Abstract
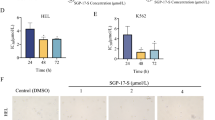
Peptides are ideal candidates for developing therapeutics. Polo-like kinase 1 is an important regulatory protein in the cell cycle and contains a C-terminal polo-box domain, which is the hallmark of this protein family. We developed a peptide inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1 that targets its polo-box domain. This new phosphopeptide, cRGDyK-S-S-CPLHSpT, preferentially penetrates the cancer cell membrane mediated by the integrin receptor, which is expressed at high levels by cancer cells. In the present study, using high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectroscopy, we determined the stability of cRGDyK-S-S-CPLHSpT and its cleavage by glutathione under typical conditions for cell culture. We further assessed the ability of the peptide to inhibit the proliferation of the U87MG glioma cell line. The phosphorylated peptide was stable, and the disulfide bond of cRGDyK-S-S-CPLHSpT was cleaved in 50 mM glutathione. This peptide inhibited the growth of cancer cells and changed their morphology. Therefore, we conclude that the phosphopeptide shows promise as a prodrug and has a high potential to act as an anticancer agent by inhibiting polo-like kinase 1 by binding its polo-box domain. These findings indicate the therapeutic potential of PLHSpT and peptides similarly targeted to surface receptors of cancer cells and to the functional domains of regulatory proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA (2004) Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(6):429–440. doi:10.1038/nrm1401
Chen K, Xie J, Chen X (2009) RGD-human serum albumin conjugates as efficient tumor targeting probes. Mol Imaging 8(2):65–73
Denny WA (2001) Prodrug strategies in cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem 36(7–8):577–595
Dietzmann K, Kirches E, von Bossanyi, Jachau K, Mawrin C (2001) Increased human polo-like kinase 1 expression in gliomas. J Neurooncol 53(1):1–11
Elia AE, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB (2003a) Proteomic screen finds pSer/pThr-binding domain localizing Plk1 to mitotic substrates. Science 299(5610):1228–1231. doi:10.1126/science.1079079
Elia AE, Rellos P, Haire LF, Chao JW, Ivins FJ, Hoepker K, Mohammad D, Cantley LC, Smerdon SJ, Yaffe MB (2003b) The molecular basis for phosphodependent substrate targeting and regulation of Plks by the polo-box domain. Cell 115(1):83–95
Garcia-Alvarez B, de Carcer G, Ibanez S, Bragado-Nilsson E, Montoya G (2007) Molecular and structural basis of polo-like kinase 1 substrate recognition: implications in centrosomal localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9):3107–3112. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609131104
Hao J, Kwissa M, Pulendran B, Murthy N (2006) Peptide crosslinked micelles: a new strategy for the design and synthesis of peptide vaccines. Int J Nanomed 1(1):97–103
Holtrich U, Wolf G, Brauninger A, Karn T, Bohme B, Rubsamen-Waigmann H, Strebhardt K (1994) Induction and down-regulation of PLK, a human serine/threonine kinase expressed in proliferating cells and tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(5):1736–1740
Jaracz S, Chen J, Kuznetsova LV, Ojima I (2005) Recent advances in tumor-targeting anticancer drug conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem 13(17):5043–5054. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.04.084
Kim SM, Yoon S, Choi N, Hong KS, Murugan RN, Cho G, Ryu EK (2012) In vivo tumor imaging using polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1 targeted peptide. Biomaterials 33(29):6915–6925. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.046
Knecht R, Elez R, Oechler M, Solbach C, von Ilberg C, Strebhardt K (1999) Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase (PLK) expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 59(12):2794–2797
Kratz F, Muller IA, Ryppa C, Warnecke A (2008) Prodrug strategies in anticancer chemotherapy. ChemMedChem 3(1):20–53. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200700159
Lansing TJ, McConnell RT, Duckett DR, Spehar GM, Knick VB, Hassler DF, Noro N, Furuta M, Emmitte KA, Gilmer TM, Mook RA Jr, Cheung M (2007) In vitro biological activity of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1. Mol Cancer Ther 6(2):450–459. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0543
Lin X, Dotson DG, Putkey JA (1996) Covalent binding of peptides to the N-terminal hydrophobic region of cardiac troponin C has limited effects on function. J Biol Chem 271(1):244–249
Liu F, Park JE, Qian WJ, Lim D, Graber M, Berg T, Yaffe MB, Lee KS, Burke TR Jr (2011) Serendipitous alkylation of a Plk1 ligand uncovers a new binding channel. Nat Chem Biol 7(9):595–601. doi:10.1038/nchembio.614
Lowery DM, Lim D, Yaffe MB (2005) Structure and function of Polo-like kinases. Oncogene 24(2):248–259. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208280
Malik DK, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Hasan S, Ali J (2007) Recent advances in protein and peptide drug delivery systems. Curr Drug Deliv 4(2):141–151
Meister A, Anderson ME (1983) Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem 52:711–760. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431
Miyata K, Kakizawa Y, Nishiyama N, Harada A, Yamasaki Y, Koyama H, Kataoka K (2004) Block catiomer polyplexes with regulated densities of charge and disulfide cross-linking directed to enhance gene expression. J Am Chem Soc 126(8):2355–2361. doi:10.1021/ja0379666
Mok H, Lee SH, Park JW, Park TG (2010) Multimeric small interfering ribonucleic acid for highly efficient sequence-specific gene silencing. Nat Mater 9(3):272–278. doi:10.1038/nmat2626
Moore A, Basilion JP, Chiocca EA, Weissleder R (1998) Measuring transferrin receptor gene expression by NMR imaging. Biochim Biophys Acta 1402(3):239–249
Park Y, Kwok KY, Boukarim C, Rice KG (2002) Synthesis of sulfhydryl cross-linking poly(ethylene glycol)-peptides and glycopeptides as carriers for gene delivery. Bioconjug Chem 13(2):232–239
Reents R, Jeyaraj DA, Waldmann H (2002) Enzymatically cleavable linker groups in polymer-supported synthesis. Drug Discov Today 7(1):71–76
Reindl W, Yuan J, Kramer A, Strebhardt K, Berg T (2008) Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 by blocking polo-box domain-dependent protein–protein interactions. Chem Biol 15(5):459–466. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.03.013
Richard JP, Melikov K, Vives E, Ramos C, Verbeure B, Gait MJ, Chernomordik LV, Lebleu B (2003) Cell-penetrating peptides. A reevaluation of the mechanism of cellular uptake. J Biol Chem 278(1):585–590. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209548200
Saito G, Swanson JA, Lee KD (2003) Drug delivery strategy utilizing conjugation via reversible disulfide linkages: role and site of cellular reducing activities. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55(2):199–215
Simizu S, Osada H (2000) Mutations in the Plk gene lead to instability of Plk protein in human tumour cell lines. Nat Cell Biol 2(11):852–854. doi:10.1038/35041102
Torchilin VP, Lukyanov AN (2003) Peptide and protein drug delivery to and into tumors: challenges and solutions. Drug Discov Today 8(6):259–266
Wang YC, Wang F, Sun TM, Wang J (2011) Redox-responsive nanoparticles from the single disulfide bond-bridged block copolymer as drug carriers for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Bioconjug Chem 22(10):1939–1945. doi:10.1021/bc200139n
Weissleder R, Cheng HC, Bogdanova A, Bogdanov A Jr (1997) Magnetically labeled cells can be detected by MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging: JMRI 7(1):258–263
Yun SM, Moulaei T, Lim D, Bang JK, Park JE, Shenoy SR, Liu F, Kang YH, Liao C, Soung NK, Lee S, Yoon DY, Lim Y, Lee DH, Otaka A, Appella E, McMahon JB, Nicklaus MC, Burke TR Jr, Yaffe MB, Wlodawer A, Lee KS (2009) Structural and functional analyses of minimal phosphopeptides targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(8):876–882. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1628
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by a grant from the Korea Basic Science Institute (D33404) and by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2012-0006388).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Sm., Yoon, S.M., Yim, M.S. et al. Targeted delivery of a phosphopeptide prodrug inhibits the proliferation of a human glioma cell line. Amino Acids 45, 1149–1156 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1570-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1570-5