Abstract
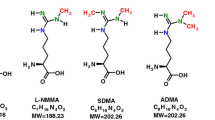
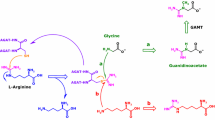
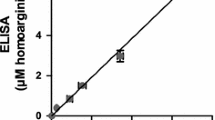
l-Homoarginine (hArg) has recently emerged as a novel cardiovascular risk factor and to herald a poor prognosis in heart failure patients. Here, we report on the development and thorough validation of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) methods for the quantitative determination of hArg in biological samples, including human plasma, urine and sputum. For plasma and serum samples, ultrafiltrate (10 µL; cutoff, 10 kDa) was used. For urine samples, native urine (10 µL) was used. For sputum, protein precipitation by acetone was performed. hArg is derivatized to its methyl ester tri(N-pentafluoropropionyl) derivative; de novo synthesized trideutero-methyl ester hArg is used as the internal standard (IS). Alternatively, [guanidino-15N2]-arginine can be used as an IS. Quantitative analyses were performed after electron-capture negative-ion chemical ionization by selected-ion monitoring in GC–MS and selected-reaction monitoring in GC–MS/MS. We obtained very similar hArg concentrations by GC–MS and GC–MS/MS, suggesting that GC–MS suffices for accurate and precise quantification of hArg in biological samples. In plasma and serum samples of the same subjects very close hArg concentrations were measured. The plasma-to-serum hArg concentration ratio was determined to be 1.12 ± 0.21 (RSD, 19 %), suggesting that blood anticoagulation is not a major preanalytical concern in hArg analysis. In healthy subjects, the creatinine-corrected urinary excretion of hArg varies considerably (0.18 ± 0.22 µmol/mmol, mean ± SD, n = 19) unlike asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA, 2.89 ± 0.89 µmol/mmol). In urine, hArg correlated with ADMA (r = 0.475, P = 0.040); in average, subjects excreted in the urine about 17.5 times more ADMA than hArg. In plasma of healthy humans, the concentration of hArg is of the order of 2 µM. hArg may be a low-abundance constituent of human plasma proteins. The GC–MS and GC-MS/MS methods we report in this article are useful to study the physiology and pathology of hArg in experimental and clinical settings.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADMA:
-
N G ,N G-Dimethyl-l-arginine
- AGAT:
-
Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase
- CID:
-
Collision-induced dissociation
- DMA:
-
Dimethyl amine
- DSQ:
-
Double-stage quadrupole
- ECNICI:
-
Electron-capture negative-ion chemical ionization
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- GC–MS/MS:
-
Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- hArg:
-
Homoarginine
- IS:
-
Internal standard
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- PFP:
-
Pentafluoropropionyl
- PFPA:
-
Pentafluoropropionic anhydride
- SDMA:
-
Symmetric dimethylarginine
- SIM:
-
Selected-ion monitoring
- SRM:
-
Selected-reaction monitoring
- TSQ:
-
Triple-stage quadrupole
References
Albsmeier J, Schwedhelm E, Schulze F, Kastner M, Böger RH (2004) Determination of NG, NG-dimethyl-l-arginine, an endogenous NO synthase inhibitor, by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 809(1):59–65
Atzler D, Mieth M, Maas R, Böger RH, Schwedhelm E (2011) Stable isotope dilution assay for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric determination of l-homoarginine in human plasma. J Chromatogr B 879:2294–2298
Bretscher LE, Li H, Poulos TL, Griffith OW (2003) Structural characterization and kinetics of nitric-oxide synthase inhibition by novel N5-(iminoalkyl)- and N5- (iminoalkenyl)-ornithines. J Biol Chem 278:46789–46797
Choe CU, Atzler D, Wild PS, Carter AM, Böger RH, Ojeda F, Simova O, Stockebrand M, Lackner K, Nabuurs C, Marescau B, Streichert T, Muller C, Luneburg N, De Deyn PP, Benndorf RA, Baldus S, Gerloff C, Blankenberg S, Heerschap A, Grant PJ, Magnus T, Zeller T, Isbrandt D, Schwedhelm E (2013) Homoarginine levels are regulated by l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase and affect stroke outcome: results from human and murine studies. Circulation 128:1451–1461
Dai Z, Wu Z, Jia S, Wu G (2014) Analysis of amino acid composition in proteins of animal tissues and foods as pre-column o-phthaldialdehyde derivatives by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.03.025
Davids M, Ndika JD, Salomons GS, Blom HJ, Teerlink T (2012a) Promiscuous activity of arginine:glycine amidinotransferase is responsible for the synthesis of the novel cardiovascular risk factor homoarginine. FEBS Lett 586:3653–3657
Davids M, Swieringa E, Palm F, Smith DE, Smulders YM, Scheffer PG, Blom HJ, Teerlink T (2012b) Simultaneous determination of asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine, L-monomethylarginine, l-arginine, and L-homoarginine in biological samples using stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 900:38–47
Drechsler C, Meinitzer A, Pilz S, Krane V, Tomaschitz A, Ritz E, März W, Wanner C (2011) Homoarginine, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death in haemodialysis patients. Eur J Heart Fail 13:852–859
Engeli S, Tsikas D, Lehmann AC, Böhnke J, Haas V, Strauß A, Janke J, Gorzelniak K, Luft FC, Jordan J (2012) Influence of dietary fat ingestion on asymmetrical dimethylarginine in lean and obese human subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 22:720–726
Horowitz JD, Heresztyn T (2007) An overview of plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in health and disease and in clinical studies: methodological considerations. J Chromatogr B 851:42–50
Kayacelebi AA, Nguyen TH, Neil C, Horowitz JD, Jordan J, Tsikas D (2014) Homoarginine and 3-nitrotyrosine in patients with takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.03.080
Khalil AA, Tsikas D, Akolekar R, Jordan J, Nicolaides KH (2013) Asymmetric dimethylarginine, arginine and homoarginine at 11–13 weeks gestation and preeclampsia: a case-control study. J Hum Hypertens 27:38–43
Leiper J, Vallance P (1999) Biological significance of endogenous methylarginines that inhibit nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res 43:542–548
Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Bode-Böger SM (2014) Mass spectrometric quantification of l-arginine and its pathway related substances in biofluids: the road to maturity. J Chromatogr B. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.10.030
Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Schwedhelm E, Tsikas D (2009) Quantification of arginine and its mono- and dimethylated analogs NMMA, ADMA and SDMA in biological fluids by LC-MS/MS: is LC superfluous? J Chromatogr B 877:3261–3266
März W, Meinitzer A, Drechsler C, Pilz S, Krane V, Kleber ME, Fischer J, Winkelmann BR, Böhm BO, Ritz E, Wanner C (2010) Homoarginine, cardiovascular risk, and mortality. Circulation 122:967–975
Moali C, Boucher JL, Sari MA, Stuehr DJ, Mansuy D (1998) Substrate specificity of NO synthases: detailed comparison of l-arginine, homo-l-arginine, their N omega-hydroxy derivatives, and N omega-hydroxynor-l-arginine. Biochemistry 37:10453–10460
Moali C, Brollo M, Custot J, Sari MA, Boucher JL, Stuehr DJ, Mansuy D (2000) Recognition of alpha-amino acids bearing various C = NOH functions by nitric oxide synthase and arginase involves very different structural determinants. Biochemistry 39:8208–8218
Moncada S, Higgs A (1993) The l-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. New Engl J Med 329:2002–2012
Pilz S, Tomaschitz A, Meinitzer A, Drechsler C, Ritz E, Krane V, Wanner C, Bohm BO, März W (2011) Low serum homoarginine is a novel risk factor for fatal strokes in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Stroke 42:1132–1134
Ryan WL, Wells IC (1964) Homocitrulline and homoarginine synthesis from lysine. Science 144:1122–1127
Ryan WL, Johnson RJ, Dimari S (1969) Homoarginine synthesis by rat kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys 131:521–526
Schwedhelm E (2005) Quantification of ADMA: analytical approaches. Vascular Med (London, England) 10(Suppl 1):S89–S95
Schwedhelm E, Maas R, Tan-Andresen J, Schulze F, Riederer U, Böger RH (2007) High-throughput liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric determination of arginine and dimethylated arginine derivatives in human and mouse plasma. J Chromatogr B 851:211–219
Sobczak A, Prokopowicz A, Radek M, Szula M, Zaciera M, Kurek J, Goniewicz ML (2014) Tobacco smoking decreases plasma concentration of the emerging cardiovascular risk marker, l-homoarginine. Circ J 78:1254–1258
Teerlink T (2007) HPLC analysis of ADMA and other methylated l-arginine analogs in biological fluids. J Chromatogr B 851:21–29
Tsikas D (2008) A critical review and discussion of analytical methods in the l-arginine/nitric oxide area of basic and clinical research. Anal Biochem 379:139–163
Tsikas D, Beckmann B (2009) Albumin from human serum does not contain asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA). Clin Biochem 42:1739–1740
Tsikas D, Kayacelebi AA (2014) Do homoarginine and asymmetric dimethylarginine act antagonistically in the cardiovascular system? Circ J 20
Tsikas D, Schubert B, Gutzki FM, Sandmann J, Frölich JC (2003) Quantitative determination of circulating and urinary asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in humans by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as methyl ester tri(N-pentafluoropropionyl) derivative. J Chromatogr B 798:87–99
Tsikas D, Engeli S, Beckmann B, Jordan J (2010) Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) is present in plasma proteins of healthy subjects at the low nmol-per-g-level. Nitric Oxide 22:316–317
Tsikas D, Beckmann B, Gutzki FM, Jordan J (2011) Simultaneous gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry quantification of symmetric and asymmetric dimethylarginine in human urine. Anal Biochem 413:60–62
Valtonen P, Laitinen T, Lyyra-Laitinen T, Raitakari OT, Juonala M, Viikari JS, Heiskanen N, Vanninen E, Punnonen K, Heinonen S (2008) Serum l-homoarginine concentration is elevated during normal pregnancy and is related to flow-mediated vasodilatation. Circ J 72:1879–1884
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Marc Rhoads J, Carey Satterfield M, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Yin Y (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37:153–168
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, Hannover Medical School, for providing us with spot urine samples for the analysis of hArg and its relatives.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kayacelebi, A.A., Beckmann, B., Gutzki, FM. et al. GC–MS and GC–MS/MS measurement of the cardiovascular risk factor homoarginine in biological samples. Amino Acids 46, 2205–2217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1774-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1774-3