Abstract
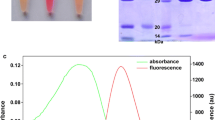
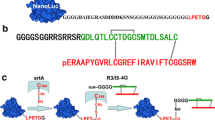
Relaxin is a prototype of the relaxin family peptide hormones and plays important biological functions by binding and activating the G protein-coupled receptor RXFP1. To study their interactions, in the present work, we applied the newly developed bioluminescent ligand–receptor binding assay to the relaxin-RXFP1 system. First, a fully active easily labeled relaxin, in which three Lys residues of human relaxin-2 were replaced by Arg, was prepared through overexpression of a single-chain precursor in Pichia pastoris and in vitro enzymatic maturation. Thereafter, the B-chain N-terminus of the easily labeled relaxin was chemically cross-linked with a C-terminal cysteine residue of an engineered NanoLuc through a disulfide linkage. Receptor-binding assays demonstrated that the NanoLuc-conjugated relaxin retained high binding affinity with the receptor RXFP1 (K d = 1.11 ± 0.08 nM, n = 3) and was able to sensitively monitor binding of a variety of ligands with RXFP1. Using the novel bioluminescent binding assay, we demonstrated that three highly conserved B-chain Arg residues of relaxin-3 had distinct contributions to binding of the receptor RXFP1. In summary, our present work provides a novel bioluminescent ligand–receptor binding assay for the relaxin-RXFP1 system to facilitate their interaction studies, such as characterization of relaxin analogues or screening novel agonists or antagonists of RXFP1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathgate RA, Lin F, Hanson NF, Otvos L Jr, Guidolin A, Giannakis C, Bastiras S, Layfield SL, Ferraro T, Ma S, Zhao C, Gundlach AL, Samuel CS, Tregear GW, Wade JD (2006) Relaxin-3: improved synthesis strategy and demonstration of its high-affinity interaction with the relaxin receptor LGR7 both in vitro and in vivo. Biochemistry 45:1043–1053
Bathgate RA, Halls ML, van der Westhuizen ET, Callander GE, Kocan M, Summers RJ (2013) Relaxin family peptides and their receptors. Physiol Rev 93:405–480
Bylund DB, Toews ML (2011) Radioligand binding methods for membrane preparations and intact cells. Methods Mol Biol 746:135–164
Cernaro V, Lacquaniti A, Lupica R, Buemi A, Trimboli D, Giorgianni G, Bolignano D, Buemi M (2014) Relaxin: new pathophysiological aspects and pharmacological perspectives for an old protein. Med Res Rev 34:77–105
Eigenbrot C, Randal M, Quan C, Burnier J, O’Connell L, Rinderknetct E, Kossiakoff AA (1991) X-ray structure of human relaxin at 1.5 Å: comparison to insulin and implications for receptor binding determinants. J Mol Biol 221:15–21
Guo YQ, Wu QP, Shao XX, Shen T, Liu YL, Zeng GX, Guo ZY (2015) Secretory overexpression and isotopic labeling of the chimeric relaxin family peptide R3/I5 in Pichia pastoris. Amino Acids 47:1117–1125
Hall MP, Unch J, Binkowski BF, Valley MP, Butler BL, Wood MG, Otto P, Zimmerman K, Vidugiris G, Machleidt T, Robers MB, Benink HA, Eggers CT, Slater MR, Meisenheimer PL, Klaubert DH, Fan F, Encell LP, Wood KV (2012) Engineered luciferase reporter from a deep sea shrimp utilizing a novel imidazopyrazinone substrate. ACS Chem Biol 7:1848–1857
He SX, Song G, Shi JP, Guo YQ, Guo ZY (2014) Nanoluciferase as a novel quantitative protein fusion tag: application for overexpression and bioluminescent receptor-binding assays of human leukemia inhibitory factor. Biochimie 106:140–148
Hisaw F (1926) Experimental relaxation of the pubic ligament of the guinea pig. Proc Soc Exper Biol Med 23:661–663
Hsu SY, Nakabayashi K, Nishi S, Kumagai J, Kudo M, Sherwood OD, Hsueh AJ (2002) Activation of orphan receptors by the hormone relaxin. Science 295:671–674
Hudson P, Haley J, Cronk M, Shine J, Niall H (1981) Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA sequences coding for rat relaxin. Nature 291:127–131
Hudson P, Haley J, John M, Cronk M, Crawford R, Haralambidis J, Tregear G, Shine J, Niall H (1983) Structure of a genomic clone encoding biologically active human relaxin. Nature 301:628–631
Hulme EC, Trevethick MA (2010) Ligand binding assays at equilibrium: validation and interpretation. Br J Pharmacol 161:1219–1237
James R, Niall H, Kwok S, Bryand-Greenwood G (1977) Primary structure of porcine relaxin: homology with insulin and related growth factors. Nature 267:544–546
Kuei C, Sutton S, Bonaventure P, Pudiak C, Shelton J, Zhu J, Nepomuceno D, Wu J, Chen J, Kamme F, Seierstad M, Hack MD, Bathgate RA, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Atack J, Lovenberg TW, Liu C (2007) R3(BDelta23-27)R/I5 chimeric peptide, a selective antagonist for GPCR135 and GPCR142 over relaxin receptor LGR7: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Biol Chem 282:25425–25435
Liu Y, Shao XX, Zhang L, Song G, Liu YL, Xu ZG, Guo ZY (2015) Novel bioluminescent receptor-binding assays for peptide hormones: using ghrelin as a model. Amino Acids 47:2237–2243
Maguire JJ, Kuc RE, Davenport AP (2012) Radioligand binding assays and their analysis. Methods Mol Biol 897:31–77
Nair VB, Samuel CS, Separovic F, Hossain MA, Wade JD (2012) Human relaxin-2: historical perspectives and role in cancer biology. Amino Acids 43:1131–1140
Schwabe C, McDonald JK (1977) Relaxin: a disulfide homolog of insulin. Science 197:914–915
Shabanpoor F, Bathgate RA, Belgi A, Chan LJ, Nair VB, Wade JD, Hossain MA (2012) Site-specific conjugation of a lanthanide chelator and its effects on the chemical synthesis and receptor binding affinity of human relaxin-2 hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420:253–256
Song G, Wu QP, Xu T, Liu YL, Xu ZG, Zhang SF, Guo ZY (2015) Quick preparation of nanoluciferase-based tracers for novel bioluminescent receptor-binding assays of protein hormones: using erythropoietin as a model. J Photochem Photobiol, B 153:311–316
Sudo S, Kumagai J, Nishi S, Layfield S, Ferraro T, Bathgate RA, Hsueh AJ (2003) H3 relaxin is a specific ligand for LGR7 and activates the receptor by interacting with both the ectodomain and the exoloop 2. J Biol Chem 278:7855–7862
Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Ponikowski P, Unemori E, Voors AA, Adams KF Jr, Dorobantu MI, Grinfeld LR, Jondeau G, Marmor A, Masip J, Pang PS, Werdan K, Teichman SL, Trapani A, Bush CA, Saini R, Schumacher C, Severin TM, Metra M (2013) Serelaxin, recombinant human relaxin-2, for treatment of acute heart failure (RELAX-AHF): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 381:29–39
Wang XY, Guo YQ, Zhang WJ, Shao XX, Liu YL, Xu ZG, Guo ZY (2014) The electrostatic interactions of relaxin-3 with receptor RXFP4 and the influence of its B-chain C-terminal conformation. FEBS J 281:2927–2936
Zhang WJ, Gao XJ, Liu YL, Shao XX, Guo ZY (2012a) Design, recombinant preparation and europium-labeling of a fully active easily-labeled INSL3 analogue for receptor-binding assays. Process Biochem 47:1856–1860
Zhang WJ, Luo X, Song G, Wang XY, Shao XX, Guo ZY (2012b) Design, recombinant expression and convenient A-chain N-terminal europium-labelling of a fully active human relaxin-3 analogue. FEBS J 279:1505–1512
Zhang L, Song G, Xu T, Wu QP, Shao XX, Liu YL, Xu ZG, Guo ZY (2013a) A novel ultrasensitive bioluminescent receptor-binding assay of INSL3 through chemical conjugation with nanoluciferase. Biochimie 95:2454–2459
Zhang WJ, Jiang Q, Wang XY, Geng S, Shao XX, Guo ZY (2013b) A convenient method for europium-labeling of a recombinant chimeric relaxin family peptide R3/I5 for receptor-binding assays. J Pept Sci 19:350–354
Zhang WJ, Wang XY, Guo YQ, Luo X, Gao XJ, Shao XX, Liu YL, Xu ZG, Guo ZY (2014) The highly conserved negatively charged Glu141 and Asp145 of the G-protein-coupled receptor RXFP3 interact with the highly conserved positively charged arginine residues of relaxin-3. Amino Acids 46:1393–1402
Acknowledgments
We thank Promega Corporation for providing the plasmids encoding NanoLuc. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470767, 31270824) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2000219098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. D. Wade.
Q.-P. Wu and L. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, QP., Zhang, L., Shao, XX. et al. Application of the novel bioluminescent ligand–receptor binding assay to relaxin-RXFP1 system for interaction studies. Amino Acids 48, 1099–1107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2146-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2146-3