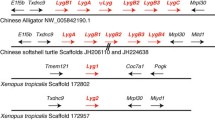
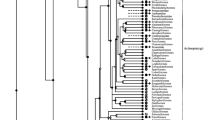
Abstract
Free d-amino acids have been found in various invertebrate phyla, while amino acid racemase genes have been identified in few species. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the distribution, function, and evolution of amino acid racemases in invertebrate animals. We searched the GenBank databases, and found 11 homologous serine racemase genes from eight species in eight different invertebrate phyla. The cloned genes were identified based on their maximum activity as Acropora millepora (Cnidaria) serine racemase (SerR) and aspartate racemase (AspR), Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda) SerR, Capitella teleta (Annelida) SerR, Crassostrea gigas (Mollusca) SerR and AspR, Dugesia japonica (Platyhelminthes) SerR, Milnesium tardigradum (Tardigrada) SerR, Penaeus monodon (Arthropoda) SerR and AspR and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Echinodermata) AspR. We found that Acropora, Aplysia, Capitella, Crassostrea and Penaeus had two amino acid racemase paralogous genes and these paralogous genes have evolved independently by gene duplication at their recent ancestral species. The transcriptome analyses using available SRA data and enzyme kinetic data suggested that these paralogous genes are expressed in different tissues and have different functions in vivo. Phylogenetic analyses clearly indicated that animal SerR and AspR are not separated by their particular racemase functions and form a serine/aspartate racemase family cluster. Our results revealed that SerR and AspR are more widely distributed among invertebrates than previously known. Moreover, we propose that the triple serine loop motif at amino acid positions 150–152 may be responsible for the large aspartate racemase activity and the AspR evolution from SerR.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AspR:
-
Aspartate racemase
- DAR1:
-
Aplysia californica d-amino acid racemase 1
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- Got1l1:
-
Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1-like 1
- OAS:
-
O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase
- PLP:
-
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate
- RPKM:
-
Reads per kilobase per million reads
- RPKMm:
-
Reads per kilobase per million mapped reads
- SerR:
-
Serine racemase
- SRA:
-
Sequence read archive
- RTPCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
References
Abe H, Yoshikawa N, Sarower MG, Okada S (2005) Physiological function and metabolism of free d-alanine in aquatic animals. Biol Pharm Bull 28(9):1571–1577
Abe K, Takahashi S, Muroki Y, Kera Y, Yamada RH (2006) Cloning and expression of the pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent aspartate racemase gene from the bivalve mollusk Scapharca broughtonii and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. J Biochem 139(2):235–244. doi:10.1093/jb/mvj028
Campbell LI, Rota-Stabelli O, Edgecombe GD, Marchioro T, Longhorn SJ, Telford MJ, Philippe H, Rebecchi L, Peterson KJ, Pisani D (2011) MicroRNAs and phylogenomics resolve the relationships of Tardigrada and suggest that velvet worms are the sister group of Arthropoda. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(38):15920–15924
Corrigan JJ, Srinivasan N (1966) The occurrence of certain d-amino acids in insects*. Biochemistry 5(4):1185–1190
D’Aniello A (2007) d-Aspartic acid: an endogenous amino acid with an important neuroendocrine role. Brain Res Rev 53(2):215–234. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.08.005
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Foltyn VN, Bendikov I, De Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Dumin E, Shleper M, Li P, Toney MD, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (2005) Serine racemase modulates intracellular d-serine levels through an alpha, beta-elimination activity. J Biol Chem 280(3):1754–1763. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405726200
Fujitani Y, Nakajima N, Ishihara K, Oikawa T, Ito K, Sugimoto M (2006) Molecular and biochemical characterization of a serine racemase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 67(7):668–674. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.01.003
Fujitani Y, Horiuchi T, Ito K, Sugimoto M (2007) Serine racemases from barley, Hordeum vulgare L., and other plant species represent a distinct eukaryotic group: gene cloning and recombinant protein characterization. Phytochemistry 68(11):1530–1536. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.03.040
Gogami Y, Kobayashi A, Ikeuchi T, Oikawa T (2010) Site-directed mutagenesis of rice serine racemase: evidence that Glu219 and Asp225 mediate the effects of Mg2+ on the activity. Chem Biodivers 7(6):1579–1590. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200900257
Goto M, Yamauchi T, Kamiya N, Miyahara I, Yoshimura T, Mihara H, Kurihara T, Hirotsu K, Esaki N (2009) Crystal structure of a homolog of mammalian serine racemase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 284(38):25944–25952. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.010470
Hamase K, Morikawa A, Zaitsu K (2002) d-Amino acids in mammals and their diagnostic value. J Chromatogr B 781(1):73–91
Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K, Hayashi T (1992) Determination of free amino acid enantiomers in rat brain and serum by high-performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with N-tert.-butyloxycarbonyl-l-cysteine and o-phthaldialdehyde. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 582(1):41–48
Hoffman HE, Jiraskova J, Ingr M, Zvelebil M, Konvalinka J (2009) Recombinant human serine racemase: enzymologic characterization and comparison with its mouse ortholog. Protein Expr Purif 63(1):62–67. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2008.09.003
Hoover DM, Lubkowski J (2002) DNAWorks: an automated method for designing oligonucleotides for PCR-based gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res 30(10):e43–e43
Horio M, Ishima T, Fujita Y, Inoue R, Mori H, Hashimoto K (2013) Decreased levels of free d-aspartic acid in the forebrain of serine racemase (Srr) knock-out mice. Neurochem Int 62(6):843–847. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.02.015
Ito T, Murase H, Maekawa M, Goto M, Hayashi S, Saito H, Maki M, Hemmi H, Yoshimura T (2012) Metal ion dependency of serine racemase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Amino Acids 43(4):1567–1576. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1232-z
Ito T, Maekawa M, Hayashi S, Goto M, Hemmi H, Yoshimura T (2013) Catalytic mechanism of serine racemase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Amino Acids 44(3):1073–1084. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1442-4
Jiraskova-Vanickova J, Ettrich R, Vorlova B, E Hoffman H, Lepsik M, Jansa P, Konvalinka J (2011) Inhibition of human serine racemase, an emerging target for medicinal chemistry. Current Drug Targets 12(7):1037–1055
Katane M, Homma H (2011) d-Aspartate–an important bioactive substance in mammals: a review from an analytical and biological point of view. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(29):3108–3121. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.062
Kim PM, Duan X, Huang AS, Liu CY, Ming GL, Song H, Snyder SH (2010) Aspartate racemase, generating neuronal d-aspartate, regulates adult neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(7):3175–3179. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914706107
Maezawa T, Tanaka H, Nakagawa H, Ono M, Aoki M, Matsumoto M, Ishida T, Horiike K, Kobayashi K (2014) Planarian d-amino acid oxidase is involved in ovarian development during sexual induction. Mech Dev 132:69–78. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2013.12.003
Matsuda S, Katane M, Maeda K, Kaneko Y, Saitoh Y, Miyamoto T, Sekine M, Homma H (2015) Biosynthesis of d-aspartate in mammals: the rat and human homologs of mouse aspartate racemase are not responsible for the biosynthesis of d-aspartate. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-1926-0
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5(7):621–628
Nylander JA, Wilgenbusch JC, Warren DL, Swofford DL (2008) AWTY (are we there yet?): a system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetics. Bioinformatics 24(4):581–583
Ohnishi M, Saito M, Wakabayashi S, Ishizuka M, Nishimura K, Nagata Y, Kasai S (2008) Purification and characterization of serine racemase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Pyrobaculum islandicum. J Bacteriol 190(4):1359–1365. doi:10.1128/JB.01184-07
Okuma E, Fujita E, Amano H, Noda H, Abe H (1995) Distribution of free d-amino acids in the tissues of Crustaceans. Fish Sci 61(1):157–160
Okuma E, Watanabe K, Abe H (1998) Distribution of free d-amino acids in Bivalve Mollusks and the effects of physiological conditions on the levels of d-and l-alanine in the tissues of the hard clam Meretrix lusoria. Fish Sci 64(4):606–611
Preston R (1987) Occurrence of d-amino acids in higher organisms: a survey of the distribution of d-amino acids in marine invertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Comp Biochem 87(1):55–62
Radkov AD, Moe LA (2014) Bacterial synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(12):5363–5374. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5726-3
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19(12):1572–1574
Rosenberg H, Ennor A (1961) The occurrence of free d-serine in the earthworm. Biochem J 79(2):424
Saitoh Y, Katane M, Kawata T, Maeda K, Sekine M, Furuchi T, Kobuna H, Sakamoto T, Inoue T, Arai H, Nakagawa Y, Homma H (2012) Spatiotemporal localization of d-amino acid oxidase and d-aspartate oxidases during development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol 32(10):1967–1983. doi:10.1128/MCB.06513-11
Shibata K, Tarui A, Todoroki N, Kawamoto S, Takahashi S, Kera Y, R-h Yamada (2001) Occurrence of N-methyl-l-aspartate in bivalves and its distribution compared with that of N-methyl-d-aspartate and D, l-aspartate. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 130(4):493–500
Shibata K, Watanabe T, Yoshikawa H, Abe K, Takahashi S, Kera Y, Yamada RH (2003) Purification and characterization of aspartate racemase from the bivalve mollusk Scapharca broughtonii. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 134(2):307–314
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Tanaka-Hayashi A, Hayashi S, Inoue R, Ito T, Konno K, Yoshida T, Watanabe M, Yoshimura T, Mori H (2015) Is d-aspartate produced by glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase-1 like 1 (Got1l1): a putative aspartate racemase? Amino Acids 47(1):79–86. doi:10.1007/s00726-014-1847-3
Uda K, Suzuki T (2007) A novel arginine kinase with substrate specificity towards d-arginine. Protein J 26(5):281–291
Uo T, Ueda M, Nishiyama T, Yoshimura T, Esaki N (2001) Purification and characterization of alanine racemase from hepatopancreas of black-tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon. J Mol Catal B Enzym 12(1):137–144
Wang L, Ota N, Romanova EV, Sweedler JV (2011) A novel pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent amino acid racemase in the Aplysia californica central nervous system. J Biol Chem 286(15):13765–13774. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.178228
Wolosker H, Sheth KN, Takahashi M, Mothet J-P, Brady RO, Ferris CD, Snyder SH (1999) Purification of serine racemase: biosynthesis of the neuromodulator d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(2):721–725
Wolosker H, D’Aniello A, Snyder S (2000) d-aspartate disposition in neuronal and endocrine tissues: ontogeny, biosynthesis and release. Neuroscience 100(1):183–189
Yamauchi T, Goto M, Wu HY, Uo T, Yoshimura T, Mihara H, Kurihara T, Miyahara I, Hirotsu K, Esaki N (2009) Serine racemase with catalytically active lysinoalanyl residue. J Biochem 145(4):421–424. doi:10.1093/jb/mvp010
Yoshikawa N, Dhomae N, Takio K, Abe H (2002) Purification, properties, and partial amino acid sequences of alanine racemase from the muscle of the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 133(3):445–453
Yoshikawa N, Okada S, Abe H (2009) Molecular characterization of alanine racemase in the kuruma prawn Marsupenaeus japonicus. J Biochem 145(2):249–258. doi:10.1093/jb/mvn162
Yoshikawa N, Ashida W, Hamase K, Abe H (2011) HPLC determination of the distribution of d-amino acids and effects of ecdysis on alanine racemase activity in kuruma prawn Marsupenaeus japonicus. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(29):3283–3288. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.04.026
Yuasa HJ, Takubo M, Takahashi A, Hasegawa T, Noma H, Suzuki T (2007) Evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenases. J Mol Evol 65(6):705–714
Zhang G, Fang X, Guo X, Li L, Luo R, Xu F, Yang P, Zhang L, Wang X, Qi H (2012) The oyster genome reveals stress adaptation and complexity of shell formation. Nature 490(7418):49–54
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research in Japan to KU (24770068 and 15K07152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: C. Schiene-Fischer.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uda, K., Abe, K., Dehara, Y. et al. Distribution and evolution of the serine/aspartate racemase family in invertebrates. Amino Acids 48, 387–402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2092-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2092-0