Abstract
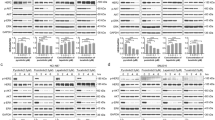
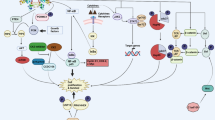
Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) is a member of the germinal center kinase family. TNIK was first identified as a kinase that is involved in regulating cytoskeletal organization in many types of cells, and it was recently proposed as a novel therapeutic target in several types of human cancers. Although previous studies suggest that TNIK plays a pivotal role in cancer cell survival and prognosis, its function in hematological cancer cell survival has not been investigated. Here we investigated the relationship between TNIK function and cell viability in multiple myeloma IM-9 cells using TNIK small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection and dovitinib treatment. Treatment of IM-9 cells with TNIK siRNA and dovitinib treatment reduced cell proliferation. The ATP competing kinase assay and western blot analysis showed that dovitinib strongly inhibited both the interaction of TNIK with ATP (K i, 13 nM) and the activation of Wnt signaling effectors such as β-catenin and TCF4. Dovitinib also induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in IM-9 cells without significant cytotoxicity in PBMCs. Our results provide new evidence that TNIK may be involved in the proliferation of multiple myeloma IM-9 cells and in the anti-cancer activity of dovitinib via inhibition of the endogenous Wnt signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angevin E, Lopez-Martin JA, Lin CC, Gschwend JE, Harzstark A, Castellano D et al (2013) Phase I study of dovitinib (TKI258), an oral FGFR, VEGFR, and PDGFR inhibitor, in advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:1257–1268
Bommert K, Bargou RC, Stühmer T (2006) Signalling and survival pathways in multiple myeloma. Eur J Cancer 42:1574–1580
Davis MI, Hunt JP, Herrgard S, Ciceri P, Wodicka LM, Pallares G et al (2011) Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 29:1046–1051
Eritja N, Domingo M, Dosil MA, Mirantes C, Santacana M, Valls J et al (2014) Combinatorial therapy using dovitinib and ICI182.780 (fulvestrant) blocks tumoral activity of endometrial cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 13:776–787
Fabian MA, Biggs WH 3rd, Treiber DK, Atteridge CE, Azimioara MD, Benedetti MG et al (2005) A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol 23:329–336
Fu CA, Shen M, Huang BC, Lasaga J, Payan DG, Luo Y (1999) TNIK, a novel member of the germinal center kinase family that activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and regulates the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 274:30729–30737. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.43.30729
Gui J, Yang B, Wu J, Zhou X (2011) Enormous influence of TNIK knockdown on intracellular signals and cell survival. Hum Cell 24:121–126
Ho KK, Parnell KM, Yuan Y, Xu Y, Kultgen SG, Hamblin S et al (2013) Discovery of 4-phenyl-2-phenylaminopyridine based TNIK inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:569–573
Hu Y, Leo C, Yu S, Huang BC, Wang H, Shen M et al (2004) Identification and functional characterization of a novel human misshapen/Nck interacting kinase-related kinase, hMINK beta. J Biol Chem 279:54387–54397
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F (2002) Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22:1172–1183
Kim KB, Chesney J, Robinson D, Gardner H, Shi MM, Kirkwood JM (2011) Phase I/II and pharmacodynamic study of dovitinib (TKI258), an inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptors and VEGF receptors, in patients with advanced melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:7451–7461
Kim J, Moon SH, Kim BT, Chae CH, Lee JY, Kim SH (2014) A novel aminothiazole KY-05009 with potential to inhibit Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) attenuates TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. PLoS One 9:e110180
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV (2008) Multiple myeloma. Blood 111:2962–2972
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Method Methods 25:402–408
Lopes de Menezes DE, Peng J, Garrett EN, Louie SG, Lee SH, Wiesmann M et al (2005) CHIR-258: a potent inhibitor of FLT3 kinase in experimental tumor xenograft models of human acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 11:5281–5291
Lustig B, Jerchow B, Sachs M, Weiler S, Pietsch T, Karsten U et al (2002) Negative feedback loop of Wnt signaling through upregulation of conductin/axin2 in colorectal and liver tumors. Mol Cell Biol 22:1184–1193
Maestro (2013) version 9.5; Schrödinger LLC, New York
Mahmoudi T, Li VS, Ng SS, Taouatas N, Vries RG, Mohammed S et al (2009) The kinase TNIK is an essential activator of Wnt target genes. EMBO J 28:3329–3340
Majno G, Joris I (1995) Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis: an overview of cell death. Am J Pathol 146:3–15
Milowsky MI, Dittrich C, Durán I, Jagdev S, Millard FE, Sweeney CJ et al (2014) Phase 2 trial of dovitinib in patients with progressive FGFR3-mutated or FGFR3 wild-type advanced urothelial carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 50:3145–3152
Porta C, Giglione P, Liguigli W, Paglino C (2015) Dovitinib (CHIR258, TKI258): structure, development and preclinical and clinical activity. Future Oncol 11:39–50
Ria R, Reale A, Vacca A (2014) Novel agents and new therapeutic approaches for treatment of multiple myeloma. World J Methodol 4:73–90
Roose J, Huls G, van Beest M, Moerer P, van der Horn K, Goldschmeding R et al (1999) Synergy between tumor suppressor APC and the beta-catenin-Tcf4 target Tcf1. Science 285:1923–1926
Schmid I, Krall WJ, Uittenbogaart CH, Braun J, Giorgi JV (1992) Dead cell discrimination with 7-amino-actinomycin D in combination with dual color immunofluorescence in single laser flow cytometry. Cytometry 13:204–208
Schürch C, Riether C, Matter MS, Tzankov A, Ochsenbein AF (2012) CD27 signaling on chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells activates Wnt target genes and promotes disease progression. J Clin Invest 122:624–638
Shitashige M, Satow R, Jigami T, Aoki K, Honda K, Shibata T et al (2010) Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase is essential for Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer growth. Cancer Res 70:5024–5033
Shkoda A, Town JA, Griese J, Romio M, Sarioglu H, Knöfel T et al (2012) The germinal center kinase TNIK is required for canonical NF-κB and JNK signaling in B-cells by the EBV oncoprotein LMP1 and the CD40 receptor. PLoS Biol 10:e1001376
Taira K, Umikawa M, Takei K, Myagmar BE, Shinzato M, Machida N et al (2004) The Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase as a putative effector of Rap2 to regulate actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 279:49488–49496
Tetsu O, McCormick F (1999) Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 398:422–426
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Yan D, Wiesmann M, Rohan M, Chan V, Jefferson AB, Guo L et al (2001) Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 9:14973–14978
Yu DH, Zhang X, Wang H, Zhang L, Chen H, Hu M et al (2014) The essential role of TNIK gene amplification in gastric cancer growth. Oncogenesis 17:e93
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and by a grant from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2014R1A1A1002349).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures that were performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the International Review Board of Eulji University (EU 15-06), with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: G. J. Peters.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chon, H.J., Lee, Y., Bae, K.J. et al. Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) is involved in the anti-cancer mechanism of dovitinib in human multiple myeloma IM-9 cells. Amino Acids 48, 1591–1599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2214-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2214-3