Abstract
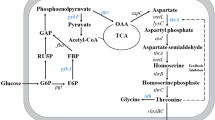
Threonine is a nutritionally essential amino acid (EAA) for the growth and development of humans and other nonruminant animals and must be provided in diets to sustain life. The aim of this study was to synthesize threonine in mammalian cells through transgenic techniques. To achieve this goal, we combined the genes involved in bacterial threonine biosynthesis pathways into a single open reading frame separated by self-cleaving peptides (2A) and then linked it into a transposon system (piggyBac). The plasmids pEF1a-IRES-GFP-E2F-his and pEF1a-IRES-GFP-M2F-his expressed Escherichia coli homoserine kinase and threonine synthase efficiently in mouse cells and enabled cells to synthesize threonine from homoserine. This biosynthetic pathway occurred with a low level of efficiency in transgenic mice. Three transgenic mice were identified by Southern blot from 72 newborn mice, raising the possibility that a high level of expression of these genes in mouse embryos might be lethal. The results indicated that it is feasible to synthesize threonine in animal cells using genetic engineering technology. Further work is required to improve the efficiency of this method for introducing genes into mammals. We propose that the transgenic technology provides a promising means to enhance the synthesis of nutritionally EAAs in farm animals and to eliminate or reduce supplementation of these nutrients in diets for livestock, poultry and fish.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EAA:
-
Nutritionally essential amino acid
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- KHB:
-
Krebs–Henseleit bicarbonate buffer
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
References
Bach A, Calsamiglia S, Stern MD (2005) Nitrogen metabolism in the rumen. J Dairy Sci 88(Suppl 1):E9–E21. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73133-7
Bawden CS, Sivaprasad AV, Verma PJ, Walker SK, Rogers GE (1995) Expression of bacterial cysteine biosynthesis genes in transgenic mice and sheep: toward a new in vivo amino acid biosynthesis pathway and improved wool growth. Transgenic Res 4:87–104
Bi M, Tong J, Chang F, Wang J, Wei H, Dai Y, Chu M, Zhao Y, Li N (2012) Pituitary-specific overexpression of porcine follicle-stimulating hormone leads to improvement of female fecundity in BAC transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 7:e42335. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042335
Bird MI, Nunn PB (1983) Metabolic homoeostasis of l-threonine in the normally-fed rat. Importance of liver threonine dehydrogenase activity. Biochem J 214:687–694
Chassagnole C, Rais B, Quentin E, Fell DA, Mazat JP (2001) An integrated study of threonine-pathway enzyme kinetics in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 356:415–423
Ciftci I, Ceylan N (2004) Effects of dietary threonine and crude protein on growth performance, carcase and meat composition of broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci 45:280–289. doi:10.1080/00071660410001715894
Dai ZL, Li XL, Xi PB, Zhang J, Wu G, Zhu WY (2013) l-Glutamine regulates amino acid utilization by intestinal bacteria. Amino Acids 45:501–512. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1264-4
Dale RA (1978) Catabolism of threonine in mammals by coupling of l-threonine 3-dehydrogenase with 2-amino-3-oxobutyrate-CoA ligase. Biochim Biophys Acta 544:496–503
Darling PB, Dunn M, Sarwar G, Brookes S, Ball RO, Pencharz PB (1999) Threonine kinetics in preterm infants fed their mothers’ milk or formula with various ratios of whey to casein. Am J Clin Nutr 69:105–114
de Felipe P, Luke GA, Hughes LE, Gani D, Halpin C, Ryan MD (2006) E unum pluribus: multiple proteins from a self-processing polyprotein. Trends Biotechnol 24:68–75. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.12.006
Eikmanns BJ, Eggeling L, Sahm H (1993) Molecular aspects of lysine, threonine, and isoleucine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 64:145–163
Fenderson CL, Bergen WG (1975) An assessment of essential amino acid requirements of growing steers. J Anim Sci 41:1759–1766
Golovan SP, Hayes MA, Phillips JP, Forsberg CW (2001) Transgenic mice expressing bacterial phytase as a model for phosphorus pollution control. Nat Biotechnol 19:429–433. doi:10.1038/88091
Gum JR Jr (1992) Mucin genes and the proteins they encode: structure, diversity, and regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 7:557–564. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb/7.6.557
Horn NL, Donkin SS, Applegate TJ, Adeola O (2009) Intestinal mucin dynamics: response of broiler chicks and White Pekin ducklings to dietary threonine. Poult Sci 88:1906–1914. doi:10.3382/ps.2009-00009
Katinka M, Cossart P, Sibilli L, Saint-Girons I, Chalvignac MA, Le Bras G, Cohen GN, Yaniv M (1980) Nucleotide sequence of the thrA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:5730–5733
Li P, Yin YL, Li DF, Kim SW, Wu G (2007) Amino acids and immune function. Br J Nutr 98:237–252
Rees WD, Hay SM (1993) The expression of Escherichia coli threonine synthase and the production of threonine from homoserine in mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J 291(Pt 1):315–322
Rees WD, Hay SM (1995) The biosynthesis of threonine by mammalian cells: expression of a complete bacterial biosynthetic pathway in an animal cell. Biochem J 309(Pt 3):999–1007
Rees WD, Flint HJ, Fuller MF (1990) A molecular biological approach to reducing dietary amino acid needs. Biotechnology (NY) 8:629–633
Rees WD, Hay SM, Flint HJ (1992) Expression of Escherichia coli homoserine kinase in mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J 281(Pt 3):865–870
Rees WD, Grant SD, Hay SM, Saqib KM (1994) Threonine synthesis from homoserine as a selectable marker in mammalian cells. Biochem J 299(Pt 3):637–644
Remond D, Buffiere C, Godin JP, Mirand PP, Obled C, Papet I, Dardevet D, Williamson G, Breuille D, Faure M (2009) Intestinal inflammation increases gastrointestinal threonine uptake and mucin synthesis in enterally fed minipigs. J Nutr 139:720–726. doi:10.3945/jn.108.101675
Ryu JM, Han HJ (2011) l-threonine regulates G1/S phase transition of mouse embryonic stem cells via PI3K/Akt, MAPKs, and mTORC pathways. J Biol Chem 286:23667–23678. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.216283
Saini KS, Byrne CR, Leish Z, Pruss CA, Rigby NW, Brownlee AG, Nancarrow CD, Ward KA (1996) Introduction and expression of the bacterial glyoxylate cycle genes in transgenic mice. Transgenic Res 5:467–473
Shyh-Chang N, Locasale JW, Lyssiotis CA, Zheng Y, Teo RY, Ratanasirintrawoot S, Zhang J, Onder T, Unternaehrer JJ, Zhu H, Asara JM, Daley GQ, Cantley LC (2013) Influence of threonine metabolism on S-adenosylmethionine and histone methylation. Science 339:222–226. doi:10.1126/science.1226603
Stoll B, Henry J, Reeds PJ, Yu H, Jahoor F, Burrin DG (1998) Catabolism dominates the first-pass intestinal metabolism of dietary essential amino acids in milk protein-fed piglets. J Nutr 128:606–614
Szymczak AL, Workman CJ, Wang Y, Vignali KM, Dilioglou S, Vanin EF, Vignali DA (2004) Correction of multi-gene deficiency in vivo using a single ‘self-cleaving’ 2A peptide-based retroviral vector. Nat Biotechnol 22:589–594. doi:10.1038/nbt957
Trichas G, Begbie J, Srinivas S (2008) Use of the viral 2A peptide for bicistronic expression in transgenic mice. BMC Biol 6:40. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-6-40
Wang X, Qiao S, Yin Y, Yue L, Wang Z, Wu G (2007) A deficiency or excess of dietary threonine reduces protein synthesis in jejunum and skeletal muscle of young pigs. J Nutr 137:1442–1446
Wang J, Alexander P, Wu L, Hammer R, Cleaver O, McKnight SL (2009) Dependence of mouse embryonic stem cells on threonine catabolism. Science 325:435–439. doi:10.1126/science.1173288
Wang WW, Zeng XF, Mao XB, Wu G, Qiao SY (2010) Optimal dietary true ileal digestible threonine for supporting mucosal barrier in the small intestine of weanling pigs. J Nutr 140:981–986
Ward KA (2000) Transgene-mediated modifications to animal biochemistry. Trends Biotechnol 18:99–102
Wei J, Yang X, Zheng M, Wang M, Dai Y, Chen Z, Li N (2011) The recombinant chimeric antibody chHAb18 against hepatocellular carcinoma can be produced in milk of transgenic mice. Transgenic Res 20:321–330. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9408-3
Wu G (2009) Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 37:1–17. doi:10.1007/s00726-009-0269-0
Wu G (2010) Functional amino acids in growth, reproduction, and health. Adv Nutr 1:31–37. doi:10.3945/an.110.1008
Wu G (2013a) Functional amino acids in nutrition and health. Amino Acids 45:407–411. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1500-6
Wu G (2013b) Amino acids: biochemistry and nutrition. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wu G, Knabe DA, Flynn NE (1994) Synthesis of citrulline from glutamine in pig enterocytes. Biochem J 299(Pt 1):115–121
Wu G, Wu ZL, Dai ZL, Yang Y, Wang WW, Liu C, Wang B, Wang JJ, Yin YL (2013a) Dietary requirements of “nutritionally nonessential amino acids” by animals and humans. Amino Acids 44:1107–1113
Wu G, Bazer FW, Satterfield MC, Li XL, Wang XQ, Johnson GA, Burghardt RC, Dai ZL, Wang JJ, Wu ZL (2013b) Impacts of arginine nutrition on embryonic and fetal development in mammals. Amino Acids 45:241–256
Wu G, Bazer FW, Dai ZL, Li DF, Wang JJ, Wu ZL (2014) Amino acid nutrition in animals: protein synthesis and beyond. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 2:387–417
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Sen Wu for providing us with the pEF1a-PB plasmid and materials for cell culture. This study was supported by the National Transgenic Breeding Project of China (grant 2013ZX08006-004), Chinese Universities Scientific Funds (2012RC024), and the Thousand-People Talent program at China Agricultural University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Dai, Z., Wu, G. et al. Expression of threonine-biosynthetic genes in mammalian cells and transgenic mice. Amino Acids 46, 2177–2188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1769-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1769-0