Abstract
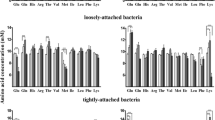
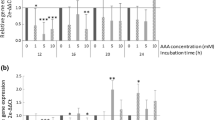
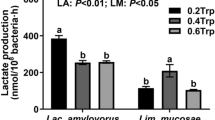
We recently reported that bacteria from the pig small intestine rapidly utilize and metabolize amino acids (AA). This study investigated the effect of l-arginine on the utilization of AA by pure bacterial strains (Streptococcus sp., Escherichia coli and Klebsiella sp.) and mixed bacterial cultures derived from the pig small intestine. Bacteria were incubated at 37°C for 3 h in anaerobic AA media containing 0–5 mmol/L of arginine to determine the effect of arginine on the bacterial utilization of AA. Amino acids in the medium plus cell extracts were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Results indicated concentration-dependent increases in the bacterial utilization of arginine and altered fluxes of arginine into ornithine and citrulline in the bacteria. Net glutamine utilization increased in pure bacterial strains with increased concentrations of arginine. With the addition of arginine, net utilization of threonine, glycine, phenylalanine and branched-chain AA increased (P < 0.05) in Streptococcus sp. and Klebsiella sp., but decreased in E. coli. Net utilization of lysine, threonine, isoleucine, leucine, glycine and alanine by jejunal or ileal mixed bacteria decreased (P < 0.05) with the addition of arginine. Complete utilization of asparagine, aspartate and serine were observed in pig small-intestinal bacteria after 3 h of incubation. Overall, the addition of arginine affected the metabolism of the arginine-family of AA and the serine- and aspartate-family of AA in small-intestinal bacteria and reduced the utilization of most AA in ileal mixed bacteria. These novel findings indicate that arginine exerts its beneficial effects on swine nutrition partially by regulating AA utilization and metabolism in the small-intestinal microbiota.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acids
- AR:
-
Acid resistance system
- EAA:
-
Nutritionally essential amino acids
- CFU:
-
Colony forming unit
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
References
Almaas E (2007) Optimal flux patterns in cellular metabolic networks. Chaos 17(2):026107
Almaas E, Kovács B, Vicsek T, Oltvai ZN, Barabási AL (2004) Global organization of metabolic fluxes in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Nature 427(6977):839–843
Bergen WG, Wu G (2009) Intestinal nitrogen recycling and utilization in health and disease. J Nutr 139:821–825
Blachier F, Davila AM, Benamouzig R, Tome D (2011) Channelling of arginine in NO and polyamine pathways in colonocytes and consequences. Front Biosci 16:1331–1343
Booijink CCGM (2009) Analysis of diversity and function of the human small intestinal microbiota. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Burnside K, Lembo A, de los Reyes M, Iliuk A, BinhTran N-T, Connelly JE, Lin W-J, Schmidt BZ, Richardson AR, Fang FC, Tao WA, Rajagopal L (2010) Regulation of hemolysin expression and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus by a serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase. PLoS ONE 5(6):e11071
Chaussee MS, Somerville GA, Reitzer L, Musser JM (2003) Rgg coordinates virulence factor synthesis and metabolism in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 185(20):6016–6024
Claus SP, Tsang TM, Wang Y, Cloarec O, Skordi E, Martin F-P, Rezzi S, Ross A, Kochhar S, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2008) Systemic multicompartmental effects of the gut microbiome on mouse metabolic phenotypes. Mol Syst Biol 4:219
Dai ZL, Zhang J, Wu G, Zhu WY (2010) Utilization of amino acids by bacteria from the pig small intestine. Amino Acids 39:1201–1215
Dai ZL, Li XL, Xi PB, Zhang J, Wu G, Zhu WY (2011a) Metabolism of select amino acids in bacteria from the pig small intestine. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0846-x
Dai ZL, Wu G, Zhu WY (2011b) Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: links between gut ecology and host health. Front Biosci 16:1768–1786
Deitch EA, Haskel Y, Cruz N, Xu D, Kvietys PR (1995) Caco-2 and IEC-18 intestinal epithelial cells exert bactericidal activity through an oxidant-dependent pathway. Shock 4(5):345–350
Dong T, Schellhorn HE (2009) Global effect of RpoS on gene expression in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933. BMC Genomics 10:349
Egert M, de Graaf AA, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Venema K (2006) Beyond diversity: functional microbiomics of the human colon. Trends Microbiol 14(2):86–91
Eller C, Crabill MR, Bryant MP (1971) Anaerobic roll tube media for nonselective enumeration and isolation of bacteria. Appl Microbiol 22(4):522–529
Fernández M, Zúñiga M (2006) Amino acid catabolic pathways of lactic acid bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 32(3):155–183
Fuller MF, Reeds PJ (1998) Nitrogen cycling in the gut. Annu Rev Nutr 18:385–411
He Q, Kong X, Wu G, Ren P, Tang H, Hao F, Huang R, Li T, Tan B, Li P, Tang Z, Yin Y, Wu Y (2009) Metabolomic analysis of the response of growing pigs to dietary l-arginine supplementation. Amino Acids 37(1):199–208
Kim SW, Wu G (2004) Dietary arginine supplementation enhances the growth of milk-fed young pigs. J Nutr 134(3):625–630
Li XL, Rezaei R, Li P, Wu G (2011) Composition of amino acids in feed ingredients for animal diets. Amino Acids 40:1159–1168
Lyte M, Vulchanova L, Brown DR (2011) Stress at the intestinal surface: catecholamines and mucosa-bacteria interactions. Cell Tissue Res 343(1):23–32
Marini JC, Didelija IC, Castillo L, Lee B (2010) Glutamine: precursor or nitrogen donor for citrulline synthesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299(1):E69–E79
Prüß BM, Nelms JM, Park C, Wolfe AJ (1994) Mutations in NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase of Escherichia coli affect growth on mixed amino acids. J Bacteriol 176:2143–2150
Resta-Lenert S, Barrett KE (2002) Enteroinvasive bacteria alter barrier and transport properties of human intestinal epithelium: role of iNOS and COX-2. Gastroenterology 122(4):1070–1087
Richard H, Foster JW (2004) Escherichia coli glutamate- and arginine-dependent acid resistance systems increase internal pH and reverse transmembrane potential. J Bacteriol 186(18):6032–6041
Russell JB (1991) A re-assessment of bacterial growth efficiency: the heat production and membrane potential of Streptococcus bovis in batch and continuous culture. Arch Microbiol 155(6):559–565
Russell JB (1993) Effect of amino acids on the heat production and growth efficiency of Streptococcus bovis: balance of anabolic and catabolic rates. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(6):1747–1751
Rychlik JL, LaVera R, Russell JB (2002) Amino acid deamination by ruminal Megasphaera elsdenii strains. Curr Microbiol 45(5):340–345
Samal A (2008) Conservation of high-flux backbone in alternate optimal and near-optimal flux distributions of metabolic networks. Syst Synth Biol 2(3–4):83–93
Sawers G (1998) The anaerobic degradation of l-serine and l-threonine in enterobacteria: networks of pathways and regulatory signals. Arch Microbiol 171:1–5
Schneider BL, Kiupakis AK, Reitzer LJ (1998) Arginine catabolism and the arginine succinyltransferase pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180(16):4278–4286
Shaibe E, Metzer E, Halpern YS (1985) Metabolic pathway for the utilization of l-arginine, l-ornithine, agmatine, and putrescine as nitrogen sources in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 163(3):933–937
Stoll B, Henry J, Reeds PJ, Yu H, Jahoor F, Burrin DG (1998) Catabolism dominates the first-pass intestinal metabolism of dietary essential amino acids in milk protein-fed piglets. J Nutr 128:606–614
Tan B, Li XG, Kong X, Huang R, Ruan Z, Yao K, Deng Z, Xie M, Shinzato I, Yin Y, Wu G (2009) Dietary l-arginine supplementation enhances the immune status in early-weaned piglets. Amino Acids 37(2):323–331
Urschel KL, Rafii M, Pencharz PB, Ball RO (2007) A multitracer stable isotope quantification of the effects of arginine intake on whole body arginine metabolism in neonatal piglets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E811–E818
Vining LC, Magasanik B (1981) Serine utilization by Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol 146(2):647–655
Wallace RJ (1996) Ruminal microbial metabolism of peptides and amino acids. J Nutr 126:1326S–1334S
Wilkinson DL, Bertolo RF, Brunton JA, Shoveller AK, Pencharz PB, Ball RO (2004) Arginine synthesis is regulated by dietary arginine intake in the enterally fed neonatal piglet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(3):E454–E462
Williams BA, Bosch MW, Boer H, Verstegen MWA, Tamminga S (2005) An in vitro batch culture method to assess potential fermentability of feed ingredients for monogastric diets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 123–124:445–462
Witthöft T, Eckmann L, Kim JM, Kagnoff MF (1998) Enteroinvasive bacteria directly activate expression of iNOS and NO production in human colon epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 275(3 Pt 1):G564–G571
Wu G (1997) Synthesis of citrulline and arginine from proline in enterocytes of postnatal pigs. Am J Physiol 272(6 Pt 1):G1382–G1390
Wu G (1998) Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J Nutr 128:1249–1252
Wu G (2009) Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 37:1–17
Wu G, Knabe DA (1995) Arginine synthesis in enterocytes of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol 269(3 Pt 2):R621–R629
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336(Pt 1):1–17
Wu G, Knabe DA, Flynn NE, Yan W, Flynn SP (1996) Arginine degradation in developing porcine enterocytes. Am J Physiol 271(5 Pt 1):G913–G919
Wu G, Davis PK, Flynn NE, Knabe DA, Davidson JT (1997) Endogenous synthesis of arginine plays an important role in maintaining arginine homeostasis in postweaning growing pigs. J Nutr 127:2342–2349
Wu G, Collins JK, Perkins-Veazie P, Siddiq M, Dolan KD, Kelly KA, Heaps CL, Meininger CJ (2007) Dietary supplementation with watermelon pomace juice enhances arginine availability and ameliorates the metabolic syndrome in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Nutr 137:2680–2685
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Marc Rhoads J, Carey Satterfield M, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Yin Y (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37(1):153–168
Wu X, Ruan Z, Gao Y, Yin Y, Zhou X, Wang L, Geng M, Hou Y, Wu G (2010) Dietary supplementation with l-arginine or N-carbamylglutamate enhances intestinal growth and heat shock protein-70 expression in weanling pigs fed a corn- and soybean meal-based diet. Amino Acids 39(3):831–839
Wu G, Bazer FW, Burghardt RC, Johnson GA, Kim SW, Knabe DA, Li P, Li XL, McKnight JR, Satterfield MC, Spencer TE (2011) Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 40:1053–1063
Yin YL, Yao K, Liu ZJ, Gong M, Ruan Z, Deng D, Tan BE, Liu ZQ, Wu G (2010) Supplementing l-leucine to a low-protein diet increases tissue protein synthesis in weanling pigs. Amino Acids 39:1477–1486
Zhang J (2009) Isolation and identification of amino acid utilizing bacteria from the porcine small intestine. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30810103909), the National Basic Research Program of China (2004CB117500-4), National Research Initiative Competitive Grants from the Animal Growth and Nutrient Utilization Program (2008-35206-18764) of the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, and Texas AgriLife Research Hatch Project (H-8200). We are grateful to Dr. J. Fleming for technical assistance, Dr. H. J. Gao and Dr. J. J. Wang for helpful discussion, and Dr. T. A. Davis for critical reading of the manuscript. Z.-L. Dai thanks the China Scholarship Council for support of his study at Texas A&M University between 17 February 2009 and 28 February 2010.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, ZL., Li, XL., Xi, PB. et al. Regulatory role for l-arginine in the utilization of amino acids by pig small-intestinal bacteria. Amino Acids 43, 233–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1067-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1067-z