Abstract
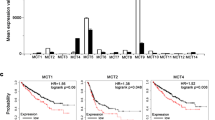
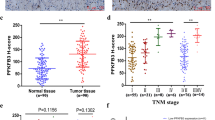
Transglutaminase 2 (TGase 2) expression and glycolysis are increased in most renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell lines compared to the HEK293 kidney cell line. Although increased glycolysis and altered tricarboxylic acid cycle are common in RCC, the detailed mechanism by which this phenomenon occurs remains to be elucidated. In the present study, TGase 2 siRNA treatment lowered glucose consumption and lactate levels by about 20–30 % in RCC cells; conversely, high expression of TGase 2 increased glucose consumption and lactate production together with decreased mitochondrial aconitase (Aco 2) levels. In addition, TGase 2 siRNA increased mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP levels by about 20–30 % and restored Aco 2 levels in RCC cells. Similarly, Aco 2 levels and ATP production decreased significantly upon TGase 2 overexpression in HEK293 cells. Therefore, TGase 2 leads to depletion of Aco 2, which promotes glycolytic metabolism in RCC cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberghini A, Recalcati S, Tacchini L, Santambrogio P, Campanella A, Cairo G (2005) Loss of the von Hippel Lindau tumor suppressor disrupts iron homeostasis in renal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 280(34):30120–30128. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500971200
Browne SE, Bowling AC, MacGarvey U, Baik MJ, Berger SC, Muqit MM, Bird ED, Beal MF (1997) Oxidative damage and metabolic dysfunction in Huntington’s disease: selective vulnerability of the basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 41(5):646–653. doi:10.1002/ana.410410514
Catchpole G, Platzer A, Weikert C, Kempkensteffen C, Johannsen M, Krause H, Jung K, Miller K, Willmitzer L, Selbig J, Weikert S (2011) Metabolic profiling reveals key metabolic features of renal cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 15(1):109–118. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00939.x
Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F, Maity A (2001) Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem 276(12):9519–9525. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010144200
Cheng Z, Tsuda M, Kishita Y, Sato Y, Aigaki T (2013) Impaired energy metabolism in a Drosophila model of mitochondrial aconitase deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 433(1):145–150. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.02.040
Degu A, Hatew B, Nunes-Nesi A, Shlizerman L, Zur N, Katz E, Fernie AR, Blumwald E, Sadka A (2011) Inhibition of aconitase in citrus fruit callus results in a metabolic shift towards amino acid biosynthesis. Planta 234(3):501–513. doi:10.1007/s00425-011-1411-2
Fesus L, Piacentini M (2002) Transglutaminase 2: an enigmatic enzyme with diverse functions. Trends Biochem Sci 27(10):534–539
Firth JD, Ebert BL, Ratcliffe PJ (1995) Hypoxic regulation of lactate dehydrogenase A. Interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cAMP response elements. J Biol Chem 270(36):21021–21027
Gu M, Gash MT, Mann VM, Javoy-Agid F, Cooper JM, Schapira AH (1996) Mitochondrial defect in Huntington’s disease caudate nucleus. Ann Neurol 39(3):385–389. doi:10.1002/ana.410390317
Icard P, Poulain L, Lincet H (2012) Understanding the central role of citrate in the metabolism of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1825(1):111–6. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.10.007
Jang GY, Jeon JH, Cho SY, Shin DM, Kim CW, Jeong EM, Bae HC, Kim TW, Lee SH, Choi Y, Lee DS, Park SC, Kim IG (2010) Transglutaminase 2 suppresses apoptosis by modulating caspase 3 and NF-kappaB activity in hypoxic tumor cells. Oncogene 29(3):356–367. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.342
Kim SY (2011) Transglutaminase 2: a new paradigm for NF-kappaB involvement in disease. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 78:161–195
Kim WY, Kaelin WG (2004) Role of VHL gene mutation in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(24):4991–5004. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.05.061
Kim SY, Marekov L, Bubber P, Browne SE, Stavrovskaya I, Lee J, Steinert PM, Blass JP, Beal MF, Gibson GE, Cooper AJ (2005) Mitochondrial aconitase is a transglutaminase 2 substrate: transglutamination is a probable mechanism contributing to high-molecular-weight aggregates of aconitase and loss of aconitase activity in Huntington disease brain. Neurochem Res 30(10):1245–1255. doi:10.1007/s11064-005-8796-x
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2006a) HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab 3(3):177–185. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.002
Kim WY, Safran M, Buckley MR, Ebert BL, Glickman J, Bosenberg M, Regan M, Kaelin WG Jr (2006b) Failure to prolyl hydroxylate hypoxia-inducible factor alpha phenocopies VHL inactivation in vivo. EMBO J 25(19):4650–4662. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601300
Kim DS, Choi YB, Han BG, Park SY, Jeon Y, Kim DH, Ahn ER, Shin JE, Lee BI, Lee H, Hong KM, Kim SY (2011) Cancer cells promote survival through depletion of the von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor by protein crosslinking. Oncogene 30(48):4780–4790. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.183
Kim SJ, Kim KH, Ahn ER, Yoo BC, Kim SY (2013) Depletion of cathepsin D by transglutaminase 2 through protein cross-linking promotes cell survival. Amino Acids 44(1):73–80. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-1089-6
Ku BM, Kim DS, Kim KH, Yoo BC, Kim SH, Gong YD, Kim SY (2013) Transglutaminase 2 inhibition found to induce p53 mediated apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 27(9):3487–3495. doi:10.1096/fj.12-224220
Lee J, Kim YS, Choi DH, Bang MS, Han TR, Joh TH, Kim SY (2004) Transglutaminase 2 induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a novel pathway in BV-2 microglia. J Biol Chem 279(51):53725–53735. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407627200
Mathupala SP, Rempel A, Pedersen PL (2001) Glucose catabolism in cancer cells: identification and characterization of a marked activation response of the type II hexokinase gene to hypoxic conditions. J Biol Chem 276(46):43407–43412. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108181200
Mehta K, Kumar A, Kim HI (2010) Transglutaminase 2: a multi-tasking protein in the complex circuitry of inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 80(12):1921–1929. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.029
Moore LE, Nickerson ML, Brennan P, Toro JR, Jaeger E, Rinsky J, Han SS, Zaridze D, Matveev V, Janout V, Kollarova H, Bencko V, Navratilova M, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Mates D, Schmidt LS, Lenz P, Karami S, Linehan WM, Merino M, Chanock S, Boffetta P, Chow WH, Waldman FM, Rothman N (2011) Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) inactivation in sporadic clear cell renal cancer: associations with germline VHL polymorphisms and etiologic risk factors. PLoS Genet 7(10):e1002312. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002312
Schapira AH (1999) Mitochondrial involvement in Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, hereditary spastic paraplegia and Friedreich’s ataxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1410(2):159–170
Ullah MS, Davies AJ, Halestrap AP (2006) The plasma membrane lactate transporter MCT4, but not MCT1, is up-regulated by hypoxia through a HIF-1alpha-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 281(14):9030–9037. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511397200
Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ (2000) Identification of novel hypoxia dependent and independent target genes of the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumour suppressor by mRNA differential expression profiling. Oncogene 19(54):6297–6305. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204012
Yamaguchi H, Wang HG (2006) Tissue transglutaminase serves as an inhibitor of apoptosis by cross-linking caspase 3 in thapsigargin-treated cells. Mol Cell Biol 26(2):569–579. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.2.569-579.2006
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research Grant (NCC1410671-1) from the National Cancer Center of Korea to S.Y.K.
Conflict of interest
We declare that none of the authors have any financial interest related to this work, and none of the authors have any financial support beyond the research grant mentioned above.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B. M. Ku and C.-H. Lee contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ku, B.M., Lee, CH., Lee, SH. et al. Increased expression of transglutaminase 2 drives glycolytic metabolism in renal carcinoma cells. Amino Acids 46, 1527–1536 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1714-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1714-2