Abstract
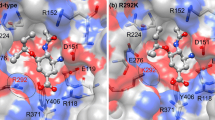
To predict the susceptibility of the probable 2009 influenza A (H1N1-2009) mutant strains to oseltamivir, MD/LIE approach was applied to oseltamivir complexed with the most frequent drug-resistant strains of neuraminidase subtypes N1 and N2: two mutations on the framework residues (N294S and H274Y) and the two others on the direct-binding residues (E119V and R292K) of oseltamivir. Relative to those of the wild type (WT), loss of drug–target interaction energies, especially in terms of electrostatic contributions and hydrogen bonds were dominantly established in the E119V and R292K mutated systems. The inhibitory potencies of oseltamivir towards the WT and mutants were predicted according to the ordering of binding-free energies: WT (−12.3 kcal mol−1) > N294S (−10.4 kcal mol−1) > H274Y (−9.8 kcal mol−1) > E119 V (−9.3 kcal mol−1) > R292K (−7.7 kcal mol−1), suggesting that the H1N1-2009 influenza with R292K substitution, perhaps, conferred a high level of oseltamivir resistance, while the other mutants revealed moderate resistance levels. This result calls for an urgent need to develop new potent anti-influenza agents against the next pandemic of potentially higher oseltamivir-resistant H1N1-2009 influenza.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed Y, Nehmé B, Baza M, Boivin G (2008) Activity of the neuraminidase inhibitor A-315675 against oseltamivir-resistant influenza neuraminidases of N1 and N2 subtypes. Antiviral Res 77:163–166
Åqvist J, Medina C, Samuelsson JE (1994) A new method for predicting binding affinity in computer-aided drug design. Protein Eng 7:385–391
Boivin G, Goyette N (2002) Susceptibility of recent Canadian influenza A and B virus isolates to different neuraminidase inhibitors. Antiviral Res 54:143–147
Case DA, Darden TA, Cheatham TE, Simmerling CL, Wang J, Duke RE, Luo R, Crowley M, Walker RC, Zhang W, Merz KM, Wang B, Hayik S, Roitberg A, Seabra G, Kolossváry I, Wong KF, Paesani F, Vanicek J, Wu X, Brozell SR, Steinbrecher T, Gohlke H, Yang L, Tan C, Mongan J, Hornak V, Cui G, Mathews DH, Seetin MG, Sagui C, Babin V, Kollman PA (2008) AMBER10 University of California San Francisco
Chachra R, Rizzo RC (2008) Origins of resistance conferred by the R292K neuraminidase mutation via molecular dynamics and free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 4:1526–1540
Collins PJ, Haire LF, Lin YP, Liu J, Russell RJ, Walker PA, Skehel JJ, Martin SR, Hay AJ, Gamblin SJ (2008) Crystal structures of oseltamivir-resistant influenza virus neuraminidase mutants. Nature 453:1258–1261
Ferraris O, Lina B (2008) Mutations of neuraminidase implicated in neuraminidase inhibitors resistance. J Clin Virol 41:13–19
Hansson T, Marelius J, Åqvist JJ (1998) Ligand binding affinity prediction by linear interaction energy methods. J Comput Aided Mol Des 12:27–35
King G, Warshel A (1989) A surface constrained all-atom solvent model for effective simulations of polar solutions. J Chem Phys 91:3647–3661
Malaisree M, Rungrotmongkol T, Decha P, Intharathep P, Aruksakunwong O, Hannongbua S (2008) Understanding of known drug-target interactions in the catalytic pocket of neuraminidase subtype N1. Proteins 71:1908–1918
Malaisree M, Rungrotmongkol T, Nunthaboot N, Aruksakunwong O, Intharathep P, Decha P, Sompornpisut P, Hannongbua S (2009) Source of oseltamivir resistance in avian influenza H5N1 virus with the H274Y mutation. Amino Acids 37:725–732
Marelius J, Kolmodin K, Feierberg I, Åqvist J (1998) Q: a molecular dynamics program for free energy calculations and empirical valence bond simulations in biomolecular systems. J Mol Graph Model 16:213–225
Mishin VP, Hayden FG, Gubareva LV (2005) Susceptibilities of antiviral-resistant influenza viruses to novel neuraminidase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4515–4520
Rungrotmongkol T, Intharathep P, Malaisree M, Nunthaboot N, Kaiyawet N, Sompornpisut P, Payungporn S, Poovorawan Y, Hannongbua S (2009a) Susceptibility of antiviral drugs against 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385:390–394
Rungrotmongkol T, Udommaneethanakit T, Malaisree M, Nunthaboot N, Intharathep P, Sompornpisut P, Hannongbua S (2009b) How does each substituent functional group of oseltamivir lose its activity against virulent H5N1 influenza mutants? Biophys Chem 145:29–36
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the Cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23:327–341
Wall ID, Leach AR, Salt DW, Ford MG, Essex JW (1999) Binding constants of neuraminidase inhibitors: an investigation of the linear interaction energy method. J Med Chem 42:5142–5152
Wang NX, Zheng JJ (2009) Computational studies of H5N1 influenza virus resistance to oseltamivir. Protein Sci 18:707–715
Yen HL, Herlocher LM, Hoffmann E, Matrosovich MN, Monto AS, Webster RG, Govorkova EA (2005) Neuraminidase inhibitor-resistant influenza viruses may differ substantially in fitness and transmissibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4075–4084
Yen HL, Ilyushina NA, Salomon R, Hoffmann E, Webster RG, Govorkova EA (2007) Neuraminidase inhibitor-resistant recombinant A/Vietnam/1203/04 (H5N1) influenza viruses retain their replication efficiency and pathogenicity in vitro and in vivo. J Virol 81:12418–12426
Zürcher T, Yates PJ, Daly J, Sahasrabudhe A, Walters M, Dash L, Tisdale M, McKimm-Breschkin JL (2006) Mutations conferring zanamivir resistance in human influenza virus N2 neuraminidases compromise virus fitness and are not stably maintained in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:723–732
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF). T.R. thanks the TRF Grant for New Research (Grant No. TRG5280035) and M.M. thanks the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program (Grant No. 3.C.CU/48/F.1) from the TRF. T.R. also thanks the Post-Doctoral Program from the Commission on Higher Education. The Computational Chemistry Unit Cell, Chulalongkorn University, provided the computing facilities. The Center of Excellence for Petroleum, Petrochemicals, and Advanced Materials, Chulalongkorn University, is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Rungrotmongkol and M. Malaisree have equally contributed to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rungrotmongkol, T., Malaisree, M., Nunthaboot, N. et al. Molecular prediction of oseltamivir efficiency against probable influenza A (H1N1-2009) mutants: molecular modeling approach. Amino Acids 39, 393–398 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0452-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0452-3