Abstract
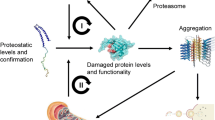
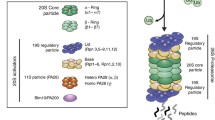
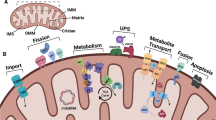
Protein damage, caused by radicals, is involved in many diseases and in the aging process. Therefore, it is crucial to understand how protein damage can be limited, repaired or removed. To degrade damaged proteins, several intracellular proteolytic systems exist. One of the most important contributors in intracellular protein degradation of oxidized, aggregated and misfolded proteins is the proteasomal system. The proteasome is not a simple, unregulated structure. It is a more complex proteolytic composition that undergoes diverse regulation in situations of oxidative stress, aging and pathology. In addition to that, numerous studies revealed that the proteasome activity is altered during life time, contributing to the aging process. In addition, in the nervous system, the proteasome plays an important role in maintaining neuronal protein homeostasis. However, alterations in the activity may have an impact on the onset of neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we discuss what is presently known about protein damage, the role of the proteasome in the degradation of damaged proteins and how the proteasome is regulated. Special emphasis was laid on the role of the proteasome in neurodegenerative diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer's disease
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- γ-IFN:
-
Interferon-gamma
- HD:
-
Huntington's disease
- HSP:
-
Heat shock protein
- MHC-I:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I
- PARP:
-
Poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PHF:
-
Tau-based paired helical filaments
- PD:
-
Parkinson's disease
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- UCH-L1:
-
Ubiquitin carboxyl terminal hydrolase L1
References
Anselmi B, Conconi M, Veyrat-Durebex C, Turlin E, Biville F, Alliot J, Friguet B (1998) Dietary self-selection can compensate an age-related decrease of rat liver 20 S proteasome activity observed with standard diet. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 53:B173–B179
Asher G, Bercovic Z, Tsvetkov P, Shaul Y, Kahana C (2005) 20S proteasomal degradation of ornithine decarboxylase is regulated by NQO1. Mol Cell 17:645–655
Avila J (2006) Tau phosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. FEBS Lett 580:2922–2927
Bajorek M, Glickman MH (2004) Keepers at the final gates: regulatory complexes and gating of the proteasome channel. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:1579–1588
Bajorek M, Finley D, Glickman MH (2003) Proteasome disassembly and downregulation is correlated with viability during stationary phase. Curr Biol 13:1140–1144
Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:205–214
Baugh JM, Pilipenko EV (2004) 20S proteasome differentially alters translation of different mRNAs via the cleavage of eIF4F and eIF3. Mol Cell 16:575–586
Beckman KB, Ames BN (1998) The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev 78:547–581
Beedholm R, Clark BF, Rattan SI (2004) Mild heat stress stimulates 20S proteasome and its 11S activator in human fibroblasts undergoing aging in vitro. Cell Stress Chaperones 9:49–57
Bennett EJ, Shaler TA, Woodman B, Ryu KY, Zaitseva TS, Becker CH, Bates GP, Schulman H, Kopito RR (2007) Global changes to the ubiquitin system in Huntington’s disease. Nature 448:704–708
Bercovich B, Stancovski H, Mayer A, Blumenfeld N, Laszlo A, Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (1997) Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of certain protein substrates in vitro requires the molecular chaperone Hsc70. J Biol Chem 272:9002–9010
Blickwedehl J, McEvoy S, Wong I, Kousis P, Clements J, Elliott R, Cresswell P, Liang P, Bangia N (2007) Proteasomes and proteasome activator 200 kDa (PA200) accumulate on chromatin in response to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 167:663–674
Bose S, Mason GG, Rivett AJ (1999) Phosphorylation of proteasomes in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Rep 26:11–14
Bossy-Wetzel E, Schwarzenbacher R, Lipton SA (2004) Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat Med 10 (Suppl):S2–S9
Breusing N, Grune T (2008) Regulation of proteasome-mediated protein degradation during oxidative stress and aging. Biol Chem 389:203–209
Bulteau AL, Petropoulos I, Friguet B (2000) Age-related alterations of proteasome structure and function in aging epidermis. Exp Gerontol 35:767–777
Butterfield DA, Boyd-Kimball D (2004) Proteomics analysis in Alzheimer’s disease: new insights into mechanisms of neurodegeneration. Int Rev Neurobiol 61:159–188
Castano JG, Mahillo E, Arizti P, Arribas J (1996) Phosphorylation of C8 and C9 subunits of the multicatalytic proteinase by casein kinase II and identification of the C8 phosphorylation sites by direct mutagenesis. Biochemistry 35:3782–3789
Castegna A, Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Thongboonkerd V, Klein JB, Pierce WM, Booze R, Markesbery WR, Butterfield DA (2002) Proteomic identification of oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Part I: creatine kinase BB, glutamine synthase, and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L-1. Free Radic Biol Med 33:562–571
Cecarini V, Bonfili L, Amici M, Angeletti M, Keller JN, Eleuteri AM (2008) Amyloid peptides in different assembly states and related effects on isolated and cellular proteasomes. Brain Res 1209:8–18
Chau KY, Ching HL, Schapira AH, Cooper JM (2009) Relationship between alpha synuclein phosphorylation, proteasomal inhibition and cell death: relevance to Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. J Neurochem 110:1005–1013
Choi J, Levey AI, Weintraub ST, Rees HD, Gearing M, Chin LS, Li L (2004) Oxidative modifications and down-regulation of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. J Biol Chem 279:13256–13264
Ciechanover A (1994) The ubiquitin–proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell 79:13–21
Ciechanover A, Brundin P (2003) The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron 40:427–446
Claverol S, Burlet-Schiltz O, Girbal-Neuhauser E, Gairin JE, Monsarrat B (2002) Mapping and structural dissection of human 20 S proteasome using proteomic approaches. Mol Cell Proteomics 1:567–578
Conconi M, Friguet B (1997) Proteasome inactivation upon aging and on oxidation-effect of HSP 90. Mol Biol Rep 24:45–50
Conconi M, Szweda LI, Levine RL, Stadtman ER, Friguet B (1996) Age-related decline of rat liver multicatalytic proteinase activity and protection from oxidative inactivation by heat-shock protein 90. Arch Biochem Biophys 331:232–240
Cookson MR, Menzies FM, Manning P, Eggett CJ, Figlewicz DA, McNeil CJ, Shaw PJ (2002) Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) mutations associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) affect cellular free radical release in the presence of oxidative stress. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 3:75–85
Coux O, Tanaka K, Goldberg AL (1996) Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu Rev Biochem 65:801–847
Croall DE, Ersfeld K (2007) The calpains: modular designs and functional diversity. Genome Biol 8:218
Davies KJ (1987) Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. I. General aspects. J Biol Chem 262:9895–9901
Davies KJ (1993) Protein modification by oxidants and the role of proteolytic enzymes. Biochem Soc Trans 21:346–353
Davies KJ (2001) Degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20S proteasome. Biochimie 83:301–310
Davies MJ (2003) Singlet oxygen-mediated damage to proteins and its consequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:761–770
Davies MJ (2005) The oxidative environment and protein damage. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:93–109
de Vrij FM, Fischer DF, van Leeuwen FW, Hol EM (2004) Protein quality control in Alzheimer’s disease by the ubiquitin proteasome system. Prog Neurobiol 74:249–270
Demasi M, Silva GM, Netto LE (2003) 20 S proteasome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is responsive to redox modifications and is S-glutathionylated. J Biol Chem 278:679–685
Deveraux Q, Ustrell V, Pickart C, Rechsteiner M (1994) A 26 S protease subunit that binds ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem 269:7059–7061
Ding Q, Keller JN (2001a) Proteasome inhibition in oxidative stress neurotoxicity: implications for heat shock proteins. J Neurochem 77:1010–1017
Ding Q, Keller JN (2001b) Proteasomes and proteasome inhibition in the central nervous system. Free Radic Biol Med 31:574–584
Dringen R, Gutterer JM, Hirrlinger J (2000) Glutathione metabolism in brain metabolic interaction between astrocytes and neurons in the defense against reactive oxygen species. Eur J Biochem 267:4912–4916
Emerit J, Edeas M, Bricaire F (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 58:39–46
Fein JA, Sokolow S, Miller CA, Vinters HV, Yang F, Cole GM, Gylys KH (2008) Co-localization of amyloid beta and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease synaptosomes. Am J Pathol 172:1683–1692
Fenteany G, Standaert RF, Lane WS, Choi S, Corey EJ, Schreiber SL (1995) Inhibition of proteasome activities and subunit-specific amino-terminal threonine modification by lactacystin. Science 268:726–731
Forster A, Masters EI, Whitby FG, Robinson H, Hill CP (2005) The 1.9 A structure of a proteasome-11S activator complex and implications for proteasome-PAN/PA700 interactions. Mol Cell 18:589–599
Friguet B, Szweda LI (1997) Inhibition of the multicatalytic proteinase (proteasome) by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal cross-linked protein. FEBS Lett 405:21–25
Fujiwara T, Tanaka K, Kumatori A, Shin S, Yoshimura T, Ichihara A, Tokunaga F, Aruga R, Iwanaga S, Kakizuka A (1989) Molecular cloning of cDNA for proteasomes (multicatalytic proteinase complexes) from rat liver: primary structure of the largest component (C2). Biochemistry 28:7332–7340
Gaczynska M, Osmulski PA, Gao Y, Post MJ, Simons M (2003) Proline- and arginine-rich peptides constitute a novel class of allosteric inhibitors of proteasome activity. Biochemistry 42:8663–8670
Gasser T (2009) Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev Mol Med 11:e22
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Goldberg AL, Cascio P, Saric T, Rock KL (2002) The importance of the proteasome and subsequent proteolytic steps in the generation of antigenic peptides. Mol Immunol 39:147–164
Gorbea C, Taillandier D, Rechsteiner M (1999) Assembly of the regulatory complex of the 26S proteasome. Mol Biol Rep 26:15–19
Groll M, Huber R (2003) Substrate access and processing by the 20S proteasome core particle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:606–616
Groll M, Huber R (2004) Inhibitors of the eukaryotic 20S proteasome core particle: a structural approach. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695:33–44
Groll M, Bajorek M, Kohler A, Moroder L, Rubin DM, Huber R, Glickman MH, Finley D (2000) A gated channel into the proteasome core particle. Nat Struct Biol 7:1062–1067
Groll M, Bochtler M, Brandstetter H, Clausen T, Huber R (2005) Molecular machines for protein degradation. Chembiochem 6:222–256
Grune T (2000) Oxidative stress, aging and the proteasomal system. Biogerontology 1:31–40
Grune T, Reinheckel T, Joshi M, Davies KJ (1995) Proteolysis in cultured liver epithelial cells during oxidative stress. Role of the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J Biol Chem 270:2344–2351
Grune T, Reinheckel T, Davies KJ (1996) Degradation of oxidized proteins in K562 human hematopoietic cells by proteasome. J Biol Chem 271:15504–15509
Grune T, Reinheckel T, Davies KJ (1997) Degradation of oxidized proteins in mammalian cells. FASEB J 11:526–534
Grune T, Klotz LO, Gieche J, Rudeck M, Sies H (2001) Protein oxidation and proteolysis by the nonradical oxidants singlet oxygen or peroxynitrite. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1243–1253
Grune T, Merker K, Sandig G, Davies KJ (2003) Selective degradation of oxidatively modified protein substrates by the proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:709–718
Grune T, Jung T, Merker K, Davies KJ (2004) Decreased proteolysis caused by protein aggregates, inclusion bodies, plaques, lipofuscin, ceroid, and ‘aggresomes’ during oxidative stress, aging, and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2519–2530
Guedes S, Vitorino R, Domingues R, Amado F, Domingues P (2009) Oxidation of bovine serum albumin: identification of oxidation products and structural modifications. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:2307–2315
Haass C, Pesold-Hurt B, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Kloetzel PM (1989) The PROS-35 gene encodes the 35 kd protein subunit of Drosophila melanogaster proteasome. EMBO J 8:2373–2379
Harding CV, France J, Song R, Farah JM, Chatterjee S, Iqbal M, Siman R (1995) Novel dipeptide aldehydes are proteasome inhibitors and block the MHC-I antigen-processing pathway. J Immunol 155:1767–1775
Harris JL, Alper PB, Li J, Rechsteiner M, Backes BJ (2001) Substrate specificity of the human proteasome. Chem Biol 8:1131–1141
Heinemeyer W, Trondle N, Albrecht G, Wolf DH (1994) PRE5 and PRE6, the last missing genes encoding 20S proteasome subunits from yeast? Indication for a set of 14 different subunits in the eukaryotic proteasome core. Biochemistry 33:12229–12237
Hernandez F, Engel T, Gomez-Ramos A, Perez M, Avila J (2005) Characterization of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by electron microscopy. Microsc Res Tech 67:121–125
Höhn A, Jung T, Grimm S, Grune T (2010) Lipofuscin-bound iron is a major intracellular source of oxidants: role in senescent cells. Free Radic Biol Med 48:1100–1108
Iwata A, Riley BE, Johnston JA, Kopito RR (2005) HDAC6 and microtubules are required for autophagic degradation of aggregated huntingtin. J Biol Chem 280:40282–40292
Jariel-Encontre I, Bossis G, Piechaczyk M (2008) Ubiquitin-independent degradation of proteins by the proteasome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1786:153–177
Jung T, Bader N, Grune T (2007) Oxidized proteins: intracellular distribution and recognition by the proteasome. Arch Biochem Biophys 462:231–237
Jung T, Catalgol B, Grune T (2009) The proteasomal system. Mol Aspects Med 30:191–296
Kabuta T, Wada K (2008) Insights into links between familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease: physical relationship between UCH-L1 variants and chaperone-mediated autophagy. Autophagy 4:827–829
Keck S, Nitsch R, Grune T, Ullrich O (2003) Proteasome inhibition by paired helical filament-tau in brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 85:115–122
Keller JN, Hanni KB, Markesbery WR (2000a) Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 75:436–439
Keller JN, Hanni KB, Markesbery WR (2000b) Possible involvement of proteasome inhibition in aging: implications for oxidative stress. Mech Ageing Dev 113:61–70
Keller JN, Gee J, Ding Q (2002) The proteasome in brain aging. Ageing Res Rev 1:279–293
Keller JN, Dimayuga E, Chen Q, Thorpe J, Gee J, Ding Q (2004) Autophagy, proteasomes, lipofuscin, and oxidative stress in the aging brain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2376–2391
Kirkin V, Lamark T, Sou YS, Bjorkoy G, Nunn JL, Bruun JA, Shvets E, McEwan DG, Clausen TH, Wild P, Bilusic I, Theurillat JP, Overvatn A, Ishii T, Elazar Z, Komatsu M, Dikic I, Johansen T (2009) A role for NBR1 in autophagosomal degradation of ubiquitinated substrates. Mol Cell 33:505–516
Kish SJ, Bergeron C, Rajput A, Dozic S, Mastrogiacomo F, Chang LJ, Wilson JM, DiStefano LM, Nobrega JN (1992) Brain cytochrome oxidase in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 59:776–779
Kisselev AF, Kaganovich D, Goldberg AL (2002) Binding of hydrophobic peptides to several non-catalytic sites promotes peptide hydrolysis by all active sites of 20 S proteasomes. Evidence for peptide-induced channel opening in the alpha-rings. J Biol Chem 277:22260–22270
Knecht E, Aguado C, Carcel J, Esteban I, Esteve JM, Ghislat G, Moruno JF, Vidal JM, Saez R (2009) Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian cells: recent developments. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2427–2443
Koegl M, Hoppe T, Schlenker S, Ulrich HD, Mayer TU, Jentsch S (1999) A novel ubiquitination factor, E4, is involved in multiubiquitin chain assembly. Cell 96:635–644
Kohno J, Koguchi Y, Nishio M, Nakao K, Kuroda M, Shimizu R, Ohnuki T, Komatsubara S (2000) Structures of TMC-95A-D: novel proteasome inhibitors from Apiospora montagnei sacc. TC 1093. J Org Chem 65:990–995
Kristiansen M, Deriziotis P, Dimcheff DE, Jackson GS, Ovaa H, Naumann H, Clarke AR, van Leeuwen FW, Menendez-Benito V, Dantuma NP, Portis JL, Collinge J, Tabrizi SJ (2007) Disease-associated prion protein oligomers inhibit the 26S proteasome. Mol Cell 26:175–188
Kwon YD, Nagy I, Adams PD, Baumeister W, Jap BK (2004) Crystal structures of the Rhodococcus proteasome with and without its pro-peptides: implications for the role of the pro-peptide in proteasome assembly. J Mol Biol 335:233–245
Kwon S, Zhang Y, Matthias P (2007) The deacetylase HDAC6 is a novel critical component of stress granules involved in the stress response. Genes Dev 21:3381–3394
Lam YA, Xu W, DeMartino GN, Cohen RE (1997) Editing of ubiquitin conjugates by an isopeptidase in the 26S proteasome. Nature 385:737–740
Lamark T, Johansen T (2009) Autophagy: links with the proteasome. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:192–198
Lasch P, Petras T, Ullrich O, Backmann J, Naumann D, Grune T (2001) Hydrogen peroxide induced structural alterations of RNase A. J Biol Chem 276:9492–9502
Lee DH, Goldberg AL (1996) Selective inhibitors of the proteasome-dependent and vacuolar pathways of protein degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 271:27280–27284
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y, Tang W, Wong E, Gao YS, Pandey UB, Kaushik S, Tresse E, Lu J, Taylor JP, Cuervo AM, Yao TP (2010) HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J 29:969–980
Levine RL (2002) Carbonyl modified proteins in cellular regulation, aging, and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32:790–796
Li X, DeMartino GN (2009) Variably modulated gating of the 26S proteasome by ATP and polyubiquitin. Biochem J 421:397–404
Liu Y, Fallon L, Lashuel HA, Liu Z, Lansbury PT Jr (2002) The UCH-L1 gene encodes two opposing enzymatic activities that affect alpha-synuclein degradation and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility. Cell 111:209–218
Loidl G, Musiol HJ, Groll M, Huber R, Moroder L (2000) Synthesis of bivalent inhibitors of eucaryotic proteasomes. J Pept Sci 6:36–46
Lopez SM, Morelli L, Castano EM, Soto EF, Pasquini JM (2000) Defective ubiquitination of cerebral proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 62:302–310
Lowe J, Stock D, Jap B, Zwickl P, Baumeister W, Huber R (1995) Crystal structure of the 20S proteasome from the archaeon T. acidophilum at 3.4 A resolution. Science 268:533–539
Luders J, Demand J, Hohfeld J (2000) The ubiquitin-related BAG-1 provides a link between the molecular chaperones Hsc70/Hsp70 and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 275:4613–4617
Ma CP, Slaughter CA, DeMartino GN (1992) Identification, purification, and characterization of a protein activator (PA28) of the 20 S proteasome (macropain). J Biol Chem 267:10515–10523
Mangold U, Hayakawa H, Coughlin M, Munger K, Zetter BR (2008) Antizyme, a mediator of ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation and its inhibitor localize to centrosomes and modulate centriole amplification. Oncogene 27:604–613
Mason GG, Hendil KB, Rivett AJ (1996) Phosphorylation of proteasomes in mammalian cells. Identification of two phosphorylated subunits and the effect of phosphorylation on activity. Eur J Biochem 238:453–462
Mason GG, Murray RZ, Pappin D, Rivett AJ (1998) Phosphorylation of ATPase subunits of the 26S proteasome. FEBS Lett 430:269–274
McNaught KS, Jnobaptiste R, Jackson T, Jengelley TA (2010) The pattern of neuronal loss and survival may reflect differential expression of proteasome activators in Parkinson’s disease. Synapse 64:241–250
Medicherla B, Goldberg AL (2008) Heat shock and oxygen radicals stimulate ubiquitin-dependent degradation mainly of newly synthesized proteins. J Cell Biol 182:663–673
Moore DJ (2006) Parkin: a multifaceted ubiquitin ligase. Biochem Soc Trans 34:749–753
Moorthy AK, Savinova OV, Ho JQ, Wang VY-F, Vu D, Gosh G (2006) The 20S proteasome processes NF-kappaB1 p105 into p50 in a translation-independent manner. EMBO J 25:1945–1956
Murakami Y, Matsufuji S, Hayashi S, Tanahashi N, Tanaka K (2000) Degradation of ornithine decarboxylase by the 26S proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:1–6
Naslund J, Haroutunian V, Mohs R, Davis KL, Davies P, Greengard P, Buxbaum JD (2000) Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid beta-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. JAMA 283:1571–1577
Nedelsky NB, Todd PK, Taylor JP (2008) Autophagy and the ubiquitin–proteasome system: collaborators in neuroprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782:691–699
Nickell S, Beck F, Scheres SH, Korinek A, Forster F, Lasker K, Mihalache O, Sun N, Nagy I, Sali A, Plitzko JM, Carazo JM, Mann M, Baumeister W (2009) Insights into the molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:11943–11947
Oh S, Hong HS, Hwang E, Sim HJ, Lee W, Shin SJ, Mook-Jung I (2005) Amyloid peptide attenuates the proteasome activity in neuronal cells. Mech Ageing Dev 126:1292–1299
Orenstein SJ, and Cuervo AM (2010) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: Molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance. Semin Cell Dev Biol
Pacifici RE, Kono Y, Davies KJ (1993) Hydrophobicity as the signal for selective degradation of hydroxyl radical-modified hemoglobin by the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J Biol Chem 268:15405–15411
Pandey UB, Nie Z, Batlevi Y, McCray BA, Ritson GP, Nedelsky NB, Schwartz SL, DiProspero NA, Knight MA, Schuldiner O, Padmanabhan R, Hild M, Berry DL, Garza D, Hubbert CC, Yao TP, Baehrecke EH, Taylor JP (2007) HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature 447:859–863
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A, Bruun JA, Outzen H, Overvatn A, Bjorkoy G, Johansen T (2007) p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem 282:24131–24145
Peters JM (1994) Proteasomes: protein degradation machines of the cell. Trends Biochem Sci 19:377–382
Petropoulos I, Conconi M, Wang X, Hoenel B, Bregegere F, Milner Y, Friguet B (2000) Increase of oxidatively modified protein is associated with a decrease of proteasome activity and content in aging epidermal cells. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 55:B220–B227
Pickart CM, Eddins MJ (2004) Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695:55–72
Pickart CM, Fushman D (2004) Polyubiquitin chains: polymeric protein signals. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:610–616
Powell SR, Davies KJ, Divald A (2007) Optimal determination of heart tissue 26S-proteasome activity requires maximal stimulating ATP concentrations. J Mol Cell Cardiol 42:265–269
Rabl J, Smith DM, Yu Y, Chang SC, Goldberg AL, Cheng Y (2008) Mechanism of gate opening in the 20S proteasome by the proteasomal ATPases. Mol Cell 30:360–368
Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S, Oroz LG, Scaravilli F, Easton DF, Duden R, O’Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2004) Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet 36:585–595
Rechsteiner M, Realini C, Ustrell V (2000) The proteasome activator 11 S REG (PA28) and class I antigen presentation. Biochem J 345(Pt 1):1–15
Reinheckel T, Sitte N, Ullrich O, Kuckelkorn U, Davies KJ, Grune T (1998) Comparative resistance of the 20S and 26S proteasome to oxidative stress. Biochem J 335(Pt 3):637–642
Reinheckel T, Grune T, Davies KJ (2000) The measurement of protein degradation in response to oxidative stress. Methods Mol Biol 99:49–60
Richly H, Rape M, Braun S, Rumpf S, Hoege C, Jentsch S (2005) A series of ubiquitin binding factors connects CDC48/p97 to substrate multiubiquitylation and proteasomal targeting. Cell 120:73–84
Rock KL, Goldberg AL (1999) Degradation of cell proteins and the generation of MHC class I-presented peptides. Annu Rev Immunol 17:739–779
Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, Clark K, Stein R, Dick L, Hwang D, Goldberg AL (1994) Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell 78:761–771
Rubinsztein DC (2006) The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature 443:780–786
Rydzewski RM, Burrill L, Mendonca R, Palmer JT, Rice M, Tahilramani R, Bass KE, Leung L, Gjerstad E, Janc JW, Pan L (2006) Optimization of subsite binding to the beta5 subunit of the human 20S proteasome using vinyl sulfones and 2-keto-1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles: syntheses and cellular properties of potent, selective proteasome inhibitors. J Med Chem 49:2953–2968
Savory PJ, Djaballah H, Angliker H, Shaw E, Rivett AJ (1993) Reaction of proteasomes with peptidylchloromethanes and peptidyldiazomethanes. Biochem J 296(Pt 3):601–605
Sdek P, Ying H, Chang DLF, Qiu W, Zhang H, Toultou R, Allday MJ, Xiao Z-XJ (2005) MDM2 promotes proteasome-dependent ubiquitin-independent degradation of retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell 20:699–708
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298:789–791
Shringarpure R, Davies KJ (2002) Protein turnover by the proteasome in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32:1084–1089
Shringarpure R, Grune T, Mehlhase J, Davies KJ (2003) Ubiquitin conjugation is not required for the degradation of oxidized proteins by proteasome. J Biol Chem 278:311–318
Sitte N, Huber M, Grune T, Ladhoff A, Doecke WD, von Zglinicki T, Davies KJ (2000) Proteasome inhibition by lipofuscin/ceroid during postmitotic aging of fibroblasts. FASEB J 14:1490–1498
Smith DM, Kafri G, Cheng Y, Ng D, Walz T, Goldberg AL (2005) ATP binding to PAN or the 26S ATPases causes association with the 20S proteasome, gate opening, and translocation of unfolded proteins. Mol Cell 20:687–698
Smith DM, Chang SC, Park S, Finley D, Cheng Y, Goldberg AL (2007) Docking of the proteasomal ATPases’ carboxyl termini in the 20S proteasome’s alpha ring opens the gate for substrate entry. Mol Cell 27:731–744
Soti C, Csermely P (2003) Aging and molecular chaperones. Exp Gerontol 38:1037–1040
Speese SD, Trotta N, Rodesch CK, Aravamudan B, Broadie K (2003) The ubiquitin proteasome system acutely regulates presynaptic protein turnover and synaptic efficacy. Curr Biol 13:899–910
Stadtman ER (1992) Protein oxidation and aging. Science 257:1220–1224
Stadtman ER, Levine RL (2000) Protein oxidation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 899:191–208
Stadtman ER, Levine RL (2003) Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 25:207–218
Sun F, Anantharam V, Zhang D, Latchoumycandane C, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2006) Proteasome inhibitor MG-132 induces dopaminergic degeneration in cell culture and animal models. Neurotoxicology 27:807–815
Tanahashi N, Murakami Y, Minami Y, Shimbara N, Hendil KB, Tanaka K (2000) Hybrid proteasomes. Induction by interferon-gamma and contribution to ATP-dependent proteolysis. J Biol Chem 275:14336–14345
Tanaka K, Kasahara M (1998) The MHC class I ligand-generating system: roles of immunoproteasomes and the interferon-gamma-inducible proteasome activator PA28. Immunol Rev 163:161–176
Tanaka K, Fujiwara T, Kumatori A, Shin S, Yoshimura T, Ichihara A, Tokunaga F, Aruga R, Iwanaga S, Kakizuka A (1990) Molecular cloning of cDNA for proteasomes from rat liver: primary structure of component C3 with a possible tyrosine phosphorylation site. Biochemistry 29:3777–3785
Unno M, Mizushima T, Morimoto Y, Tomisugi Y, Tanaka K, Yasuoka N, Tsukihara T (2002) Structure determination of the constitutive 20S proteasome from bovine liver at 2.75 A resolution. J Biochem 131:171–173
Upadhya SC, Hegde AN (2005) Ubiquitin–proteasome pathway components as therapeutic targets for CNS maladies. Curr Pharm Des 11:3807–3828
Ustrell V, Hoffman L, Pratt G, Rechsteiner M (2002) PA200, a nuclear proteasome activator involved in DNA repair. EMBO J 21:3516–3525
Verdoes M, Florea BI, van der Linden WA, Renou D, van den Nieuwendijk AM, van der Marel GA, Overkleeft HS (2007) Mixing of peptides and electrophilic traps gives rise to potent, broad-spectrum proteasome inhibitors. Org Biomol Chem 5:1416–1426
Verma R, Aravind L, Oania R, McDonald WH, Yates JR III, Koonin EV, Deshaies RJ (2002) Role of Rpn11 metalloprotease in deubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome. Science 298:611–615
Viteri G, Carrard G, Birlouez-Aragon I, Silva E, Friguet B (2004) Age-dependent protein modifications and declining proteasome activity in the human lens. Arch Biochem Biophys 427:197–203
Walters BJ, Campbell SL, Chen PC, Taylor AP, Schroeder DG, Dobrunz LE, Rtavanis-Tsakonas K, Ploegh HL, Wilson JA, Cox GA, Wilson SM (2008) Differential effects of Usp14 and Uch-L1 on the ubiquitin proteasome system and synaptic activity. Mol Cell Neurosci 39:539–548
Williams A, Jahreiss L, Sarkar S, Saiki S, Menzies FM, Ravikumar B, Rubinsztein DC (2006) Aggregate-prone proteins are cleared from the cytosol by autophagy: therapeutic implications. Curr Top Dev Biol 76:89–101
Yin DZ (1992) Lipofuscin-like fluorophores can result from reactions between oxidized ascorbic acid and glutamine. Carbonyl-protein cross-linking may represent a common reaction in oxygen radical and glycosylation-related ageing processes. Mech Ageing Dev 62:35–45
Yin D (1996) Biochemical basis of lipofuscin, ceroid, and age pigment-like fluorophores. Free Radic Biol Med 21:871–888
Zhang F, Su K, Yang X, Bowe DB, Paterson AJ, Kudlow JE (2003a) O-GlcNAc modification is an endogenous inhibitor of the proteasome. Cell 115:715–725
Zhang M, Pickart CM, Coffino P (2003b) Determinants of proteasome recognition of ornithine decarboxylase, a ubiquitin-independent substrate. EMBO J 22:1488–1496
Zhang M, MacDonald AI, Hoyt MA, Coffino P (2004) Proteasomes begin ornithine decarboxylase digestion at the C terminus. J Biol Chem 279:20959–20965
Zhang X, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Yong S, Salas-Burgos A, Koomen J, Olashaw N, Parsons JT, Yang XJ, Dent SR, Yao TP, Lane WS, Seto E (2007) HDAC6 modulates cell motility by altering the acetylation level of cortactin. Mol Cell 27:197–213
Zwickl P, Ng D, Woo K, Klenk H-P, Goldberg AL (1999) An archaebacterial ATPase, homologous to ATPases in the eukaryotic 26S proteasome, activates protein breakdown by 20S proteasomes. J Biol Chem 274(37):26008–26014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimm, S., Höhn, A. & Grune, T. Oxidative protein damage and the proteasome. Amino Acids 42, 23–38 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0646-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0646-8