Abstract
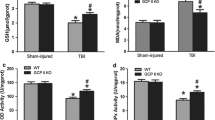
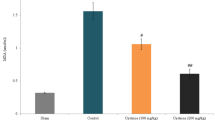
Excitatory amino acid carrier type 1 (EAAC1), a high-affinity glutamate transporter, can expend energy to move glutamate into neurons. However, under normal physiological conditions, EAAC1 does not have a great effect on glutamate clearance but rather participates in the neuronal uptake of cysteine. This process is critical to maintaining neuronal antioxidant function by providing cysteine for glutathione synthesis. Previous study showed that mice lacking EAAC1 show increased neuronal oxidative stress following transient cerebral ischemia. In the present study, we sought to characterize the role of EAAC1 in neuronal resistance after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Young adult C57BL/6 wild-type or EAAC1 −/− mice were subjected to a controlled cortical impact model for TBI. Neuronal death after TBI showed more than double the number of degenerating neurons in the hippocampus in EAAC1 −/− mice compared with wild-type mice. Superoxide production, zinc translocation and microglia activation similarly showed a marked increase in the EAAC1 −/− mice. Pretreatment with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) reduced TBI-induced neuronal death, superoxide production and zinc translocation. These findings indicate that cysteine uptake by EAAC1 is important for neuronal antioxidant function and survival following TBI. This study also suggests that administration of NAC has therapeutic potential in preventing TBI-induced neuronal death.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA (2006) Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci 9(1):119–126. doi:10.1038/nn1609
Aoyama K, Watabe M, Nakaki T (2008) Regulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Pharmacol Sci 108(3):227–238. pii: JST.JSTAGE/jphs/08R01CR
Bains JS, Shaw CA (1997) Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25(3):335–358. pii: S0165017397000453
Banbury-Conference (1997) Mutant mice and neuroscience: recommendations concerning genetic background. Banbury Conference on genetic background in mice. Neuron 19(4):755–759. pii: S0896-6273(00)80958-7
Bullock R, Kuroda Y, Teasdale GM, McCulloch J (1992) Prevention of post-traumatic excitotoxic brain damage with NMDA antagonist drugs: a new strategy for the nineties. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 55:49–55
Chen Y, Swanson RA (2003) The glutamate transporters EAAT2 and EAAT3 mediate cysteine uptake in cortical neuron cultures. J Neurochem 84(6):1332–1339. pii: 1630
Choi BY, Jang BG, Kim JH, Lee BE, Sohn M, Song HK, Suh SW (2012) Prevention of traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal death by inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation. Brain Res 1481:49–58. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.032
Choi BY, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Lee BE, Kim IY, Sohn M, Suh SW (2014) EAAC1 gene deletion increases neuronal death and blood brain barrier disruption after transient cerebral ischemia in female mice. Int J Mol Sci 15(11):19444–19457. doi:10.3390/ijms151119444
Clark RS, Schiding JK, Kaczorowski SL, Marion DW, Kochanek PM (1994) Neutrophil accumulation after traumatic brain injury in rats: comparison of weight drop and controlled cortical impact models. J Neurotrauma 11(5):499–506
d’Avila JC, Lam TI, Bingham D, Shi J, Won SJ, Kauppinen TM, Massa S, Liu J, Swanson RA (2012) Microglial activation induced by brain trauma is suppressed by post-injury treatment with a PARP inhibitor. J Neuroinflamm 9:31. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-31
De Vries N, De Flora S (1993) N-acetyl-l-cysteine. J Cell Biochem Suppl 17F:270–277
Dringen R (2000) Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 62(6):649–671. pii: S030100829900060X
Faden AI, Demediuk P, Panter SS, Vink R (1989) The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science 244(4906):798–800
Frederickson CJ, Kasarskis EJ, Ringo D, Frederickson RE (1987) A quinoline fluorescence method for visualizing and assaying the histochemically reactive zinc (bouton zinc) in the brain. J Neurosci Methods 20(2):91–103
Himi T, Ikeda M, Yasuhara T, Nishida M, Morita I (2003) Role of neuronal glutamate transporter in the cysteine uptake and intracellular glutathione levels in cultured cortical neurons. J Neural Transm 110(12):1337–1348. doi:10.1007/s00702-003-0049-z
Jang BG, Won SJ, Kim JH, Choi BY, Lee MW, Sohn M, Song HK, Suh SW (2012) EAAC1 gene deletion alters zinc homeostasis and enhances cortical neuronal injury after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26(2–3):85–88. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.04.010
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (1992) Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 360(6403):467–471. doi:10.1038/360467a0
Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, Hovda DA (1990) Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury. J Neurosurg 73(6):889–900. doi:10.3171/jns.1990.73.6.0889
Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA (2005) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 promotes microglial activation, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated neuron death. J Immunol 174(4):2288–2296. pii: 174/4/2288
Kauppinen TM, Higashi Y, Suh SW, Escartin C, Nagasawa K, Swanson RA (2008) Zinc triggers microglial activation. J Neurosci 28(22):5827–5835. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1236-08.2008
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2012) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8(6):e1000412. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412
Lane MC, Jackson JG, Krizman EN, Rothstein JD, Porter BE, Robinson MB (2014) Genetic deletion of the neuronal glutamate transporter, EAAC1, results in decreased neuronal death after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurochem Int 73:152–158. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.013
Lee SA, Choi JG, Zuo Z (2009) Volatile anesthetics attenuate oxidative stress-reduced activity of glutamate transporter type 3. Anesth Analg 109(5):1506–1510. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181b6709a
Li L, Zuo Z (2011) Glutamate transporter type 3 knockout reduces brain tolerance to focal brain ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(5):1283–1292. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.222
Mazor D, Golan E, Philip V, Katz M, Jafe A, Ben-Zvi Z, Meyerstein N (1996) Red blood cell permeability to thiol compounds following oxidative stress. Eur J Haematol 57(3):241–246
Murakami K, Kondo T, Kawase M, Li Y, Sato S, Chen SF, Chan PH (1998) Mitochondrial susceptibility to oxidative stress exacerbates cerebral infarction that follows permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mutant mice with manganese superoxide dismutase deficiency. J Neurosci 18(1):205–213
Peghini P, Janzen J, Stoffel W (1997) Glutamate transporter EAAC-1-deficient mice develop dicarboxylic aminoaciduria and behavioral abnormalities but no neurodegeneration. EMBO J 16(13):3822–3832. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.13.3822
Ramlackhansingh AF, Brooks DJ, Greenwood RJ, Bose SK, Turkheimer FE, Kinnunen KM, Gentleman S, Heckemann RA, Gunanayagam K, Gelosa G, Sharp DJ (2011) Inflammation after trauma: microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol 70(3):374–383. doi:10.1002/ana.22455
Rao VL, Dogan A, Todd KG, Bowen KK, Kim BT, Rothstein JD, Dempsey RJ (2001) Antisense knockdown of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1, but not the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1, exacerbates transient focal cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage in rat brain. J Neurosci 21(6):1876–1883. pii: 21/6/1876
Rothstein JD, Dykes-Hoberg M, Pardo CA, Bristol LA, Jin L, Kuncl RW, Kanai Y, Hediger MA, Wang Y, Schielke JP, Welty DF (1996) Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16(3):675–686
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874(2):123–130. pii: S0006-8993(00)02513-0
Schulz JB, Lindenau J, Seyfried J, Dichgans J (2000) Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Eur J Biochem 267(16):4904–4911. pii: ejb1595
Singh P (2003) Missile injuries of the brain: results of less aggressive surgery. Neurol India 51(2):215–219
Stence N, Waite M, Dailey ME (2001) Dynamics of microglial activation: a confocal time-lapse analysis in hippocampal slices. Glia 33(3):256–266. doi:10.1002/1098-1136(200103)33:3<256:AID-GLIA1024>3.0.CO;2-J
Suh SW, Chen JW, Motamedi M, Bell B, Listiak K, Pons NF, Danscher G, Frederickson CJ (2000) Evidence that synaptically-released zinc contributes to neuronal injury after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 852(2):268–273. pii: S0006899399020958
Suh SW, Frederickson CJ, Danscher G (2006) Neurotoxic zinc translocation into hippocampal neurons is inhibited by hypothermia and is aggravated by hyperthermia after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(2):161–169. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600176
Suh SW, Gum ET, Hamby AM, Chan PH, Swanson RA (2007) Hypoglycemic neuronal death is triggered by glucose reperfusion and activation of neuronal NADPH oxidase. J Clin Invest 117(4):910–918. doi:10.1172/JCI30077
Suh SW, Hamby AM, Gum ET, Shin BS, Won SJ, Sheline CT, Chan PH, Swanson RA (2008) Sequential release of nitric oxide, zinc, and superoxide in hypoglycemic neuronal death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(10):1697–1706. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2008.61
Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, Yamada K, Watanabe M, Takahashi K, Iwama H, Nishikawa T, Ichihara N, Kikuchi T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hori S, Takimoto M, Wada K (1997) Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 276(5319):1699–1702
Uchida K (2003) 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal: a product and mediator of oxidative stress. Prog Lipid Res 42(4):318–343
van Landeghem FK, Stover JF, Bechmann I, Bruck W, Unterberg A, Buhrer C, von Deimling A (2001) Early expression of glutamate transporter proteins in ramified microglia after controlled cortical impact injury in the rat. Glia 35(3):167–179
Watabe M, Aoyama K, Nakaki T (2008) A dominant role of GTRAP3-18 in neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Neurosci 28(38):9404–9413. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3351-08.2008
Watase K, Hashimoto K, Kano M, Yamada K, Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Okuyama S, Sakagawa T, Ogawa S, Kawashima N, Hori S, Takimoto M, Wada K, Tanaka K (1998) Motor discoordination and increased susceptibility to cerebellar injury in GLAST mutant mice. Eur J Neurosci 10(3):976–988
Won SJ, Yoo BH, Brennan AM, Shin BS, Kauppinen TM, Berman AE, Swanson RA, Suh SW (2010) EAAC1 gene deletion alters zinc homeostasis and exacerbates neuronal injury after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 30(46):15409–15418. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2084-10.2010
Zerangue N, Kavanaugh MP (1996) Interaction of l-cysteine with a human excitatory amino acid transporter. J Physiol 493(Pt 2):419–423
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (2012R1A2A2A01046132) and by Hallym University Specialization Fund (HRF-S-52).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. I. Closs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, B.Y., Kim, I.Y., Kim, J.H. et al. Decreased cysteine uptake by EAAC1 gene deletion exacerbates neuronal oxidative stress and neuronal death after traumatic brain injury. Amino Acids 48, 1619–1629 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2221-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2221-4