Abstract
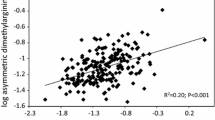
Elevated plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) were found in various clinical settings including coronary heart disease. To assess ADMA and SDMA diagnostic validity in patients with different stages of ischemic heart disease, we studied these markers in patients having stable angina pectoris (SAP), unstable angina (USAP), and acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The results were compared with the values of healthy individuals. Plasma ADMA and SDMA levels were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. In all patient groups both markers were significantly elevated in comparison with control ones (p < 0.001). In SAP patients, the median ADMA value was 0.75 (0.31–2.73) μmol/L, and SDMA 1.11 (0.69–0.1.42) μmol/L, in USAP patients, the marker values were 0.94 (0.34–3.13) μmol/L and 1.23 (0.88–4.72) μmol/L, and in AMI patients, 0.98 (0.48–2.01) μmol/L and 1.26 (0.75–2.93) μmol/L, while in healthy subjects they were 0.31 (0.17–0.87) μmol/L and 0.29 (0.20–0.83) μmol/L, respectively. SDMA was found significantly different in SAP and AMI patients (p < 0.05). Diagnostic accuracy was determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The highest area under the ROC (AUC) for ADMA was obtained in AMI patients (0.976), while for SDMA in USAP patients (1.000). There was no significant difference between the AUCs. The greatest sensitivity and specificity were found in the USAP group (95.65 and 96.30 % for ADMA, and 100 % for each characteristic of SDMA). Considering these results, SDMA showed better clinical accuracy in assessing ischemic disease, where it could be used as a valid marker and a therapeutic target.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae SW, Stuhlinger MC, Yoo HS, Yu KH, Park HK, Choi BY et al (2005) Plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine concentrations in newly diagnosed patients with acute myocardial infarction or unstable angina pectoris during two weeks of medical treatment. Am J Cardiol 95:729–733
Blokhin IO, Stevens JW, Murry DJ, Galagudza MM, Shlyakhto EV, Leiper JM, Lentz SR (2009) Deficiency of dimethylarginine dimethylaminotransferase-1 exacerbates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Circulation 120:S784
Busch M, Fleck C, Wolf G, Stein G (2006) Asymmetrical (ADMA) and symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA) as potential risk factors for cardiovascular and renal outcome in chronic kidney disease-possible candidates for paradoxical epidemiology? Amino Acids 30(3):225–232
Chen JW, Hsu NW, Wu TC, Lin SJ, Chang MS (2002) Long-term angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition reduces plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine and improves endothelial nitric oxide bioavailability and coronary microvascular function in patients with syndrome X. Am J Cardiol 90(9):974–982
Cooke JP (2000) Does ADMA cause endothelial dysfunction? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2032–2037
Cooke JP (2004) Asymmetrical dimethylarginine: the Uber marker? Circulation 109:1813–1818
Delles C, Schneider MP, John S, Gekle M, Schmieder RE (2002) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II AT1-receptor blockade reduce the levels of asymmetrical N(G), N(G)-dimethylarginine in human essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 15(7 Pt 1):590–593
Djordjević BV, Stojanović I, Ćosić V, Zvezdanović L, Deljanin-Ilić M, Dimić S, Kundalić B, Cvetković T, Jevtović-Stoimenov T (2008) Serum neopterin, nitric oxide, inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in patients with ischemic heart disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 46(8):1149–1155
Fleck C, Janz A, Schweitzer F, Karge E, Schwertfeger M, Stein G (2001) Serum concentrations of asymmetric (ADMA) and symmetric (SDMA) dimethylarginine in renal failure patients. Kidney Int 78:S14–S18
Fleck C, Schweitzer F, Karge E, Busch M, Stein G (2003) Serum concentrations of asymmetric (ADMA) and symmetric (SDMA) dimethylarginine in patients with chronic kidney diseases. Clin Chim Acta 336(1–2):1–12
Fliser D, Kronenberg F, Kielstein JT et al (2005) Asymmetric dimethylarginine and progression of chronic kidney disease: the mild to moderate kidney disease study. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2456–2461
Hamm CW, Braunwald E (2000) A classification of unstable angina revisited. Circulation 102:118–122
Hov GG, Sagen E, Bigonah A, Asberg A (2007) Health-associated reference values for arginine, asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) measured with high-performance liquid chromatography. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 67(8):868–876
Kielstein JT, Zoccali C (2005) Asymmetric dimethylarginine: a cardiovascular risk factor and a uremic toxin coming of age? Am J Kidney Dis 46:186–202
Kielstein JT, Salpeter SR, Bode-Böger SM, Cooke JP, Fliser D (2006) Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) as endogenous marker of renal function—a meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 21:2446–2451
Leong T, Zylberstein D, Graham I, Lissner L, Ward D, Fogarty J, Bengtsson C, Bjorkelund C, Thelle D (2008) Asymmetric dimethylarginine independently predicts fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarction and stroke in women. 24-year follow up of the population study of women in Gothenburg. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:961–967
Meinitzer A, Puchinger M, Winklhofer-Roob BM, Rock E, Ribalta J, Roob JM, Sundl I, Halwachs-Baumann G, Marz W (2007) Reference values for plasma concentrations of asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA) and other arginine metabolites in men after validation of a chromatographic method. Clin Chim Acta 384:141–148
Meinitzer A, Keilstein JT, Pilz S, Drechsler C, Ritz E, Boehm BO, Winkelmann BR, Marz W (2011) Symmetrical and asymmetrical dimethylarginine as predictors for mortality in patients referred for coronary angiography: the ludwigshafen risk and cardiovascular health study. Clin Chem 57(1):112–121
Nijveldt RJ, Teerlink T, Siroen MP, van Lambalgen AA, Rauwerda JA, van Leeuwen PA (2003) The liver is an important organ in the metabolism of asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA). Clin Nutr 22(1):17–22
Päivä H, Laakso J, Lehtimäki T, Isomustajärvi M, Ruokonen I, Laaksonen R (2003) Effect of high-dose statin treatment on plasma concentrations of endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 41(2):219–222
Paroni R, Fermo I, Fiorina P, Cighetti G (2005) Determination of asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginines in plasma of hyperhomocysteinemic subjects. Amino Acids 28(4):389–394
Ravani P, Tripepi G, Malberti F, Testa S, Mallamaci F, Zoccali C (2005) Asymmetrical dimethylarginine predicts progression to dialysis and death in patients with chronic kidney disease: a competing risks modeling approach. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2449–2455
Rust HL, Zurita-Lopez CI, Clarke S, Thompson PR (2011) Mechanistic studies on transcriptional coactivator protein arginine methyltransferase 1. Biochemistry 50(16):3332–3345
Schulze F, Lenzen H, Hanefeld C, Bartling A, Osterziel KJ, Goudeva L, Schmidt-Lucke C, Kusus M, Maas R, Schwedhelm E, Strodter D, Simon BC, Mugge A, Daniel WG, Tillmanns H, Maisch B, Streichert T, Boger RH (2006) Asymmetric dimethylarginine is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease: results from the multicenter Coronary Artery Risk Determination investigating the Influence of ADMA Concentration (CARDIAC) study. Am Heart J 152(3):493.e1–e8
Schulze F, Carter AM, Schwedhelm E, Ajjan R, Maas R, von Holten RA, Atzler D, Grant PJ, Boger RH (2010) Symmetric dimethylarginine predicts all-cause mortality following ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis 208(2):518–523
Schwedhelm E, Xanthakis V, Maas R, Sullivan LM, Schulze F, Riederer U, Benndorf RA, Boger RH, Vasan RS (2009) Asymmetric dimethylarginine reference intervals determined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: results from the Framingham offspring cohort. Clin Chem 55(8):1539–1545
Sibal L, Agarwal SC, Schwedhelm E, Luneburg N, Boger RH, Home PD (2009) A study of endothelial function and circulating asymmetric dimethylarginine levels in people with Type 1 diabetes without macrovascular disease or microalbuminuria. Cardiovasc Diabetol 8:27
Sibal L, Agarwal SC, Home PD, Boger RH (2010) The role of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Curr Cardiol Rev 6(2):82–90
Stuhlinger MC, Conci E, Haubner BJ, Stocker E-M, Schwaighofer J, Cooke JP, Tsao PS, Pachinger O, Metzler B (2007) Asymmetric dimethyl l-arginine (ADMA) is a critical regulator of myocardial reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 75:417–425
Surdacki A, Nowicki M, Sandmann J, Tsikas D, Boeger RH, Bode-Boeger SM, Kruszelnicka-Kwiatkowska O, Kokot F, Dubiel JS, Froelich JC (1999) Reduced urinary excretion of nitric oxide metabolites and increased plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in men with essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 33:652–658
Tarnow L, Hovind P, Teerlink T, Stehouwer CD, Parving HH (2004) Elevated plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine as a marker of cardiovascular morbidity in early diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27(3):765–769
Teerlink T, Nijveldt RJ, de Jong S, van Leeuwen PA (2002) Determination of arginine, asymmetric dimethylarginine, and symmetric dimethylarginine in human plasma and other biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 303:131–137
Valkonen VP, Laakso J, Paiva H, Lehtimaki T, Lakka TA, Isomustajarvi M et al (2003) Asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA) and risk of acute coronary events. Does statin treatment influence plasma ADMA levels? Atheroscler Suppl 4:19–22
Van de Werf F, Ardissino D, Betriu A, Cokkinos DV, Falk E, Fox KAA et al (2003) Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 24:28–66
Wahbi N, Dalton RN, Turner C, Denton M, Abbs I, Swaminathan R (2001) Dimethylarginines in chronic renal failure. J Clin Pathol 54(6):470–473
Ziegler S, Mittermayer F, Plank C, Minar E, Wolzt M, Schernthaner G-H (2005) Homocyst(e)ine-lowering therapy does not affect plasma asymmetrical dimethylarginine concentrations in patients with peripheral artery disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 90(4):2175–2178
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of Serbia. English language was restyled by Ljiljana Markovic, senior lector, English Department, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Nis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djordjević, B.V., Pavlović, R., Ćosić, V. et al. High clinical accuracy of asymmetric dimethylarginine and symmetric dimethylarginine in patients with ischemic heart disease. Amino Acids 43, 2293–2300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1307-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1307-x