu B, Han X, Pang J, Rivera CA, Huang S (2010) The antitumor activity of the fungicide ciclopirox. Int J Cancer 127:2467–2477
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the NCI Comprehensive Cancer Center Grant P30-CA076292 to the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals that were performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. Agostinelli.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakanishi, S., Cleveland, J.L. Targeting the polyamine-hypusine circuit for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Amino Acids 48, 2353–2362 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2275-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2275-3