Abstract
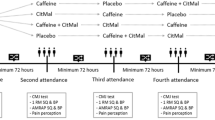
This study aimed at investigating the effects of a commercially available energy drink on shooting precision, jump performance and endurance capacity in young basketball players. Sixteen young basketball players (first division of a junior national league; 14.9 ± 0.8 years; 73.4 ± 12.4 kg; 182.3 ± 6.5 cm) volunteered to participate in the research. They ingested either (a) an energy drink that contained 3 mg of caffeine per kg of body weight or (b) a placebo energy drink with the same appearance and taste. After 60 min for caffeine absorption, they performed free throw shooting and three-point shooting tests. After that, participants performed a maximal countermovement jump (CMJ), a repeated maximal jumps test for 15 s (RJ-15), and the Yo–Yo intermittent recovery test level 1 (Yo–Yo IR1). Urine samples were obtained before and 30 min after testing. In comparison to the placebo, the ingestion of the caffeinated energy drink did not affect precision during the free throws (Caffeine = 70.7 ± 11.8 % vs placebo = 70.3 ± 11.0 %; P = 0.45), the three-point shooting test (39.9 ± 11.8 vs 38.1 ± 12.8 %; P = 0.33) or the distance covered in the Yo–Yo IR1 (2,000 ± 706 vs 1,925 ± 702 m; P = 0.19). However, the energy drink significantly increased jump height during the CMJ (38.3 ± 4.4 vs 37.5 ± 4.4 cm; P < 0.05) mean jump height during the RJ-15 (30.2 ± 3.6 vs 28.8 ± 3.4 cm; P < 0.05) and the excretion of urinary caffeine (1.2 ± 0.7 vs 0.1 ± 0.1 μg/mL; P < 0.05). The intake of a caffeine-containing energy drink (3 mg/kg body weight) increased jump performance although it did not affect basketball shooting precision.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkrim NB, El Fazaa S, El Ati J (2007) Time-motion analysis and physiological data of elite under-19-year-old basketball players during competition. Br J Sports Med 41(2):69–75. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2006.032318 (discussion 75)
Astorino TA, Matera AJ, Basinger J, Evans M, Schurman T, Marquez R (2012) Effects of red bull energy drink on repeated sprint performance in women athletes. Amino Acids 42(5):1803–1808. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0900-8
Baker LB, Dougherty KA, Chow M, Kenney WL (2007) Progressive dehydration causes a progressive decline in basketball skill performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(7):1114–1123
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Coburn JW, Malek MH (2006) The acute effects of a caffeine-containing supplement on strength, muscular endurance, and anaerobic capabilities. J Strength Cond Res 20(3):506–510. doi:10.1519/18285.1
Button C, MacLeod M, Sanders R, Coleman S (2003) Examining movement variability in the basketball free-throw action at different skill levels. Res Q Exerc Sport 74(3):257–269
Castagna C, Impellizzeri FM, Chamari K, Carlomagno D, Rampinini E (2006) Aerobic fitness and yo–yo continuous and intermittent tests performances in soccer players: a correlation study. J Strength Cond Res 20(2):320–325. doi:10.1519/R-18065.1
Castagna C, Abt G, Manzi V, Annino G, Padua E, D’Ottavio S (2008a) Effect of recovery mode on repeated sprint ability in young basketball players. J Strength Cond Res 22(3):923–929
Castagna C, Impellizzeri FM, Rampinini E, D’Ottavio S, Manzi V (2008b) The Yo–Yo intermittent recovery test in basketball players. J Sci Med Sport 11(2):202–208
Cormack SJ, Newton RU, McGuigan MR, Doyle TL (2008) Reliability of measures obtained during single and repeated countermovement jumps. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 3(2):131–144
Del Coso J, Estevez E, Mora-Rodriguez R (2008) Caffeine effects on short-term performance during prolonged exercise in the heat. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(4):744–751. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181621336
Del Coso J, Munoz G, Munoz-Guerra J (2011) Prevalence of caffeine use in elite athletes following its removal from the World Anti-Doping Agency list of banned substances. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 36(4):555–561. doi:10.1139/h11-052
Del Coso J, Munoz-Fernandez VE, Munoz G, Fernandez-Elias VE, Ortega JF, Hamouti N, Barbero JC, Munoz-Guerra J (2012a) Effects of a caffeine-containing energy drink on simulated soccer performance. PLoS One 7(2):e31380
Del Coso J, Salinero JJ, Gonzalez-Millan C, Abian-Vicen J, Perez-Gonzalez B (2012b) Dose response effects of a caffeine-containing energy drink on muscle performance: a repeated measures design. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 9(1):21
Del Coso J, Portillo J, Munoz G, Abian-Vicen J, Gonzalez-Millan C, Munoz-Guerra J (2013a) Caffeine-containing energy drink improves sprint performance during an international rugby sevens competition. Amino Acids 44(6):1511–1519. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1473-5
Del Coso J, Ramírez JA, Muñoz G, Portillo LJ, Gonzalez-Millan C, Muñoz V, Barbero-Alvarez JC, Muñoz-Guerra J (2013b) Caffeine-containing energy drink improves physical performance of elite rugby players during a simulated match. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 38(4):368–374
Dougherty KA, Baker LB, Chow M, Kenney WL (2006) Two percent dehydration impairs and six percent carbohydrate drink improves boys basketball skills. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(9):1650–1658
Drinkwater EJ, Pyne DB, McKenna MJ (2008) Design and interpretation of anthropometric and fitness testing of basketball players. Sports Med 38(7):565–578
Duncan MJ, Lyons M, Hankey J (2009) Placebo effects of caffeine on short-term resistance exercise to failure. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 4(2):244–253
Foskett A, Ali A, Gant N (2009) Caffeine enhances cognitive function and skill performance during simulated soccer activity. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 19(4):410–423
Franks HM, Hagedorn H, Hensley VR, Hensley WJ, Starmer GA (1975) The effect of caffeine on human performance, alone and in combination with ethanol. Psychopharmacologia 45(2):177–181
Gant N, Ali A, Foskett A (2010) The influence of caffeine and carbohydrate coingestion on simulated soccer performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 20(3):191–197
Green JM, Wickwire PJ, McLester JR, Gendle S, Hudson G, Pritchett RC, Laurent CM (2007) Effects of caffeine on repetitions to failure and ratings of perceived exertion during resistance training. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2(3):250–259
Hoffman JR (2010) Caffeine and energy drinks. Strength Cond J 32(1):15–20
Hoffman JR, Tenenbaum G, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ (1996) Relationship between athletic performance tests and playing time in elite college basketball players. J Strength Cond Res 10(2):67–71
Hudson GM, Green JM, Bishop PA, Richardson MT (2008) Effects of caffeine and aspirin on light resistance training performance, perceived exertion, and pain perception. J Strength Cond Res 22(6):1950–1957. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31818219cb
Jacobson BH, Edgley BM (1987) Effects of caffeine on simple reaction time and movement time. Aviat Space Environ Med 58(12):1153–1156
Klusemann MJ, Pyne DB, Foster C, Drinkwater EJ (2012) Optimising technical skills and physical loading in small-sided basketball games. J Sports Sci 30(14):1463–1471. doi:10.1080/02640414.2012.712714
Krustrup P, Mohr M, Amstrup T, Rysgaard T, Johansen J, Steensberg A, Pedersen PK, Bangsbo J (2003) The yo–yo intermittent recovery test: physiological response, reliability, and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(4):697–705
MacIntosh BR, Wright BM (1995) Caffeine ingestion and performance of a 1,500-metre swim. Canadian journal of applied physiology. Revue canadienne de physiologie appliquee 20(2):168–177
McInnes SE, Carlson JS, Jones CJ, McKenna MJ (1995) The physiological load imposed on basketball players during competition. J Sports Sci 13(5):387–397. doi:10.1080/02640419508732254
Mohr M, Nielsen JJ, Bangsbo J (2011) Caffeine intake improves intense intermittent exercise performance and reduces muscle interstitial potassium accumulation. J Appl Physiol 111(5):1372–1379
Share B, Sanders N, Kemp J (2009) Caffeine and performance in clay target shooting. J Sports Sci 27(6):661–666
Stuart GR, Hopkins WG, Cook C, Cairns SP (2005) Multiple effects of caffeine on simulated high-intensity team-sport performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(11):1998–2005
Thomas A, Dawson B, Goodman C (2006) The yo–yo test: reliability and association with a 20-m shuttle run and VO(2max). Int J Sports Physiol Perform 1(2):137–149
Tucker MA, Hargreaves JM, Clarke JC, Dale DL, Blackwell GJ (2013) The effect of a caffeine on maximal oxygen uptake and vertical jump performance in male basketball players. J Strength Cond Res 27(2):382–387
Vernillo G, Silvestri A, Torre AL (2012) The yo–yo intermittent recovery test in junior basketball players according to performance level and age group. J Strength Cond Res 26(9):2490–2494
Wiles JD, Bird SR, Hopkins J, Riley M (1992) Effect of caffeinated coffee on running speed, respiratory factors, blood lactate and perceived exertion during 1500-m treadmill running. Br J Sports Med 26(2):116–120
World Anti-doping Web Site [Internet]. Montreal (Canada): World Anti-doping Agency. Available from: http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/World_Anti-Doping_Program/WADP-Prohibited-list/WADA_Prohibited_List_2004_EN.pdf. Accessed 1 Jun 2012
Zuzik P (2011) Free throw shooting effectiveness in basketball matches of men and women. Sports Sci Rev 20(3):149–160
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the participants for their contribution to the study. Additionally, they thank the Fuenlabrada Basketball SAD for its invaluable help for the purposes of this investigation. This study did not receive any funding.
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest derived from the outcomes of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abian-Vicen, J., Puente, C., Salinero, J.J. et al. A caffeinated energy drink improves jump performance in adolescent basketball players. Amino Acids 46, 1333–1341 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1702-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1702-6