Abstract
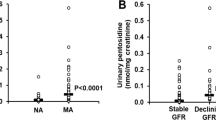
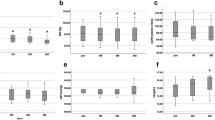
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of the angiotensin II receptor blocker Irbesartan on protein damage by glycation, oxidation and nitration in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. In a double-masked randomised crossover trial of 52 hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients, antihypertensive treatment was replaced with bendroflumethiazide. After 2-months wash-out, patients were treated randomly with Irbesartan 300, 600, and 900 mg o.d., each dose for 2 months in a three-way crossover study. Glycation, oxidation and nitration adduct residues in plasma protein and related urinary free adducts were determined by stable isotopic dilution analysis liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Treatment with Irbesartan decreased urinary excretion of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs)—methylglyoxal- and glyoxal-derived hydroimidazolones, MG-H1 and G-H1. Urinary AGEs were decreased by 30–32%. In plasma protein, treatment with Irbesartan increased content of glycation adducts N ε-fructosyl-lysine, AGEs N ε-carboxymethyl-lysine, N ε-carboxyethyl-lysine and pentosidine, and also increased content of oxidation markers N-formylkynurenine and dityrosine. This was attributed to decreased clearance of plasma protein modified by N ε-fructosyl-lysine and oxidative markers through the glomerular filter tightened by Irbesartan treatment. Treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes with Irbesartan decreased urinary excretion of MG-H1, G-H1 and 3-NT, which may result from decreased exposure to these AGEs. This is likely achieved by blocking angiotensin II signalling and related down-regulation of glyoxalase 1 and may contribute to health benefits of Irbesartan therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MU, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW (1986) Identification of Nε-carboxymethyl-lysine as a degradation product of fructoselysine in glycated protein. J Biol Chem 261:4889–4894
Ahmed N, Argirov OK, Minhas HS, Cordeiro CA, Thornalley PJ (2002) Assay of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs): surveying AGEs by chromatographic assay with derivatisation by aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccimidyl-carbamate and application to Nε-carboxymethyl-lysine- and Nε-(1-carboxyethyl)lysine-modified albumin. Biochem J 364:1–14
Ahmed N, Babaei-Jadidi R, Howell SK, Beisswenger PJ, Thornalley PJ (2005) Degradation products of proteins damaged by glycation, oxidation and nitration in clinical type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 48:1590–1603
American Diabetes Association (2009) Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2009. Diabetes Care 32:S13–S61
Busch M, Franke S, Wolf G, Rohde RD, Stein G (2008) Serum levels of the advanced glycation end products N-epsilon-carboxymethyllysine and pentosidine are not influenced by treatment with the angiotensin receptor II type 1 blocker irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy and hypertension. Nephron Clin Pract 108:C291–C297
Ceriello A, Assaloni R, Da Ros R, Maier A, Piconi L, Quagliaro L, Esposito K, Giugliano D (2005) Effect of atorvastatin and Irbesartan, alone and in combination, on postprandial endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients. Circulation 111:2518–2524
Cha T, Tahara Y, Yamoto E, Yoneda H, Ikegami H, Noma Y, Shima K, Ogihara T (1991) Renal handling of glycated albumin in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 12:149–156
Cohen RM, Holmes YR, Chenier TC, Joiner CH (2003) Discordance between HbA1c and fructosamine. Diabetes Care 26:163–167
Dobler D, Ahmed N, Song LJ, Eboigbodin KE, Thornalley PJ (2006) Increased dicarbonyl metabolism in endothelial cells in hyperglycemia induces anoikis and impairs angiogenesis by RGD and GFOGER motif modification. Diabetes 55:1961–1969
Dyer DG, Blackledge JA, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW (1991) Formation of pentosidine during nonenzymatic browning of protein by glucose: identification of glucose and other carbohydrates as possible precursors of pentosidine in vivo. J Biol Chem 266:11654–11660
Karachalias N, Babaei-Jadidi R, Rabbani N, Thornalley P (2010) Increased protein damage in renal glomeruli, retina, nerve, plasma and urine and its prevention by thiamine and benfotiamine therapy in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetologia 53:1506–1516
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I, The Collaborative Study Group (2001) Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist Irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 345:851–860
Miller AG, Tan G, Binger KJ, Pickering RJ, Thomas MC, Nagaraj RH, Cooper ME, Wilkinson-Berka JL (2010) Candesartan attenuates diabetic retinal vascular pathology by restoring glyoxalase 1 function. Diabetes 59:3208–3215
Ohshima H, Friesen M, Brouet I, Bartsch H (1990) Nitrotyrosine as a new marker for endogenous nitrosation and nitration of proteins. Food Chem Toxicol 28:647–652
Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P, The Irbesartan in Patients with Type (2001) The effect of Irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 345:870–878
Persson F, Rossing P, Hovind P, Stehouwer CDA, Schalkwijk C, Tarnow L, Parving HH (2006) Irbesartan treatment reduces biomarkers of inflammatory activity in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria—an IRMA substudy. Diabetes 55:3550–3555
Peters T (1996) All about albumin. Academic Press, New York
Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ (2008) Assay of 3-nitrotyrosine in tissues and body fluids by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection. Methods Enzymol 440:337–359
Rabbani N, Sebekova K, Sebekova K Jr, Heidland A, Thornalley PJ (2007) Protein glycation, oxidation and nitration free adduct accumulation after bilateral nephrectomy and ureteral ligation. Kidney Int 72:1113–1121
Remuzzi A, Perico N, Sangalli F, Vendramin G, Moriggi M, Ruggenenti P, Remuzzi G (1999) ACE inhibition and ANG II receptor blockade improve glomerular size-selectivity in IgA nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F457–F466
Rosca MG, Mustata TG, Kinter MT, Ozdemir AM, Kern TS, Szweda LI, Brownlee M, Monnier VM, Weiss MF (2005) Glycation of mitochondrial proteins from diabetic rat kidney is associated with excess superoxide formation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F420–F430
Rossing K, Schjoedt KJ, Jensen BR, Boomsma F, Parving HH (2005) Enhanced renoprotective effects of ultrahigh doses of irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Kidney Int 68:1190–1198
Sattarahmady N, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Ahmad F, Hakimelahi GH, Habibi-Rezaei M, Saboury AA, Sheibani N (2007) Formation of the molten globule-like state during prolonged glycation of human serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subjects 1770:933–942
Segal MS, Bihorac A, Koc M (2002) Circulating endothelial cells: tea leaves for renal disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F11–F19
Szwergold BS, Howell S, Beisswenger PJ (2001) Human fructosamine-3-kinase. Purification, sequencing, substrate specificity, and evidence of activity in vivo. Diabetes 50:2139–2147
Thornalley PJ (1993) The glyoxalase system in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med 14:287–371
Thornalley PJ (2005) Dicarbonyl intermediates in the Maillard reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1043:111–117
Thornalley PJ (2006) Quantitative screening of protein glycation, oxidation, and nitration adducts by LC––MS/MS: protein damage in diabetes, uremia, cirrhosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. In: Dalle-Donne I, Scaloni A, Butterfield DA (eds) Redox proteomics. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 681–728
Thornalley PJ, Langborg A, Minhas HS (1999) Formation of glyoxal, methylglyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in the glycation of proteins by glucose. Biochem J 344:109–116
Thornalley PJ, Battah S, Ahmed N, Karachalias N, Agalou S, Babaei-Jadidi R, Dawnay A (2003) Quantitative screening of advanced glycation endproducts in cellular and extracellular proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Biochem J 375:581–592
Westwood ME, Thornalley PJ (1995) Molecular characteristics of methylglyoxal-modified bovine and human serum albumins. Comparison with glucose-derived advanced glycation endproduct-modified serum albumins. J Prot Chem 14:359–372
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by 6th Framework Programme Priority 1, Life Sciences, Genomics and Biotechnology for Health, LSHM-CT-2005-018733, acronym PREDICTIONS (PREvention of DIabetic ComplicaTIONS) and by an unrestricted study grant from Sanofi-Aventis, who also provided the study medication. Peter Rossing has received research support from Novartis, and speakers honorarium from Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Boehringer Ingelheim, and MSD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabbani, N., Adaikalakoteswari, A., Rossing, K. et al. Effect of Irbesartan treatment on plasma and urinary markers of protein damage in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Amino Acids 42, 1627–1639 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0857-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0857-7