Abstract
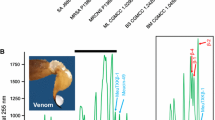
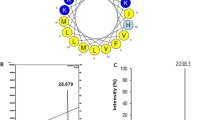
Two novel antimicrobial peptides, named halictines, were isolated from the venom of the eusocial bee Halictus sexcinctus. Their primary sequences were established by ESI-QTOF mass spectrometry, Edman degradation and enzymatic digestion as Gly-Met-Trp-Ser-Lys-Ile-Leu-Gly-His-Leu-Ile-Arg-NH2 (HAL-1), and Gly-Lys-Trp-Met-Ser-Leu-Leu-Lys–His-Ile-Leu-Lys-NH2 (HAL-2). Both peptides exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria but also noticeable hemolytic activity. The CD spectra of HAL-1 and HAL-2 measured in the presence of trifluoroethanol or SDS showed ability to form an amphipathic α-helical secondary structure in an anisotropic environment such as bacterial cell membrane. NMR spectra of HAL-1 and HAL-2 measured in trifluoroethanol/water confirmed formation of helical conformation in both peptides with a slightly higher helical propensity in HAL-1. Altogether, we prepared 51 of HAL-1 and HAL-2 analogs to study the effect of such structural parameters as cationicity, hydrophobicity, α-helicity, amphipathicity, and truncation on antimicrobial and hemolytic activities. The potentially most promising analogs in both series are those with increased net positive charge, in which the suitable amino acid residues were replaced by Lys. This improvement basically relates to the increase of antimicrobial activity against pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa and to the mitigation of hemolytic activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajesh K, Sreejith K (2009) Peptide antibiotics: an alternative and effective antimicrobial strategy to circumvent fungal infections. Peptides 30:999–1006
Backlund B-M, Wikander G, Peeters T, Graslund A (1994) Induction of secondary structure in the peptide hormone motilin by interaction with phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1190:337–344
Billeter M, Braun W, Wuthrich K (1982) Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Computation of sterically allowed proton-proton distance and statistical analysis of proton-proton distance in single crystal protein conformations. J Mol Biol 155:321–346
Biswas KM, DeVido DR, Dorsey JG (2003) Evaluation of methods for measuring amino acid hydrophobicities and interactions. J Chromatogr A 1000:637–655
Bütner K, Blondelle SE, Ostresh JM, Houghten RA (1992) Perturbation of peptide conformations induced in anisotropic environments. Biopolymers 32:575–583
Čeřovský V, Hovorka O, Cvačka J, Voburka Z, Bednárová L, Borovičková L, Slaninová J, Fučík V (2008a) Melectin: a novel antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the cleptoparasitic bee Melecta albifrons. ChemBioChem 9:2815–2821
Čeřovský V, Slaninová J, Fučík V, Hulačová H, Borovičková L, Ježek R, Bednárová L (2008b) New potent antimicrobial peptides from the venom of Polistinae wasps and their analogs. Peptides 29:992–1003
Čeřovský V, Buděšínský M, Hovorka O, Cvačka J, Voburka Z, Slaninová J, Borovičková L, Fučík V, Bednárová L, Votruba I, Straka J (2009) Lasioglossins: three novel antimicrobial peptides from the venom of the eusocial bee Lasioglossum laticeps (Hymenoptera: Halictidae). ChemBioChem 10:2089–2099
Chen Y, Mant CT, Farmer SW, Hancock REW, Vasil ML, Hodges RS (2005) Rational design of α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced activities and specificity/therapeutic index. J Biol Chem 280:12316–12329
Chen Y, Guarnieri MT, Vasil AI, Vasil ML, Mant CT, Hodges RS (2007) Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:1398–1406
Conlon JM, Al-Ghaferi N, Abraham B, Leprince J (2007) Strategies for transformation of naturally-occurring amphibian antimicrobial peptides into therapeutically valuable anti-infective agents. Methods 42:349–357
Cornut I, Büttner K, Dasseux J-L, Dufourcq J (1994) The amphipathic α-helical concept. Application to the de novo design of ideally amphipathic Leu, Lys peptides with hemolytic activity higher than that of melittin. FEBS Lett 349:29–33
Dennison SR, Wallace J, Harris F, Phoenix DA (2005) Amphiphilic α-helical antimicrobial peptides and their structure/function relationships. Prot Pept Lett 12:31–39
Dennison SR, Whittaker M, Hartus F, Phoenix DA (2006) Anticancer α-helical peptides and structure/function relationships underpinning their interactions with tumor cell membranes. Curr Protein Peptide Sci 7:487–499
Eisenberg D, Schwarz E, Komaromy M, Wall R (1984) Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol 179:125–142
Giuliani A, Pirri G, Nicoletto SF (2007) Antimicrobial peptides: an overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Cent Eur J Biol 2:1–33
Gordon YJ, Romanowski EG, McDermott AM (2005) A review of antimicrobial peptides and their therapeutical potential as anti-infective drugs. Curr Eye Res 30:505–515
Hultmark D, Steiner H, Rasmuson T, Boman HG (1980) Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bacterial proteins from haemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem 106:7–16
Jiang Z, Vasil AI, Hale JD, Hancock REW, Vasil ML, Hodges RS (2008) Effect of net charge and the number of positively charged residues on the biological activity of amphipathic α-helical cationic antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers (Peptide Science) 90:369–383
Konno K, Hisada M, Fontana R, Lorenzi CCB, Naoki H, Itagaki Y, Miwa A, Kawai N, Nakata Y, Yasuhara T, Neto JR, de Azevedo WF Jr, Palma MS, Nakajima T (2001) Anoplin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the solitary wasp Anoplius samariensis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1550:70–80
Konno K, Hisada M, Naoki H, Itagaki Y, Fontana R, Rangel M, Oliveira JS, Cabrera MPS, Neto JR, Hide I, Nakata Y, Yasuhara T, Nakajima T (2006) Eumenitin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the solitary eumenine wasp Eumenes rubronotatus. Peptides 27:2624–2631
Konno K, Rangel M, Oliveira JS, dos Santos Cabrera MP, Fontana R, Hirata IY, Hide I, Nakata Y, Mori K, Kawano M, Fuchino H, Sekita S, Neto JR (2007) Decoralin, a novel linear cationic α-helical peptide from the venom of the solitary eumenine wasps Oreumenes decoratus. Peptides 28:2320–2327
Kuhn-Nentwig L (2003) Antimicrobial and cytolytic peptides of venomous arthropods. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:2651–2668
Kuntz ID, Kosen PA, Craig EC (1991) Amide chemical shifts in many helices in peptides and protein are periodic. J Am Chem Soc 113:1406–1408
Lequin O, Ladram A, Chabbert L, Bruston F, Convert O, Vanhoye D, Chassaing G, Nicolas P, Amiche M (2006) Dermaseptin S9, an alpha/helical antimicrobial peptide with a hydrophobic core and cationic termini. Biochemistry 45:468–480
Merutka G, Dyson HJ, Wright PE (1995) “Random coil” 1H chemical shifts obtained as a function of temperature and trifluoroethanol concentration for the peptide series GGXGG. J Biomol NMR 5:14–24
Monincová L, Slaninová J, Voburka Z, Hovorka O, Fučík V, Borovičková L, Bednárová L, Buděšínský M, Straka J, Čeřovský V (2009) Novel biologically active peptides from the venom of the solitary bee Macropis fulvipes (Hymenoptera: Melittidae). In: Slaninová J (ed) Collection symposium series, vol 11, Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague 2009, pp 77–80
Oren Z, Shai Y (1997) Selective lysis of bacteria but not mammalian cells by dia-stereoisomers of mellitin: structure function study. Biochemistry 36:1826–1835
Oren Z, Shai Y (1998) Mode of action of linear amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers 47:451–463
Parisien A, Allain B, Zhang J, Mandeville R, Lan CQ (2008) Novel alternatives to antibiotics: bacteriophages, bacterial cell wall hydrolases, and antimicrobial peptides. J Appl Microb 104:1–13
Pathak N, Salas-Auvert R, Ruche G, Janna M-H, McCarthy D, Harrison RG (1995) Comparison of the effect of hydrophobicity, amphiphilicity, and α-helicity on the activities of antimicrobial peptides. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 22:182–186
Peschel A, Collins LV (2001) Staphylococcal resistance to antimicrobial peptides of mammalian and bacterial origin. Peptides 22:1651–1659
Rivas L, Luque-Ortega JR, Andreu D (2009) Amphibian antimicrobial peptides and protozoa: lessons from parasites. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:1570–1581
Rohl CA, Baldwin RL (1998) Deciphering rules of helix stability in peptides. Methods Enzymol 295:1–26
Schiffer M, Edmundson AB (1967) Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J 7:121–135
Selsted ME, Novotny MJ, Morris WL, Tang YQ, Smith W, Cullor JS (1992) Indolicidin, a novel bactericidal tridecapeptide amide from neutrophils. J Biol Chem 267:4292–4295
Shin SY, Lee S-H, Yang S-T, Park EJ, Lee DG, Lee MK, Eom SH, Song WK, Kim Y, Hahm K-S, Kim JI (2001) Antibacterial, antitumor and hemolytic activities of α-helical antibiotic peptide, P18 and its analogs. J Peptide Res 58:504–514
Sieprawska-Lupa M, Mydel P, Krawczyk K, Wojcik K, Puklo M, Lupa B, Suder P, Silberring J, Reed M, Pohl J, Shafer W, McAleese F, Foster T, Travis J, Potempa J (2004) Degradation of human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by Staphylococcus aureus-derived proteinases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:4673–4679
Souza BM, Mendes MA, Santos LD, Marques MR, César LMM, Almeida RNA, Pagnocca FC, Konno K, Palma MS (2005) Structural and functional characterization of two novel peptide toxins isolated from the venom of the social wasp Polybia paulista. Peptides 26:2157–2164
Suh J-Y, Lee K-H, Chi S-W, Hong S-Y, Choi B-W, Moon H-M, Choi B-S (1996) Unusually stable helical kink in the antimicrobial peptide—a derivative of gaegurin. FEBS Lett 392:309–312
Suh J-Y, Lee Y-T, Park C-B, Lee K-H, Kim S-C, Choi B-S (1999) Structural and functional implications of a proline residue in the antimicrobial peptide gaegurin. Eur J Biochem 266:665–674
Toke O (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: new candidates in the fight against bacterial infection. Biopolymers (Peptide Science) 80:717–735
Tossi A, Sandri L, Giangaspero A (2000) Amphipathic, α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers (Peptide Science) 55:4–30
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2009) APD2: the updated antimicrobial peptide database and its application in peptide design. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D933–D937
Wechselberger C (1998) Cloning of cDNA encoding new peptides of the dermaseptin-family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1388:279–283
Wieprecht T, Dathe M, Krause M, Beyermann M, Maloy WL, MacDonnald DL, Bienert M (1997) Modulation of membrane activity of amphipathic, antimicrobial peptides by slight modification of hydrophobic moment. FEBS Lett 417:135–140
Wishart DS, Nip AM (1998) Protein chemical shift analysis: a practical guide. Biochem Cell Biol 76:153–163
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) Chemical shifts as a tool for structure determination. Methods Enzymol 239:363–392
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharm Rev 55:27–55
Zaiou M (2007) Multifunctional antimicrobial peptides: therapeutic targets in several human diseases. J Mol Med 85:317–329
Zhou NE, Zhu B, Sykes BD, Hodges RS (1992) Relationship between amide proton chemical shifts and hydrogen bonding in amphipathic α-helical peptides. J Am Chem Soc 114:4320–4326
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation, Grant No. 203/08/0536, and by research project no. Z40550506 of the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. We thank our technical assistants Mrs. Hana Hulačová and Mrs. Jitka Čermáková for the help with peptide synthesis. We also thank Gale A. Kirking at English Editorial Services, S. R .O. for assistance with the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monincová, L., Buděšínský, M., Slaninová, J. et al. Novel antimicrobial peptides from the venom of the eusocial bee Halictus sexcinctus (Hymenoptera: Halictidae) and their analogs. Amino Acids 39, 763–775 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0519-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0519-1