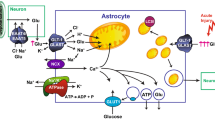
Abstract
Glutamate is the main excitatory amino acid, but its presence in the extracellular milieu has deleterious consequences. It may induce excitotoxicity and also compete with cystine for the use of the cystine–glutamate exchanger, blocking glutathione neosynthesis and inducing an oxidative stress-induced cell death. Both mechanisms are critical in the brain where up to 20% of total body oxygen consumption occurs. In normal conditions, the astrocytes ensure that extracellular concentration of glutamate is kept in the micromolar range, thanks to their coexpression of high-affinity glutamate transporters (EAATs) and glutamine synthetase (GS). Their protective function is nevertheless sensitive to situations such as oxidative stress or inflammatory processes. On the other hand, macrophages and microglia do not express EAATs and GS in physiological conditions and are the principal effector cells of brain inflammation. Since the late 1990s, a number of studies have now shown that both microglia and macrophages display inducible EAAT and GS expression, but the precise significance of this still remains poorly understood. Brain macrophages and microglia are sister cells but yet display differences. Both are highly sensitive to their microenvironment and can perform a variety of functions that may oppose each other. However, in the very particular environment of the healthy brain, they are maintained in a repressed state. The aim of this review is to present the current state of knowledge on brain macrophages and microglial cells activation, in order to help clarify their role in the regulation of glutamate under pathological conditions as well as its outcome.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- AEG:
-
Astrocyte elevated gene
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CCR:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor
- CX3CL:
-
Chemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand
- CX3CR:
-
Chemokine (C-X3-C motif) receptor
- EAAT:
-
Excitatory amino acid transporter
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- FIZZ1:
-
Found in Inflammatory Zone 1, a marker of alternative activation in murine macrophages
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- GSH:
-
l-γ-Glutamyl-l-cysteinyl-glycine (glutathione)
- GSSG:
-
Oxidised form of glutathione
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- ITIM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif
- MDM:
-
Monocyte-derived macrophages
- mGluR:
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB.
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PG:
-
Prostaglandin
- SIRPα:
-
Signal-regulatory protein α
- SIV:
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus
- TGF:
-
Transforming growth factor
- TNF:
-
Tumour necrosis factor
- TREM2:
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- VGLUT:
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter
- xCT:
-
Light chain subunit of the x −c cystine/glutamate exchanger
- Ym1:
-
A heparin-binding lectin, a marker of alternative activation in murine macrophages
References
Adams RA, Bauer J, Flick MJ, Sikorski SL, Nuriel T, Lassmann H, Degen JL, Akassoglou K (2007) The fibrin-derived gamma 377–395 peptide inhibits microglia activation and suppresses relapsing paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 204:571–582
Alliot F, Godin I, Pessac B (1999) Microglia derive from progenitors, originating from the yolk sac, and which proliferate in the brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 117:145–152
Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA (2006) Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci 9:119–126
Arriza JL, Eliasof S, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG (1997) Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4155–4160
Attwell D, Barbour B, Szatkowski M (1993) Nonvesicular release of neurotransmitter. Neuron 11:401–407
Bannai S (1986) Exchange of cystine and glutamate across plasma membrane of human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 261:2256–2263
Broer S, Brookes N (2001) Transfer of glutamine between astrocytes and neurons. J Neurochem 77:705–719
Broer A, Brookes N, Ganapathy V, Dimmer KS, Wagner CA, Lang F, Broer S (1999) The astroglial ASCT2 amino acid transporter as a mediator of glutamine efflux. J Neurochem 73:2184–2194
Brooke SM, Sapolsky RM (2003) Effects of glucocorticoids in the gp120-induced inhibition of glutamate uptake in hippocampal cultures. Brain Res 972:137–141
Buechler C, Ritter M, Orso E, Langmann T, Klucken J, Schmitz G (2000) Regulation of scavenger receptor CD163 expression in human monocytes and macrophages by pro- and antiinflammatory stimuli. J Leukoc Biol 67:97–103
Byrnes KR, Loane DJ, Faden AI (2009) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as targets for multipotential treatment of neurological disorders. Neurotherapeutics 6:94–107
Cardona AE, Pioro EP, Sasse ME, Kostenko V, Cardona SM, Dijkstra IM, Huang D, Kidd G, Dombrowski S, Dutta R, Lee JC, Cook DN, Jung S, Lira SA, Littman DR, Ransohoff RM (2006) Control of microglial neurotoxicity by the fractalkine receptor. Nat Neurosci 9:917–924
Chaudhry FA, Reimer RJ, Krizaj D, Barber D, Storm-Mathisen J, Copenhagen DR, Edwards RH (1999) Molecular analysis of system N suggests novel physiological roles in nitrogen metabolism and synaptic transmission. Cell 99:769–780
Chretien F, Vallat-Decouvelaere AV, Bossuet C, Rimaniol AC, Le Grand R, Le Pavec G, Creminon C, Dormont D, Gray F, Gras G (2002) Expression of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT-2) and glutamine synthetase (GS) in brain macrophages and microglia of SIVmac251-infected macaques. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28:410–417
Chretien F, Le Pavec G, Vallat-Decouvelaere AV, Delisle MB, Uro-Coste E, Ironside JW, Gambetti P, Parchi P, Creminon C, Dormont D, Mikol J, Gray F, Gras G (2004) Expression of excitatory amino acid transporter-1 (EAAT-1) in brain macrophages and microglia of patients with prion diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:1058–1071
Colton CA, Mott RT, Sharpe H, Xu Q, Van Nostrand WE, Vitek MP (2006) Expression profiles for macrophage alternative activation genes in AD and in mouse models of AD. J Neuroinflammation 3:27
Daikhin Y, Yudkoff M (2000) Compartmentation of brain glutamate metabolism in neurons and glia. J Nutr 130:1026S–1031S
Davalos D, Grutzendler J, Yang G, Kim JV, Zuo Y, Jung S, Littman DR, Dustin ML, Gan WB (2005) ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nat Neurosci 8:752–758
De Simone R, Ajmone-Cat MA, Tirassa P, Minghetti L (2003) Apoptotic PC12 cells exposing phosphatidylserine promote the production of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective molecules by microglial cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:208–216
De Simone R, Ajmone-Cat MA, Minghetti L (2004) Atypical antiinflammatory activation of microglia induced by apoptotic neurons: possible role of phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylserine receptor interaction. Mol Neurobiol 29:197–212
Derouiche A, Frotscher M (1991) Astroglial processes around identified glutamatergic synapses contain glutamine synthetase: evidence for transmitter degradation. Brain Res 552:346–350
Derouiche A, Rauen T (1995) Coincidence of l-glutamate/l-aspartate transporter (GLAST) and glutamine synthetase (GS) immunoreactions in retinal glia: evidence for coupling of GLAST and GS in transmitter clearance. J Neurosci Res 42:131–143
Derouiche A, Hartig W, Brauer K, Bruckner G (1996) Spatial relationship of lectin-labelled extracellular matrix and glutamine synthetase-immunoreactive astrocytes in rat cortical forebrain regions. J Anat 189:363–372
Dreyer EB, Lipton SA (1995) The coat protein gp120 of HIV-1 inhibits astrocyte uptake of excitatory amino acids via macrophage arachidonic acid. Eur J Neurosci 7:2502–2507
Fabriek BO, Van Haastert ES, Galea I, Polfliet MM, Dopp ED, Van Den Heuvel MM, Van Den Berg TK, De Groot CJ, Van Der Valk P, Dijkstra CD (2005) CD163-positive perivascular macrophages in the human CNS express molecules for antigen recognition and presentation. Glia 51:297–305
Fairman WA, Vandenberg RJ, Arriza JL, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG (1995) An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 375:599–603
Figiel M, Maucher T, Rozyczka J, Bayatti N, Engele J (2003) Regulation of glial glutamate transporter expression by growth factors. Exp Neurol 183:124–135
Fine SM, Angel RA, Perry SW, Epstein LG, Rothstein JD, Dewhurst S, Gelbard HA (1996) Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits glutamate uptake by primary human astrocytes. Implications for pathogenesis of HIV-1 dementia. J Biol Chem 271:15303–15306
Fonnum F (1984) Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem 42:1–11
Fremeau RT Jr, Burman J, Qureshi T, Tran CH, Proctor J, Johnson J, Zhang H, Sulzer D, Copenhagen DR, Storm-Mathisen J, Reimer RJ, Chaudhry FA, Edwards RH (2002) The identification of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 suggests novel modes of signaling by glutamate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14488–14493
Galea I, Palin K, Newman TA, Van Rooijen N, Perry VH, Boche D (2005) Mannose receptor expression specifically reveals perivascular macrophages in normal, injured, and diseased mouse brain. Glia 49:375–384
Gegelashvili G, Schousboe A (1997) High affinity glutamate transporters: regulation of expression and activity. Mol Pharmacol 52:6–15
Geissmann F, Jung S, Littman DR (2003) Blood monocytes consist of two principal subsets with distinct migratory properties. Immunity 19:71–82
Gras G, Chretien F, Vallat-Decouvelaere AV, Le Pavec G, Porcheray F, Bossuet C, Leone C, Mialocq P, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Clayette P, Le Grand R, Creminon C, Dormont D, Rimaniol AC, Gray F (2003) Regulated expression of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters and synthetase: a neuroprotective role for activated microglia and macrophages in HIV infection? Brain Pathol 13:211–222
Gras G, Porcheray F, Samah B, Leone C (2006) The glutamate–glutamine cycle as an inducible, protective face of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol 80:1067–1075
Gu S, Roderick HL, Camacho P, Jiang JX (2000) Identification and characterization of an amino acid transporter expressed differentially in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3230–3235
Had-Aissouni L (2011) Toward a new role for plasma membrane sodium-dependent glutamate transporters of astrocytes: maintenance of antioxidant defenses beyond extracellular glutamate clearance. Amino Acids (this issue)
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10:1387–1394
Himi T, Ikeda M, Yasuhara T, Nishida M, Morita I (2003) Role of neuronal glutamate transporter in the cysteine uptake and intracellular glutathione levels in cultured cortical neurons. J Neural Transm 110:1337–1348
Hogger P, Dreier J, Droste A, Buck F, Sorg C (1998) Identification of the integral membrane protein RM3/1 on human monocytes as a glucocorticoid-inducible member of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich family (CD163). J Immunol 161:1883–1890
Jacobsson J, Persson M, Hansson E, Ronnback L (2006) Corticosterone inhibits expression of the microglial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in vitro. Neuroscience 139:475–483
Jimenez S, Baglietto-Vargas D, Caballero C, Moreno-Gonzalez I, Torres M, Sanchez-Varo R, Ruano D, Vizuete M, Gutierrez A, Vitorica J (2008) Inflammatory response in the hippocampus of PS1M146L/APP751SL mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: age-dependent switch in the microglial phenotype from alternative to classic. J Neurosci 28:11650–11661
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (1992) Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 360:467–471
Kang DC, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, Emdad L, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB (2005) Cloning and characterization of HIV-1-inducible astrocyte elevated gene-1, AEG-1. Gene 353:8–15
Kaushal V, Schlichter LC (2008) Mechanisms of microglia-mediated neurotoxicity in a new model of the stroke penumbra. J Neurosci 28:2221–2230
Kida S, Steart PV, Zhang ET, Weller RO (1993) Perivascular cells act as scavengers in the cerebral perivascular spaces and remain distinct from pericytes, microglia and macrophages. Acta Neuropathol 85:646–652
Kodelja V, Goerdt S (1994) Dissection of macrophage differentiation pathways in cutaneous macrophage disorders and in vitro. Exp Dermatol 3:257–268
Koizumi S, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Nasu-Tada K, Shinozaki Y, Ohsawa K, Tsuda M, Joshi BV, Jacobson KA, Kohsaka S, Inoue K (2007) UDP acting at P2Y6 receptors is a mediator of microglial phagocytosis. Nature 446:1091–1095
Kort JJ (1998) Impairment of excitatory amino acid transport in astroglial cells infected with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 14:1329–1339
Lawson LJ, Perry VH, Gordon S (1992) Turnover of resident microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 48:405–415
Lehmann J, Schaefer P, Ferkany JW, Coyle JT (1983) Quinolinic acid evokes [3H]acetylcholine release in striatal slices: mediation by NMDA-type excitatory amino acid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 96:111–115
Leone C, Le Pavec G, Meme W, Porcheray F, Samah B, Dormont D, Gras G (2006) Characterization of human monocyte-derived microglia-like cells. Glia 54:183–192
Liu Y, Hao W, Letiembre M, Walter S, Kulanga M, Neumann H, Fassbender K (2006) Suppression of microglial inflammatory activity by myelin phagocytosis: role of p47-PHOX-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species. J Neurosci 26:12904–12913
Loane DJ, Stoica BA, Pajoohesh-Ganji A, Byrnes KR, Faden AI (2009) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 modulates microglial reactivity and neurotoxicity by inhibiting NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem 284:15629–15639
Lopez-Redondo F, Nakajima K, Honda S, Kohsaka S (2000) Glutamate transporter GLT-1 is highly expressed in activated microglia following facial nerve axotomy. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76:429–435
Magnus T, Chan A, Grauer O, Toyka KV, Gold R (2001) Microglial phagocytosis of apoptotic inflammatory T cells leads to down-regulation of microglial immune activation. J Immunol 167:5004–5010
Martinez-Hernandez A, Bell KP, Norenberg MD (1977) Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in brain. Science 195:1356–1358
Meisner F, Neuen-Jacob E, Sopper S, Schmidt M, Schlammes S, Scheller C, Vosswinkel D, Ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2008) Disruption of excitatory amino acid transporters in brains of SIV-infected rhesus macaques is associated with microglia activation. J Neurochem 104:202–209
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308:1314–1318
Norenberg MD (1979) Distribution of glutamine synthetase in the rat central nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 27:756–762
Norenberg MD, Martinez-Hernandez A (1979) Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res 161:303–310
O’Shea RD, Lau CL, Farso MC, Diwakarla S, Zagami CJ, Svendsen BB, Feeney SJ, Callaway JK, Jones NM, Pow DV, Danbolt NC, Jarrott B, Beart PM (2006) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on glial phenotype and activity of glutamate transporters: evidence for delayed up-regulation and redistribution of GLT-1. Neurochem Int 48:604–610
Okada K, Yamashita U, Tsuji S (2005) Modulation of Na(+)-dependent glutamate transporter of murine astrocytes by inflammatory mediators. J Uoeh 27:161–170
Ottersen OP, Zhang N, Walberg F (1992) Metabolic compartmentation of glutamate and glutamine: morphological evidence obtained by quantitative immunocytochemistry in rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 46:519–534
Patton HK, Zhou ZH, Bubien JK, Benveniste EN, Benos DJ (2000) gp120-induced alterations of human astrocyte function: Na(+)/H(+) exchange, K(+) conductance, and glutamate flux. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C700–C708
Perry VH, Hume DA, Gordon S (1985) Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience 15:313–326
Persson M, Brantefjord M, Hansson E, Ronnback L (2005) Lipopolysaccharide increases microglial GLT-1 expression and glutamate uptake capacity in vitro by a mechanism dependent on TNF-alpha. Glia 51:111–120
Persson J, Gardestrom P, Nasholm T (2006) Uptake, metabolism and distribution of organic and inorganic nitrogen sources by Pinus sylvestris. J Exp Bot 57:2651–2659
Persson M, Brantefjord M, Liljeqvist JA, Bergstrom T, Hansson E, Ronnback L (2007) Microglial GLT-1 is upregulated in response to herpes simplex virus infection to provide an antiviral defence via glutathione. Glia 55:1449–1458
Pines G, Danbolt NC, Bjoras M, Zhang Y, Bendahan A, Eide L, Koepsell H, Storm-Mathisen J, Seeberg E, Kanner BI (1992) Cloning and expression of a rat brain l-glutamate transporter. Nature 360:464–467
Pocock JM, Kettenmann H (2007) Neurotransmitter receptors on microglia. Trends Neurosci 30:527–535
Ponomarev ED, Maresz K, Tan Y, Dittel BN (2007) CNS-derived interleukin-4 is essential for the regulation of autoimmune inflammation and induces a state of alternative activation in microglial cells. J Neurosci 27:10714–10721
Porcheray F, Viaud S, Rimaniol AC, Leone C, Samah B, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Dormont D, Gras G (2005) Macrophage activation switching: an asset for the resolution of inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 142:481–489
Porcheray F, Leone C, Samah B, Rimaniol A-C, Dereuddre-Bosquet N and Gras G (2006) Glutamate metabolism in HIV-infected macrophages: implications for the CNS. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291
Raivich G (2005) Like cops on the beat: the active role of resting microglia. Trends Neurosci 28:571–573
Ransohoff RM, Perry VH (2009) Microglial physiology: unique stimuli, specialized responses. Annu Rev Immunol 27:119–145
Reichelt W, Stabel-Burow J, Pannicke T, Weichert H, Heinemann U (1997) The glutathione level of retinal Muller glial cells is dependent on the high-affinity sodium-dependent uptake of glutamate. Neuroscience 77:1213–1224
Riepe RE, Norenburg MD (1977) Muller cell localisation of glutamine synthetase in rat retina. Nature 268:654–655
Rimaniol AC, Haik S, Martin M, Le Grand R, Boussin FD, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Gras G, Dormont D (2000) Na+-dependent high-affinity glutamate transport in macrophages. J Immunol 164:5430–5438
Rimaniol AC, Mialocq P, Clayette P, Dormont D, Gras G (2001) Role of glutamate transporters in the regulation of glutathione levels in human macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1964–C1970
Rosenstiel P, Lucius R, Deuschl G, Sievers J, Wilms H (2001) From theory to therapy: implications from an in vitro model of ramified microglia. Microsc Res Tech 54:18–25
Rothman S (1984) Synaptic release of excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter mediates anoxic neuronal death. J Neurosci 4:1884–1891
Rothman SM (1985) The neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids is produced by passive chloride influx. J Neurosci 5:1483–1489
Rothstein JD, Martin L, Levey AI, Dykes-Hoberg M, Jin L, Wu D, Nash N, Kuncl RW (1994) Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13:713–725
Rothstein JD, Dykes-Hoberg M, Pardo CA, Bristol LA, Jin L, Kuncl RW, Kanai Y, Hediger MA, Wang Y, Schielke JP, Welty DF (1996) Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16:675–686
Rozyczka J, Figiel M, Engele J (2004) Endothelins negatively regulate glial glutamate transporter expression. Brain Pathol 14:406–414
Schmidtmayer J, Jacobsen C, Miksch G, Sievers J (1994) Blood monocytes and spleen macrophages differentiate into microglia-like cells on monolayers of astrocytes: membrane currents. Glia 12:259–267
Shaked I, Tchoresh D, Gersner R, Meiri G, Mordechai S, Xiao X, Hart RP, Schwartz M (2005) Protective autoimmunity: interferon-gamma enables microglia to remove glutamate without evoking inflammatory mediators. J Neurochem 92:997–1009
Sierra A, Gottfried-Blackmore A, Milner TA, McEwen BS, Bulloch K (2008) Steroid hormone receptor expression and function in microglia. Glia 56:659–674
Sievers J, Parwaresch R, Wottge HU (1994) Blood monocytes and spleen macrophages differentiate into microglia-like cells on monolayers of astrocytes: morphology. Glia 12:245–258
Sitcheran R, Gupta P, Fisher PB, Baldwin AS (2005) Positive and negative regulation of EAAT2 by NF-kappaB: a role for N-myc in TNFalpha-controlled repression. EMBO J 24:510–520
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N, Gordon S (1992) Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor activity: a marker of alternative immunologic macrophage activation. J Exp Med 176:287–292
Storck T, Schulte S, Hofmann K, Stoffel W (1992) Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10955–10959
Tacke F, Randolph GJ (2006) Migratory fate and differentiation of blood monocyte subsets. Immunobiology 211:609–618
Takahashi K, Prinz M, Stagi M, Chechneva O, Neumann H (2007) TREM2-transduced myeloid precursors mediate nervous tissue debris clearance and facilitate recovery in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS Med 4:e124
Takamori S, Rhee JS, Rosenmund C, Jahn R (2000) Identification of a vesicular glutamate transporter that defines a glutamatergic phenotype in neurons. Nature 407:189–194
Tanaka K (1993) Expression cloning of a rat glutamate transporter. Neurosci Res 16:149–153
Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, Yamada K, Watanabe M, Takahashi K, Iwama H, Nishikawa T, Ichihara N, Kikuchi T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hori S, Takimoto M, Wada K (1997) Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 276:1699–1702
Taylor DL, Diemel LT, Pocock JM (2003) Activation of microglial group III metabotropic glutamate receptors protects neurons against microglial neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 23:2150–2160
Vallat-Decouvelaere AV, Chretien F, Gras G, Le Pavec G, Dormont D, Gray F (2003) Expression of excitatory amino acid transporter-1 in brain macrophages and microglia of HIV-infected patients. A neuroprotective role for activated microglia? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:475–485
van Beek EM, Cochrane F, Barclay AN, van den Berg TK (2005) Signal regulatory proteins in the immune system. J Immunol 175:7781–7787
van Landeghem FK, Stover JF, Bechmann I, Bruck W, Unterberg A, Buhrer C, von Deimling A (2001) Early expression of glutamate transporter proteins in ramified microglia after controlled cortical impact injury in the rat. Glia 35:167–179
Varoqui H, Zhu H, Yao D, Ming H, Erickson JD (2000) Cloning and functional identification of a neuronal glutamine transporter. J Biol Chem 275:4049–4054
Vermeiren C, Najimi M, Vanhoutte N, Tilleux S, de Hemptinne I, Maloteaux JM, Hermans E (2005) Acute up-regulation of glutamate uptake mediated by mGluR5a in reactive astrocytes. J Neurochem 94:405–416
Vesce S, Bezzi P, Rossi D, Meldolesi J, Volterra A (1997) HIV-1 gp120 glycoprotein affects the astrocyte control of extracellular glutamate by both inhibiting the uptake and stimulating the release of the amino acid. FEBS Lett 411:107–109
Voutsinos-Porche B, Bonvento G, Tanaka K, Steiner P, Welker E, Chatton JY, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L (2003) Glial glutamate transporters mediate a functional metabolic crosstalk between neurons and astrocytes in the mouse developing cortex. Neuron 37:275–286
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Agency for Research against AIDS and Viral Hepatitis (ANRS) and the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM), as well as funding by the Atomic Energy Commission (CEA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gras, G., Samah, B., Hubert, A. et al. EAAT expression by macrophages and microglia: still more questions than answers. Amino Acids 42, 221–229 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0866-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0866-6