Abstract
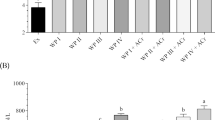
We compared immediate post-exercise whey protein (WP, 500 mg) versus l-leucine (LEU, 54 mg) feedings on skeletal muscle protein synthesis (MPS) mechanisms and ribosome biogenesis markers 3 h following unilateral plantarflexor resistance exercise in male, Wistar rats (~250 g). Additionally, in vitro experiments were performed on differentiated C2C12 myotubes to compare nutrient (i.e., WP, LEU) and ‘exercise-like’ treatments (i.e., caffeine, hydrogen peroxide, and AICAR) on ribosome biogenesis markers. LEU and WP significantly increased phosphorylated-rpS6 (Ser235/236) in the exercised (EX) leg 2.4-fold (P < 0.01) and 2.7-fold (P < 0.001) compared to the non-EX leg, respectively, whereas vehicle-fed control (CTL) did not (+65 %, P > 0.05). Compared to the non-EX leg, MPS levels increased 32 % and 52 % in the EX leg of CTL (P < 0.01) and WP rats (P < 0.001), respectively, but not in LEU rats (+15 %, P > 0.05). Several genes associated with ribosome biogenesis robustly increased in the EX versus non-EX legs of all treatments; specifically, c-Myc mRNA, Nop56 mRNA, Bop1 mRNA, Ncl mRNA, Npm1 mRNA, Fb1 mRNA, and Xpo-5 mRNA. However, only LEU significantly increased 45S pre-rRNA levels in the EX leg (63 %, P < 0.001). In vitro findings confirmed that ‘exercise-like’ treatments similarly altered markers of ribosome biogenesis, but only LEU increased 47S pre-rRNA levels (P < 0.01). Collectively, our data suggests that resistance exercise, as well as ‘exercise-like’ signals in vitro, acutely increase the expression of genes associated with ribosome biogenesis independent of nutrient provision. Moreover, while EX with or without WP appears superior for enhancing translational efficiency (i.e., increasing MPS per unit of RNA), LEU administration (or co-administration) may further enhance ribosome biogenesis over prolonged periods with resistance exercise.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Hoeflich KP, Woodgett JR (2001) Glycogen synthase kinase-3: properties, functions, and regulation. Chem Rev 101:2527–2540
Anthony TG, Anthony JC (2008) AMPing down leucine action in skeletal muscle. J Nutr 138:2307–2308. doi:10.3945/jn.108.098392
Anthony JC, Yoshizawa F, Anthony TG, Vary TC, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR (2000) Leucine stimulates translation initiation in skeletal muscle of postabsorptive rats via a rapamycin-sensitive pathway. J Nutr 130:2413–2419
Anthony TG, McDaniel BJ, Knoll P, Bunpo P, Paul GL, McNurlan MA (2007) Feeding meals containing soy or whey protein after exercise stimulates protein synthesis and translation initiation in the skeletal muscle of male rats. J Nutr 137:357–362
Apro W, Blomstrand E (2010) Influence of supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in combination with resistance exercise on p70S6 kinase phosphorylation in resting and exercising human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 200:237–248. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1708.2010.02151.x
Armstrong RB, Phelps RO (1984) Muscle fiber type composition of the rat hindlimb. Am J Anat 171:259–272. doi:10.1002/aja.1001710303
Balage M, Dardevet D (2010) Long-term effects of leucine supplementation on body composition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:265–270. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328336f6b8
Barres R et al (2012) Acute exercise remodels promoter methylation in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab 15:405–411. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.001
Beaton LJ, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM (2002) Contraction-induced muscle damage in humans following calcium channel blocker administration. The Journal of physiology 544:849–859
Bird SP, Tarpenning KM, Marino FE (2006) Independent and combined effects of liquid carbohydrate/essential amino acid ingestion on hormonal and muscular adaptations following resistance training in untrained men. Eur J Appl Physiol 97:225–238. doi:10.1007/s00421-005-0127-z
Blomstrand E, Eliasson J, Karlsson HK, Kohnke R (2006) Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. J Nutr 136:269S–273S
Bodine SC et al (2001) Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol 3:1014–1019. doi:10.1038/ncb1101-1014
Bolster DR, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR (2004) Regulation of protein synthesis associated with skeletal muscle hypertrophy by insulin-, amino acid- and exercise-induced signalling. Proc Nutr Soc 63:351–356. doi:10.1079/PNS2004355
Burd NA, Tang JE, Moore DR, Phillips SM (2009) Exercise training and protein metabolism: influences of contraction, protein intake, and sex-based differences. J Appl Physiol 106:1692–1701. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.91351.2008
Burke DG, Chilibeck PD, Davidson KS, Candow DG, Farthing J, Smith-Palmer T (2001) The effect of whey protein supplementation with and without creatine monohydrate combined with resistance training on lean tissue mass and muscle strength. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 11:349–364
Chaillou T, Lee JD, England JH, Esser KA, McCarthy JJ (2013) Time course of gene expression during mouse skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 115:1065–1074. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00611.2013
Chaillou T, Kirby TJ, McCarthy JJ (2014) Ribosome biogenesis: emerging evidence for a central role in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass. J Cell Physiol 229:1584–1594. doi:10.1002/jcp.24604
Churchward-Venne TA et al (2012) Supplementation of a suboptimal protein dose with leucine or essential amino acids: effects on myofibrillar protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in men. J Physiol 590:2751–2765. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.228833
Cribb PJ, Williams AD, Carey MF, Hayes A (2006) The effect of whey isolate and resistance training on strength, body composition, and plasma glutamine. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16:494–509
Dardevet D, Sornet C, Balage M, Grizard J (2000) Stimulation of in vitro rat muscle protein synthesis by leucine decreases with age. J Nutr 130:2630–2635
Davies B, Morris T (1993) Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm Res 10:1093–1095
DeLong AD, Pratt R, McLoughlin TJ (2011) FoxO1-mediated disruption of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in skeletal myotubes. FASEB J 25:LB603
Dreyer HC, Fujita S, Cadenas JG, Chinkes DL, Volpi E, Rasmussen BB (2006) Resistance exercise increases AMPK activity and reduces 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 576:613–624. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113175
Dreyer HC et al (2008) Leucine-enriched essential amino acid and carbohydrate ingestion following resistance exercise enhances mTOR signaling and protein synthesis in human muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:E392–E400. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00582.2007
Drummond MJ et al (2011) Skeletal muscle amino acid transporter expression is increased in young and older adults following resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol 111:135–142. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01408.2010
Eckert WA, Kaffenberger W (1980) Regulation of rRNA metabolism in Tetrahymena pyriformis. I nutritional shift-down. Eur J Cell Biol 21:53–62
Egawa T et al (2014) AICAR-induced activation of AMPK negatively regulates myotube hypertrophy through the HSP72-mediated pathway in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E344–E354. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00495.2013
Farnfield MM, Carey KA, Gran P, Trenerry MK, Cameron-Smith D (2009) Whey protein ingestion activates mTOR-dependent signalling after resistance exercise in young men: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 1:263–275. doi:10.3390/nu1020263
Farnfield MM, Breen L, Carey KA, Garnham A, Cameron-Smith D (2012) Activation of mTOR signalling in young and old human skeletal muscle in response to combined resistance exercise and whey protein ingestion. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37:21–30. doi:10.1139/h11-132
Gonzalez AM et al (2015) Association between myosin heavy chain protein isoforms and intramuscular anabolic signaling following resistance exercise in trained men Physiol Rep 3:e12268. doi:10.14814/phy2.12268
Goodman CA, Hornberger TA (2013) Measuring protein synthesis with SUnSET: a valid alternative to traditional techniques? Exerc Sport Sci Rev 41:107–115. doi:10.1097/JES.0b013e3182798a95
Grandori C, Gomez-Roman N, Felton-Edkins ZA, Ngouenet C, Galloway DA, Eisenman RN, White RJ (2005) c-Myc binds to human ribosomal DNA and stimulates transcription of rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I. Nat Cell Biol 7:311–318. doi:10.1038/ncb1224
Guo QM et al (2000) Identification of c-myc responsive genes using rat cDNA microarray. Cancer Res 60:5922–5928
Ha E, Zemel MB (2003) Functional properties of whey, whey components, and essential amino acids: mechanisms underlying health benefits for active people (review). J Nutr Biochem 14:251–258
Haddad F, Adams GR (2006) Aging-sensitive cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 100:1188–1203. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01227.2005
Hulmi JJ, Tannerstedt J, Selanne H, Kainulainen H, Kovanen V, Mero AA (2009) Resistance exercise with whey protein ingestion affects mTOR signaling pathway and myostatin in men. J Appl Physiol 106:1720–1729. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00087.2009
Hulmi JJ, Lockwood CM, Stout JR (2010) Effect of protein/essential amino acids and resistance training on skeletal muscle hypertrophy: a case for whey protein. Nutr Metab (Lond) 7:51. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-7-51
Iadevaia V, Huo Y, Zhang Z, Foster LJ, Proud CG (2012) Roles of the mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR, in controlling ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Biochem Soc Trans 40:168–172. doi:10.1042/BST20110682
Izumi H, Kosaka N, Shimizu T, Sekine K, Ochiya T, Takase M (2013) Purification of RNA from milk whey. Method Mol Biol 1024:191–201. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-453-1_15
Jaffe AE et al (2015) Developmental regulation of human cortex transcription and its clinical relevance at single base resolution. Nat Neurosci 18:154–161. doi:10.1038/nn.3898
Jakubowicz D, Froy O (2013) Biochemical and metabolic mechanisms by which dietary whey protein may combat obesity and type 2 diabetes. J Nutr Biochem 24:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.07.008
Karlsson HK, Nilsson PA, Nilsson J, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR, Blomstrand E (2004) Branched-chain amino acids increase p70S6 k phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise. Am J physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:E1–E7. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00430.2003
Katsanos CS, Chinkes DL, Paddon-Jones D, Zhang XJ, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR (2008) Whey protein ingestion in elderly persons results in greater muscle protein accrual than ingestion of its constituent essential amino acid content. Nutr Res 28:651–658. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2008.06.007
Koopman R et al (2005) Combined ingestion of protein and free leucine with carbohydrate increases postexercise muscle protein synthesis in vivo in male subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E645–E653. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00413.2004
Koopman R, Pennings B, Zorenc AH, van Loon LJ (2007) Protein ingestion further augments S6K1 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle following resistance type exercise in males. J Nutr 137:1880–1886
Koopman R et al (2008) Co-ingestion of leucine with protein does not further augment post-exercise muscle protein synthesis rates in elderly men. Br J Nutr 99:571–580. doi:10.1017/S0007114507812013
Li F, Yin Y, Tan B, Kong X, Wu G (2011) Leucine nutrition in animals and humans: mTOR signaling and beyond. Amino Acids 41:1185–1193. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0983-2
Madureira AR, Tavares T, Gomes AM, Pintado ME, Malcata FX (2010) Invited review: physiological properties of bioactive peptides obtained from whey proteins. J Dairy Sci 93:437–455. doi:10.3168/jds.2009-2566
Magne H, Savary-Auzeloux I, Migne C, Peyron MA, Combaret L, Remond D, Dardevet D (2012) Contrarily to whey and high protein diets, dietary free leucine supplementation cannot reverse the lack of recovery of muscle mass after prolonged immobilization during ageing. J Physiol 590:2035–2049. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.226266
Mayer C, Grummt I (2006) Ribosome biogenesis and cell growth: mTOR coordinates transcription by all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases. Oncogene 25:6384–6391. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209883
Mayer C, Zhao J, Yuan X, Grummt I (2004) mTOR-dependent activation of the transcription factor TIF-IA links rRNA synthesis to nutrient availability. Genes Dev 18:423–434. doi:10.1101/gad.285504
McClung JM, Van Gammeren DV, Whidden MA, Falk DJ, Kavazis AN, Hudson MB, Gayan-Ramirez G, Decramer M, DeRuisseau KC, Powers SP (2009) Apocynin attenuates diaphragm oxidative stress and protease activation during prolonged mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 37:1373–1379. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819cef63
McGinnis GR, Ballmann C, Peters B, Nanayakkara G, Roberts M, Amin R, Quindry JC (2015) Interleukin-6 mediates exercise preconditioning against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 308:H1423–H1433. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00850.2014
Mobley CB et al (2015) Effects of protein type and composition on postprandial markers of skeletal muscle anabolism, adipose tissue lipolysis, and hypothalamic gene expression. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 12:14. doi:10.1186/s12970-015-0076-9
Nader GA, von Walden F, Liu C, Lindvall J, Gutmann L, Pistilli EE, Gordon PM (2014) Resistance exercise training modulates acute gene expression during human skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 116:693–702. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01366.2013
Nie Z et al (2012) c-Myc is a universal amplifier of expressed genes in lymphocytes and embryonic stem cells. Cell 151:68–79. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.033
Norton LE, Layman DK, Bunpo P, Anthony TG, Brana DV, Garlick PJ (2009) The leucine content of a complete meal directs peak activation but not duration of skeletal muscle protein synthesis and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in rats. J Nutr 139:1103–1109. doi:10.3945/jn.108.103853
Norton LE, Wilson GJ, Layman DK, Moulton CJ, Garlick PJ (2012) Leucine content of dietary proteins is a determinant of postprandial skeletal muscle protein synthesis in adult rats. Nutr Metab (Lond) 9:67. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-9-67
Olszewski U, Deally A, Tacke M, Hamilton G (2012) Alterations of phosphoproteins in NCI-H526 small cell lung cancer cells involved in cytotoxicity of cisplatin and titanocene Y. Neoplasia 14:813–822
Pestov DG, Shcherbik N (2012) Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of yeast ribosomes in response to rapamycin inhibition of TOR. Mol Cell Biol 32:2135–2144. doi:10.1128/MCB.06763-11
Phillips SM (2014) A brief review of critical processes in exercise-induced muscular hypertrophy Sports Med 44(Suppl 1):S71–S77. doi:10.1007/s40279-014-0152-3
Phillips SM, Tipton KD, Aarsland A, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR (1997) Mixed muscle protein synthesis and breakdown after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol 273:E99–E107
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 22:659–661. doi:10.1096/fj.07-9574LSF
Reid MB, Durham WJ (2002) Generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in contracting skeletal muscle: potential impact on aging. Ann NY Acad Sci 959:108–116
Roberts MD, Dalbo VJ, Hassell SE, Brown R, Kerksick CM (2010) Effects of preexercise feeding on markers of satellite cell activation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1861–1869. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181da8a29
Rommel C et al (2001) Mediation of IGF-1-induced skeletal myotube hypertrophy by PI(3)K/Akt/mTOR and PI(3)K/Akt/GSK3 pathways. Nat Cell Biol 3:1009–1013. doi:10.1038/ncb1101-1009
Ropelle ER et al (2008) A central role for neuronal AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in high-protein diet-induced weight loss. Diabetes 57:594–605. doi:10.2337/db07-0573
Saha AK, Xu XJ, Lawson E, Deoliveira R, Brandon AE, Kraegen EW, Ruderman NB (2010) Downregulation of AMPK accompanies leucine- and glucose-induced increases in protein synthesis and insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 59:2426–2434. doi:10.2337/db09-1870
Sakamoto K, Hirshman MF, Aschenbach WG, Goodyear LJ (2002) Contraction regulation of Akt in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 277:11910–11917. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112410200
Stec MJ, Mayhew DL, Bamman MM (2015) The effects of age and resistance loading on skeletal muscle ribosome biogenesis J Appl Physiol:jap 00489 02015 doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00489.2015
Tang JE, Moore DR, Kujbida GW, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM (2009) Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. J Appl Physiol 107:987–992. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00076.2009
Thomson E, Ferreira-Cerca S, Hurt E (2013) Eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis at a glance. J Cell Sci 126:4815–4821. doi:10.1242/jcs.111948
Tipton KD, Phillips SM (2013) Dietary protein for muscle hypertrophy. Nestle Nutr Inst Worksh Ser 76:73–84. doi:10.1159/000350259
Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Cree MG, Aarsland AA, Sanford AP, Wolfe RR (2007) Stimulation of net muscle protein synthesis by whey protein ingestion before and after exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E71–E76. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00166.2006
Victoni T et al (2014) Roflumilast N-oxide prevents cytokine secretion induced by cigarette smoke combined with LPS through JAK/STAT and ERK1/2 inhibition in airway epithelial cells. PLoS One 9:e85243. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085243
Volek JS et al (2013) Whey protein supplementation during resistance training augments lean body mass. J Am Coll Nutr 32:122–135. doi:10.1080/07315724.2013.793580
Vyas DR, Spangenburg EE, Abraha TW, Childs TE, Booth FW (2002) GSK-3beta negatively regulates skeletal myotube hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C545–C551. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00049.2002
Wang X, Proud CG (2006) The mTOR pathway in the control of protein synthesis. Physiology (Bethesda) 21:362–369. doi:10.1152/physiol.00024.2006
Wilkinson DJ et al (2013) Effects of leucine and its metabolite beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate on human skeletal muscle protein metabolism. J Physiol 591:2911–2923. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2013.253203
Wilson GJ et al (2011) Leucine or carbohydrate supplementation reduces AMPK and eEF2 phosphorylation and extends postprandial muscle protein synthesis in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 301:E1236–E1242. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00242.2011
Wong TS, Booth FW (1990) Protein metabolism in rat gastrocnemius muscle after stimulated chronic concentric exercise. J Appl Physiol 69:1709–1717
Woodgett JR (1994) Regulation and functions of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 subfamily. Semin Cancer Biol 5:269–275
Woodgett JR (2001) Judging a protein by more than its name: GSK-3. Sci STKE 2001:re12. doi:10.1126/stke.2001.100.re1
Zaghlool A, Ameur A, Nyberg L, Halvardson J, Grabherr M, Cavelier L, Feuk L (2013) Efficient cellular fractionation improves RNA sequencing analysis of mature and nascent transcripts from human tissues. BMC Biotechnol 13:99. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-13-99
Zhang HH, Lipovsky AI, Dibble CC, Sahin M, Manning BD (2006) S6K1 regulates GSK3 under conditions of mTOR-dependent feedback inhibition of Akt. Mol Cell 24:185–197. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.09.019
Acknowledgments
We graciously thank Dr. Troy Horberger for his insight into the SUnSET technique as well as Dr. John McCarthy and Tyler Kirby for their intellectual insight on ribosome biogenesis. Funding from MusclePharm Research Institute was used to fund the direct costs of this study, undergraduate technical support, and publication costs of these data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Besides M.K. and J.R.M., none of the authors have non-financial and/or financial competing interests. M.K. and J.R.M. are employed by the MusclePharm Research Institute, but both intellectually contributed to study design and data write-up. Therefore, all co-authors agreed that their intellectual input into this project warranted co-authorship.
Statement on the welfare of animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All of the proposed animal studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Auburn University. When applicable, replacement of rats with cell culture experiments, a reduction in the number of rats used, and refinement of methods to alleviate animal discomfort were used in the animal protocol.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. Rawson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mobley, C.B., Fox, C.D., Thompson, R.M. et al. Comparative effects of whey protein versus l-leucine on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and markers of ribosome biogenesis following resistance exercise. Amino Acids 48, 733–750 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2121-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2121-z