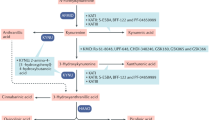
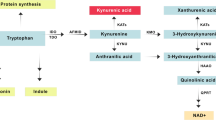
Abstract
The kynurenine pathway is the major route for the oxidative degradation of the amino acid tryptophan. Activity of the pathway is involved in several disease conditions, both in the periphery and the central nervous system, including cancer, inflammatory disorders, neurological conditions, psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Three enzymes are now known to catalyze the first and rate-limiting step in the catabolism of tryptophan along this pathway: tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO, subsequently named IDO1), both of which have been extensively studied, and a third enzyme, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2), a relative newcomer to the kynurenine pathway field. The adjuvant chemotherapeutic agent, 1-methyl-d-tryptophan, was intially suggested to target IDO2, implying involvement of IDO2 in tumorigenesis. Subsequently this compound has been suggested to have alternative actions and the physiological and pathophysiological roles of IDO2 are unclear. Targeted genetic interventions and selective inhibitors provide approaches for investigating the biology of IDO2. This review focuses on the current knowledge of IDO2 biology and discusses tools that will assist in further characterizing the enzymes of the kynurenine pathway.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- IDO:
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- LIP:
-
Liver-enriched inhibitory protein
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- 1DMT:
-
1-Methyl-d-tryptophan
- 1LMT:
-
1-Methyl-l-tryptophan
- 1MT:
-
1-Methyltryptophan
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- NAD+ :
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- rmIDO:
-
Recombinant mouse indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- rhIDO:
-
Recombinant human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- TDO:
-
Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase
- l-Trp:
-
l-Tryptophan
References
Alexander AM, Crawford M, Bertera S, Rudert WA, Takikawa O, Robbins PD, Trucco M (2002) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in transplanted NOD Islets prolongs graft survival after adoptive transfer of diabetogenic splenocytes. Diabetes 51(2):356–365
Austin CJ, Mailu BM, Maghzal GJ, Sanchez-Perez A, Rahlfs S, Zocher K, Yuasa HJ, Arthur JW, Becker K, Stocker R, Hunt NH, Ball HJ (2010) Biochemical characteristics and inhibitor selectivity of mouse indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2. Amino Acids 39(2):565–578. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0475-9
Axelrod HE, Morgan AF, Lepkovsky S (1945) The fate of tryptophane in pyridoxine-deficient and normal dogs. J Biol Chem 160:155–164
Baban B, Chandler P, McCool D, Marshall B, Munn DH, Mellor AL (2004) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression is restricted to fetal trophoblast giant cells during murine gestation and is maternal genome specific. J Reprod Immunol 61(2):67–77. doi:101016/jjri200311003S0165037803001530
Badawy AA (1981) Possible involvement of the enhanced tryptophan pyrrolase activity in the corticosterone- and starvation-induced increases in concentrations of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides (phosphates) in rat liver. Biochem J 196(1):217–224
Bakmiwewa SM, Fatokun AA, Tran A, Payne RJ, Hunt NH, Ball HJ (2012) Identification of selective inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(24):7641–7646. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.010
Ball HJ, Sanchez-Perez A, Weiser S, Austin CJ, Astelbauer F, Miu J, McQuillan JA, Stocker R, Jermiin LS, Hunt NH (2007) Characterization of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like protein found in humans and mice. Gene 396(1):203–213. doi:S0378-1119(07)00168-0101016/jgene200704010
Ball HJ, Yuasa HJ, Austin CJ, Weiser S, Hunt NH (2009) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2; a new enzyme in the kynurenine pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41(3):467–471. doi:101016/jbiocel200801005
Beadle GW, Mitchell HK, Nyc JF (1947) Kynurenine as an intermediate in the formation of nicotinic acid from tryptophane by neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 33(6):155–158
Byrne GI, Lehmann LK, Landry GJ (1986) Induction of tryptophan catabolism is the mechanism for gamma-interferon-mediated inhibition of intracellular Chlamydia psittaci replication in T24 cells. Infect Immun 53(2):347–351
Cady SG, Sono M (1991) 1-Methyl-DL-tryptophan, beta-(3-benzofuranyl)-DL-alanine (the oxygen analog of tryptophan), and beta-[3-benzo(b)thienyl]-DL-alanine (the sulfur analog of tryptophan) are competitive inhibitors for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 291(2):326–333
Chang MY, Smith C, DuHadaway JB, Pyle JR, Boulden J, Soler AP, Muller AJ, Laury-Kleintop LD, Prendergast GC (2011) Cardiac and gastrointestinal liabilities caused by deficiency in the immune modulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Cancer Biol Ther 12(12):1050–1058. doi:10.4161/cbt.12.12.18142
Changsirivathanathamrong D, Wang Y, Rajbhandari D, Maghzal GJ, Mak WM, Woolfe C, Duflou J, Gebski V, dos Remedios CG, Celermajer DS, Stocker R (2011) Tryptophan metabolism to kynurenine is a potential novel contributor to hypotension in human sepsis. Crit Care Med 39(12):2678–2683. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31822827f2
Chauhan N, Thackray SJ, Rafice SA, Eaton G, Lee M, Efimov I, Basran J, Jenkins PR, Mowat CG, Chapman SK, Raven EL (2009) Reassessment of the reaction mechanism in the heme dioxygenases. J Am Chem Soc 131(12):4186–4187. doi:10.1021/ja808326g
Christen S, Peterhans E, Stocker R (1990) Antioxidant activities of some tryptophan metabolites: possible implication for inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(7):2506–2510
Criado G, Simelyte E, Inglis JJ, Essex D, Williams RO (2009) Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan catabolism regulates accumulation of Th1/Th17 cells in the joint in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60(5):1342–1351. doi:10.1002/art.24446
Croitoru-Lamoury J, Lamoury FM, Caristo M, Suzuki K, Walker D, Takikawa O, Taylor R, Brew BJ (2011) Interferon-gamma regulates the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activation of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO). PLoS ONE 6(2):e14698. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014698
Darlington LG, Mackay GM, Forrest CM, Stoy N, George C, Stone TW (2007) Altered kynurenine metabolism correlates with infarct volume in stroke. Eur J Neurosci 26(8):2211–2221. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05838.x
Divanovic S, Sawtell NM, Trompette A, Warning JI, Dias A, Cooper AM, Yap GS, Arditi M, Shimada K, Duhadaway JB, Prendergast GC, Basaraba RJ, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Aliberti J, Karp CL (2012) Opposing biological functions of tryptophan catabolizing enzymes during intracellular infection. J Infect Dis 205(1):152–161. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir621
Eldredge H, DeNittis A, DuHadaway J, Metz R, Prendergast G (2012) Whole-brain radiation therapy and chloroquine in patients with brain metastases: outcome and response related to IDO2 gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Int J Rad Oncol 84(3):S75
Friberg M, Jennings R, Alsarraj M, Dessureault S, Cantor A, Extermann M, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Antonia SJ (2002) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to tumor cell evasion of T cell-mediated rejection. Int J Cancer 101(2):151–155. doi:10.1002/ijc.10645
Fukunaga M, Yamamoto Y, Kawasoe M, Arioka Y, Murakami Y, Hoshi M, Saito K (2012) Studies on tissue and cellular distribution of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2: the absence of IDO1 upregulates IDO2 expression in the epididymis. J Histochem Cytochem 60(11):854–860. doi:10.1369/0022155412458926
Godin-Ethier J, Hanafi LA, Piccirillo CA, Lapointe R (2011) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in human cancers: clinical and immunologic perspectives. Clin Cancer Res 17(22):6985–6991. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1331
Guidetti P, Reddy PH, Tagle DA, Schwarcz R (2000) Early kynurenergic impairment in Huntington’s disease and in a transgenic animal model. Neurosci Lett 283(3):233–235
Guillemin GJ, Williams KR, Smith DG, Smythe GA, Croitoru-Lamoury J, Brew BJ (2003) Quinolinic acid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 527:167–176
Haber R, Bessette D, Hulihan-Giblin B, Durcan MJ, Goldman D (1993) Identification of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase RNA in rodent brain. J Neurochem 60(3):1159–1162
Hayaishi O, Rothberg S, Mehler AH, Saito Y (1957) Studies on oxygenases; enzymatic formation of kynurenine from tryptophan. J Biol Chem 229(2):889–896
Heidelberger C, Gullberg ME et al (1949) Tryptophan metabolism; concerning the mechanism of the mammalian conversion of tryptophan into kynurenine, kynurenic acid, and nicotinic acid. J Biol Chem 179(1):143–150
Heyes MP, Rubinow D, Lane C, Markey SP (1989) Cerebrospinal fluid quinolinic acid concentrations are increased in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 26(2):275–277. doi:10.1002/ana.410260215
Hilmas C, Pereira EF, Alkondon M, Rassoulpour A, Schwarcz R, Albuquerque EX (2001) The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: physiopathological implications. J Neurosci 21(19):7463–7473
Hou DY, Muller AJ, Sharma MD, DuHadaway J, Banerjee T, Johnson M, Mellor AL, Prendergast GC, Munn DH (2007) Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells by stereoisomers of 1-methyl-tryptophan correlates with antitumor responses. Cancer Res 67(2):792–801. doi:67/2/792101158/0008-5472CAN-06-2925
Hunt NH, Golenser J, Chan-Ling T, Parekh S, Rae C, Potter S, Medana IM, Miu J, Ball HJ (2006) Immunopathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Int J Parasitol 36(5):569–582. doi:101016/jijpara200602016
Igari T, Obara K, Ono S, Toba Y (1975) Tryptophan metabolism in the joint diseases. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol 29(1–6):194–197
Jrad-Lamine A, Henry-Berger J, Gourbeyre P, Damon-Soubeyrand C, Lenoir A, Combaret L, Saez F, Kocer A, Tone S, Fuchs D, Zhu W, Oefner PJ, Munn DH, Mellor AL, Gharbi N, Cadet R, Aitken RJ, Drevet JR (2011) Deficient tryptophan catabolism along the kynurenine pathway reveals that the epididymis is in a unique tolerogenic state. J Biol Chem 286(10):8030–8042. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.172114
Kanai M, Funakoshi H, Takahashi H, Hayakawa T, Mizuno S, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (2009) Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase is a key modulator of physiological neurogenesis and anxiety-related behavior in mice. Mol Brain 2:8. doi:1756-6606-2-810.1186/1756-6606-2-8
Knox WE (1951) Two mechanisms which increase in vivo the liver tryptophan peroxidase activity: specific enzyme adaptation and stimulation of the pituitary adrenal system. Br J Exp Pathol 32(5):462–469
Knox WE, Auerbach VH (1955) The hormonal control of tryptophan peroxidase in the rat. J Biol Chem 214(1):307–313
Leklem JE (1971) Quantitative aspects of tryptophan metabolism in humans and other species: a review. Am J Clin Nutr 24(6):659–672
Liu X, Shin N, Koblish HK, Yang G, Wang Q, Wang K, Leffet L, Hansbury MJ, Thomas B, Rupar M, Waeltz P, Bowman KJ, Polam P, Sparks RB, Yue EW, Li Y, Wynn R, Fridman JS, Burn TC, Combs AP, Newton RC, Scherle PA (2010) Selective inhibition of IDO1 effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity. Blood 115(17):3520–3530. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-246124
Lo BK, Jalili RB, Zloty D, Ghahary A, Cowan B, Dutz JP, Carr N, Shapiro J, McElwee KJ (2011) CXCR3 ligands promote expression of functional indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in basal cell carcinoma keratinocytes. Br J Dermatol 165(5):1030–1036. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10489.x
Lob S, Konigsrainer A, Schafer R, Rammensee HG, Opelz G, Terness P (2008) Levo- but not dextro-1-methyl tryptophan abrogates the IDO activity of human dendritic cells. Blood 111(4):2152–2154. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-10-116111
Lob S, Konigsrainer A, Zieker D, Brucher BL, Rammensee HG, Opelz G, Terness P (2009) IDO1 and IDO2 are expressed in human tumors: levo- but not dextro-1-methyl tryptophan inhibits tryptophan catabolism. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58(1):153–157. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0513-6
Macchiarulo A, Camaioni E, Nuti R, Pellicciari R (2009) Highlights at the gate of tryptophan catabolism: a review on the mechanisms of activation and regulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), a novel target in cancer disease. Amino Acids 37(2):219–229. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0137-3
Maghzal GJ, Thomas SR, Hunt NH, Stocker R (2008) Cytochrome b5, not superoxide anion radical, is a major reductant of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human cells. J Biol Chem 283(18):12014–12025. doi:M710266200101074/jbcM710266200
Meininger D, Zalameda L, Liu Y, Stepan LP, Borges L, McCarter JD, Sutherland CL (2011) Purification and kinetic characterization of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases 1 and 2 (IDO1 and IDO2) and discovery of selective IDO1 inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta 12:1947–1954. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.07.023
Metz R, Duhadaway JB, Kamasani U, Laury-Kleintop L, Muller AJ, Prendergast GC (2007) Novel tryptophan catabolic enzyme IDO2 is the preferred biochemical target of the antitumor indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory compound D-1-methyl-tryptophan. Cancer Res 67(15):7082–7087. doi:67/15/7082101158/0008-5472CAN-07-1872
Metz R, Rust S, Duhadaway JB, Mautino MR, Munn DH, Vahanian NN, Link CJ, Prendergast GC (2012) IDO inhibits a tryptophan sufficiency signal that stimulates mTOR: a novel IDO effector pathway targeted by D-1-methyl-tryptophan. Oncoimmunology 1(9):1460–1468. doi:10.4161/onci.21716
Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I, Conway SJ, Marshall B, Brown C, Mellor AL (1998) Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science 281(5380):1191–1193
Munn DH, Sharma MD, Baban B, Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D, Mellor AL (2005) GCN2 kinase in T cells mediates proliferative arrest and anergy induction in response to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunity 22(5):633–642. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2005.03.013
Murray MF (2007) The human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase gene and related human genes. Curr Drug Metab 8(3):197–200
Ogawa T, Matson WR, Beal MF, Myers RH, Bird ED, Milbury P, Saso S (1992) Kynurenine pathway abnormalities in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 42(9):1702–1706
Pallotta MT, Orabona C, Volpi C, Vacca C, Belladonna ML, Bianchi R, Servillo G, Brunacci C, Calvitti M, Bicciato S, Mazza EM, Boon L, Grassi F, Fioretti MC, Fallarino F, Puccetti P, Grohmann U (2011) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a signaling protein in long-term tolerance by dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 12(9):870–878. doi:10.1038/ni.2077
Perkins MN, Stone TW (1982) An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res 247(1):184–187
Perkins MN, Stone TW (1983) Pharmacology and regional variations of quinolinic acid-evoked excitations in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226(2):551–557
Peterson AC, Migawa MT, Martin MJ, Hamaker LK, Czerwinski KM, Zhang W, Arend RA, Fisette PL, Ozaki Y, Will JA, Brown RR, Cook JM (1994) Evaluation of functionalized tryptophan derivatives and related compunds as competitive inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dixoygenase. Med Chem Res 3:531–544
Pfefferkorn ER, Guyre PM (1984) Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured fibroblasts by human recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun 44(2):211–216
Pilotte L, Larrieu P, Stroobant V, Colau D, Dolusic E, Frederick R, De Plaen E, Uyttenhove C, Wouters J, Masereel B, Van den Eynde BJ (2012) Reversal of tumoral immune resistance by inhibition of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(7):2497–2502. doi:10.1073/pnas.1113873109
Qian F, Villella J, Wallace PK, Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Tario JD Jr, Andrews C, Matsuzaki J, Valmori D, Ayyoub M, Frederick PJ, Beck A, Liao J, Cheney R, Moysich K, Lele S, Shrikant P, Old LJ, Odunsi K (2009) Efficacy of levo-1-methyl tryptophan and dextro-1-methyl tryptophan in reversing indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-mediated arrest of T-cell proliferation in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 69(13):5498–5504. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-2106
Qian F, Liao J, Villella J, Edwards R, Kalinski P, Lele S, Shrikant P, Odunsi K (2012) Effects of 1-methyltryptophan stereoisomers on IDO2 enzyme activity and IDO2-mediated arrest of human T cell proliferation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61(11):2013–2020. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1265-x
Romani L, Fallarino F, De Luca A, Montagnoli C, D’Angelo C, Zelante T, Vacca C, Bistoni F, Fioretti MC, Grohmann U, Segal BH, Puccetti P (2008) Defective tryptophan catabolism underlies inflammation in mouse chronic granulomatous disease. Nature 451(7175):211–215. doi:10.1038/nature06471
Sanni LA, Thomas SR, Tattam BN, Moore DE, Chaudhri G, Stocker R, Hunt NH (1998) Dramatic changes in oxidative tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway in experimental cerebral and noncerebral malaria. Am J Pathol 152(2):611–619
Schwarcz R, Whetsell W, Mangano R (1983) Quinolinic acid: an endogenous metabolite that produces axon-sparing lesions in rat brain. Science 219(4582):316–318. doi:10.1126/science.6849138
Shimizu T, Nomiyama S, Hirata F, Hayaishi O (1978) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem 253(13):4700–4706
Sono M, Cady SG (1989) Enzyme kinetic and spectroscopic studies of inhibitor and effector interactions with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. 1. Norharman and 4-phenylimidazole binding to the enzyme as inhibitors and heme ligands. Biochemistry 28(13):5392–5399
Sono M, Taniguchi T, Watanabe Y, Hayaishi O (1980) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Equilibrium studies of the tryptophan binding to the ferric, ferrous, and CO-bound enzymes. J Biol Chem 255(4):1339–1345
Sun T, Chen XH, Tang ZD, Cai J, Wang XY, Wang SC, Li ZL (2010) Novel 1-alkyl-tryptophan derivatives downregulate IDO1 and IDO2 mRNA expression induced by interferon-gamma in dendritic cells. Mol Cell Biochem 342(1–2):29–34. doi:10.1007/s11010-010-0465-y
Takikawa O, Kuroiwa T, Yamazaki F, Kido R (1988) Mechanism of interferon-gamma action. Characterization of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in cultured human cells induced by interferon-gamma and evaluation of the enzyme-mediated tryptophan degradation in its anticellular activity. J Biol Chem 263(4):2041–2048
Uyttenhove C, Pilotte L, Theate I, Stroobant V, Colau D, Parmentier N, Boon T, Van den Eynde BJ (2003) Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nat Med 9(10):1269–1274. doi:10.1038/nm934
Vottero E, Mitchell DA, Page MJ, MacGillivray RT, Sadowski IJ, Roberge M, Mauk AG (2006) Cytochrome b(5) is a major reductant in vivo of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expressed in yeast. FEBS Lett 580(9):2265–2268. doi:S0014-5793(06)00337-1101016/jfebslet200603034
Wang Y, Liu H, McKenzie G, Witting PK, Stasch JP, Hahn M, Changsirivathanathamrong D, Wu BJ, Ball HJ, Thomas SR, Kapoor V, Celermajer DS, Mellor AL, Keaney JF Jr, Hunt NH, Stocker R (2010) Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation. Nat Med 16(3):279–285. doi:nm2092101038/nm2092
Werner-Felmayer G, Werner ER, Fuchs D, Hausen A, Reibnegger G, Wachter H (1990) Neopterin formation and tryptophan degradation by a human myelomonocytic cell line (THP-1) upon cytokine treatment. Cancer Res 50(10):2863–2867
Witkiewicz AK, Costantino CL, Metz R, Muller AJ, Prendergast GC, Yeo CJ, Brody JR (2009) Genotyping and expression analysis of IDO2 in human pancreatic cancer: a novel, active target. J Am Coll Surg 208(5):781–787. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2008.12.018 discussion 787–789
Yamamoto S, Hayaishi O (1967) Tryptophan pyrrolase of rabbit intestine. D- and L-tryptophan-cleaving enzyme or enzymes. J Biol Chem 242(22):5260–5266
Yoshida R, Hayaishi O (1978) Induction of pulmonary indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by intraperitoneal injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75(8):3998–4000
Yuasa HJ, Ball HJ (2013) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases with very low catalytic activity are well conserved across kingdoms: iDOs of Basidiomycota. Fungal Genet Biol. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2013.03.003
Yuasa HJ, Takubo M, Takahashi A, Hasegawa T, Noma H, Suzuki T (2007) Evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases. J Mol Evol 65(6):705–714. doi:10.1007/s00239-007-9049-1
Yuasa HJ, Ball HJ, Ho YF, Austin CJ, Whittington CM, Belov K, Maghzal GJ, Jermiin LS, Hunt NH (2009) Characterization and evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenases IDOs from monotremes and marsupials. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 153(2):137–144. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2009.02.002
Yuasa HJ, Ball HJ, Austin CJ, Hunt NH (2010) 1-L-methyltryptophan is a more effective inhibitor of vertebrate IDO2 enzymes than 1-D-methyltryptophan. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 157(1):10–15. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.04.006
Zheng X, Koropatnick J, Li M, Zhang X, Ling F, Ren X, Hao X, Sun H, Vladau C, Franek JA, Feng B, Urquhart BL, Zhong R, Freeman DJ, Garcia B, Min WP (2006) Reinstalling antitumor immunity by inhibiting tumor-derived immunosuppressive molecule IDO through RNA interference. J Immunol 177(8):5639–5646
Acknowledgments
Dr. Fatokun was funded by an International Visiting Research Fellowship (IVRF) Award from the University of Sydney, Australia, and was a Visiting Fellow (from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, USA) in the laboratory of Prof. Nicholas Hunt. The work was supported by grants from the Australian Research Council and National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia to NH and HB.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatokun, A.A., Hunt, N.H. & Ball, H.J. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) and the kynurenine pathway: characteristics and potential roles in health and disease. Amino Acids 45, 1319–1329 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1602-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1602-1