Abstract
Homoarginine (hArg) is a non-essential amino acid that was identified as a risk marker for cardiovascular disease. Several analytical methods have been described for the quantification of hArg in biological samples. The aim of this study was to compare a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric (LC–MS/MS) approach with a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Determination of hArg concentrations in ELISA calibration standards measured by both methods revealed a correlation coefficient r 2 of 0.99, for LC–MS/MS calibrators r 2 was 0.997. However, linear regression analysis between the two assays for hArg concentrations in human plasma samples revealed a correlation coefficient r 2 of 0.78. Plasma concentrations obtained from LC–MS/MS are on average 29 % higher than those by ELISA. We investigated the hArg-isobaric N ε-trimethyllysine as potential source for the higher observed values, but evaluation of mass spectra indicated that N ε-trimethyllysine did not interfere with hArg quantification in our LC–MS/MS method. Both quantification methods were applied to measure hArg in (1) a case–control study of acute coronary syndrome and (2) l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase-deficient mice. Our LC–MS/MS and the commercially available ELISA assay are suitable for hArg measurement in human and mouse plasma, but different reference values for each method need to be considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACS:
-
Acute coronary syndrome
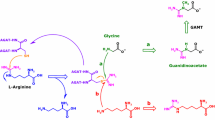
- AGAT:
-
L-Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CID:
-
Collision-induced dissociation
- CV:
-
Cardiovascular
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ESI(+):
-
Positive electrospray ionization
- GC–MS/MS:
-
Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- hArg:
-
Homoarginine
- 13C6-hArg:
-
[13C6]-Homoarginine
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- m/z :
-
Mass-to-charge ratio
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- QC:
-
Quality control
- SAP:
-
Stable angina pectoris
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SPE:
-
Solid-phase extraction
- UPLC-MS/MS:
-
Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- Wt:
-
Wild-type
References
Araujo P (2009) Key aspects of analytical method validation and linearity evaluation. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 877:2224–2234
Atzler D, Mieth M, Maas R, Böger RH, Schwedhelm E (2011) Stable isotope dilution assay for liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric determination of L-homoarginine in human plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:2294–2298
Atzler D, Rosenberg M, Anderssohn M, Choe CU, Lutz M, Zugck C, Böger RH, Frey N, Schwedhelm E (2013) Homoarginine—an independent marker of mortality in heart failure. Int J Cardiol 168:4907–4909
Choe CU, Atzler D, Wild PS, Carter AM, Böger RH, Ojeda F, Simova O, Stockebrand M, Lackner K, Nabuurs C, Marescau B, Streichert T, Müller C, Lüneburg N, De Deyn PP, Benndorf RA, Baldus S, Gerloff C, Blankenberg S, Heerschap A, Grant PJ, Magnus T, Zeller T, Isbrandt D, Schwedhelm E (2013) Homoarginine levels are regulated by l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase and affect stroke outcome: results from human and murine studies. Circulation 128:1451–1461
Davids M, Swieringa E, Palm F, Smith DE, Smulders YM, Scheffer PG, Blom HJ, Teerlink T (2012) Simultaneous determination of asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine, L-monomethylarginine, l-arginine, and L-homoarginine in biological samples using stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 900:38–47
Di Gangi IM, Chiandetti L, Gucciardi A, Moret V, Naturale M, Giordano G (2010) Simultaneous quantitative determination of N(G), N(G)-dimethyl-l-arginine or asymmetric dimethylarginine and related pathway’s metabolites in biological fluids by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 677:140–148
Hrabák A, Bajor T, Temesi A (1994) Comparison of substrate and inhibitor specificity of arginase and nitric oxide (NO) synthase for arginine analogues and related compounds in murine and rat macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198:206–212
Jones CE, Darcy CJ, Woodberry T, Anstey NM, McNeil YR (2010) HPLC analysis of asymmetric dimethylarginine, symmetric dimethylarginine, homoarginine and arginine in small plasma volumes using a Gemini-NX column at high pH. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878:8–12
Kayacelebi AA, Beckmann B, Gutzki FM, Jordan J, Tsikas D (2014) GC-MS and GC–MS/MS measurement of the cardiovascular risk factor homoarginine in biological samples. Amino Acids 46:2205–2217
Lehman LJ, Olson AL, Rebouche CJ (1987) Measurement of epsilon-N-trimethyllysine in human blood plasma and urine. Anal Biochem 162:137–142
März W, Meinitzer A, Drechsler C, Pilz S, Krane V, Kleber ME, Fischer J, Winkelmann BR, Böhm BO, Ritz E, Wanner C (2010) Homoarginine, cardiovascular risk, and mortality. Circulation 122:967–975
Meinitzer A, Puchinger M, Winklhofer-Roob BM, Rock E, Ribalta J, Roob JM, Sundl I, Halwachs-Baumann G, März W (2007) Reference values for plasma concentrations of asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA) and other arginine metabolites in men after validation of a chromatographic method. Clin Chim Acta 384:141–148
Midttun Ø, Kvalheim G, Ueland PM (2013) High-throughput, low-volume, multianalyte quantification of plasma metabolites related to one-carbon metabolism using HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:2009–2017
Moali C, Boucher JL, Sari MA, Stuehr DJ, Mansuy D (1998) Substrate specificity of NO synthases: detailed comparison of l-arginine, homo-L-arginine, their N omega-hydroxy derivatives, and N omega-hydroxynor-L-arginine. Biochemistry 37:10453–10460
Pilz S, Tomaschitz A, Meinitzer A, Drechsler C, Ritz E, Krane V, Wanner C, Böhm BO, März W (2011a) Low serum homoarginine is a novel risk factor for fatal strokes in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Stroke 42:1132–1134
Pilz S, Meinitzer A, Tomaschitz A, Drechsler C, Ritz E, Krane V, Wanner C, Boehm BO, März W (2011b) Low homoarginine concentration is a novel risk factor for heart disease. Heart 97:1222–1227
Pilz S, Teerlink T, Scheffer PG, Meinitzer A, Rutters F, Tomaschitz A, Drechsler C, Kienreich K, Nijpels G, Stehouwer CD, März W, Dekker JM (2014) Homoarginine and mortality in an older population: the Hoorn study. Eur J Clin Invest 44:200–208
Pilz S, Putz-Bankuti C, Meinitzer A, März W, Kienreich K, Stojakovic T, Pieber TR, Stauber RE (2015) Association of homoarginine and methylarginines with liver dysfunction and mortality in chronic liver disease. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-2000-7
Sitar ME, Kayacelebi AA, Beckmann B, Kielstein JT, Tsikas D (2015) Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in human blood: effects of extended haemodialysis in the critically ill patient with acute kidney injury, protein binding to human serum albumin and proteolysis by thermolysin. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-1991-4
Acknowledgments
We thank Mariola Kastner and Anna Steenpaß for their excellent technical support. This study was funded by a grant from the European Commission (Grant 278397 EuRhythDia) and supported by a grant from the DZHK (Grant 81Z1710102). Dr Atzler acknowledges the support of the European Union under a Marie Curie Intra-European Fellowship for Career Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical statement
The study complied with the standards set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf. All patients gave their written informed consent prior to inclusion into the study. The German animal welfare laws for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
E. Schwedhelm and C. Choe contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordts, K., Atzler, D., Qaderi, V. et al. Measurement of homoarginine in human and mouse plasma by LC–MS/MS and ELISA: a comparison and a biological application. Amino Acids 47, 2015–2022 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2037-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2037-7