Abstract
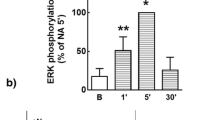
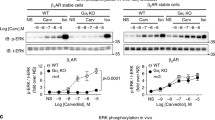
β-Adrenergic receptors can activate extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) via different mechanisms. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism of β1-adrenergic receptor (β1AR)-mediated ERK activation in African green monkey kidney COS-7 cells. Treatment of cells with isoproterenol (ISO), a β1AR selective agonist, induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in a dose-dependent manner. ISO-stimulated ERK phosphorylation was not influenced by the Gβγ inhibitor, βAR kinase carboxyl terminal (βARKct) or by the Gi inhibitor, pertussis toxin (PTX), but it was clearly abolished via inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA) with H89, or of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK1) with PD98059, revealing that the Gαs subunit is involved in ERK regulation through the PKA/MEK1 pathway. We also tested the effect of the adenylate cyclase activator forskolin on ERK activation, and the result was identical to that of ISO stimulation. Moreover, pretreatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 or with the Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP2 did not affect ERK activation. These observations suggest a mechanism of β1AR-mediated ERK activity that involves the Gαs subunit, but not EGFR or Src tyrosine kinase.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COS-7:
-
African green monkey kidney cells
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- ISO:
-
Isoproterenol
- β1AR:
-
β1-Adrenergic receptor
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- G protein:
-
GTP binding regulatory protein
- MAP:
-
Mitogen-activated protein
- ERK:
-
The mitogen-activated protein kinases extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- βARK:
-
β-Adrenergic receptor kinase
- CT:
-
Carboxyl terminal
- FSK:
-
Forskolin
- AC:
-
Adenylate cyclase
- PTX:
-
Pertussis toxin
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic AMP
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- H89:
-
N-[2-((p-bromocinnamyl)amino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide
- PP2:
-
4-Amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl) pyrazolo [3,4-d]pyrimidine
- MEK1:
-
Mitogen-activated ERK kinase 1
- PD98059:
-
2-(2-Amino-3-methoxyphenol)-oxanaphthalen-4-one
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- AG1478:
-
2-(2-Amino-3-methoxyphenyl)-oxanaphthalen-4-one, and 4-(3-chloroanilino)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density-95
- MAGI-2:
-
Membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted-2
- CNrasGEF:
-
cAMP-dependent guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- GIPC:
-
GAIP-interacting protein carboxyl terminus
- CAL:
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-associated ligand
- MAGUK:
-
Membrane-associated guanylate kinase
References
Ahmet I, Lakatta EG, Talan MI (2005) Pharmacological stimulation of beta2-adrenergic receptors (beta2AR) enhances therapeutic effectiveness of beta1AR blockade in rodent dilated ischemic cardiomyopathy. Heart Fail Rev 10:289–296. doi:10.1007/s10741-005-7543-3
Bristow MR (1997) Mechanism of action of beta-blocking agents in heart failure. Am J Cardiol 80:26L–40L. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(97)00846-1
Brodde OE (1991) Beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in the human heart: properties, function, and alterations in chronic heart failure. Pharmacol Rev 43:203–242
Cao W, Luttrell LM, Medvedev AV, Pierce KL, Daniel KW, Dixon TM, Lefkowitz RJ, Collins S (2000) Direct binding of activated c-Src to the beta 3-adrenergic receptor is required for MAP kinase activation. J Biol Chem 275:38131–38134. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000592200
Chaudhry A, MacKenzie RG, Georgic LM, Granneman JG (1994) Differential interaction of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenergic receptors with Gi in rat adipocytes. Cell Signal 6:457–465. doi:10.1016/0898-6568(94)90093-0
Cheon MS, Bajo M, Kim SH, Claudio JO, Stewart AK, Patterson D, Kruger WD, Kondoh H, Lubec G (2003) Protein levels of genes encoded on chromosome 21 in fetal Down syndrome brain: challenging the gene dosage effect hypothesis (Part II). Amino Acids 24:119–125
Chesley A, Lundberg MS, Asai T, Xiao RP, Ohtani S, Lakatta EG, Crow MT (2000) The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor delivers an antiapoptotic signal to cardiac myocytes through G(i)-dependent coupling to phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase. Circ Res 87:1172–1179
Communal C, Colucci WS, Singh K (2000) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway protects adult rat ventricular myocytes against beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated apoptosis. Evidence for Gi-dependent activation. J Biol Chem 275:19395–19400. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910471199
Crespo P, Cachero TG, Xu N, Gutkind JS (1995) Dual effect of beta-adrenergic receptors on mitogen-activated protein kinase. Evidence for a beta gamma-dependent activation and a G alpha s-cAMP-mediated inhibition. J Biol Chem 270:25259–25265. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.42.25259
Daaka Y, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ (1997) Switching of the coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to different G proteins by protein kinase A. Nature 390:88–91. doi:10.1038/36362
Daaka Y, Luttrell LM, Ahn S, Della Rocca GJ, Ferguson SS, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1998) Essential role for G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 273:685–688. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.2.685
de Groote P, Lamblin N, Helbecque N, Mouquet F, Mc Fadden E, Hermant X, Amouyel P, Dallongeville J, Bauters C (2005) The impact of beta-adrenoreceptor gene polymorphisms on survival in patients with congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7:966–973. doi:10.1016/j.ejheart.2004.10.006
Flamigni F, Stanic I, Facchini A, Cetrullo S, Tantini B, Borzi RM, Guarnieri C, Caldarera CM (2007) Polyamine biosynthesis as a target to inhibit apoptosis of non-tumoral cells. Amino Acids 33:197–202. doi:10.1007/s00726-007-0514-3
Galandrin S, Bouvier M (2006) Distinct signaling profiles of beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptor ligands toward adenylyl cyclase and mitogen-activated protein kinase reveals the pluridimensionality of efficacy. Mol Pharmacol 70:1575–1584. doi:10.1124/mol.106.026716
Galandrin S, Oligny-Longpre G, Bonin H, Ogawa K, Gales C, Bouvier M (2008) Conformational rearrangements and signaling cascades involved in ligand-biased mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling through the beta1-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol 74:162–172. doi:10.1124/mol.107.043893
Gauthier C, Tavernier G, Charpentier F, Langin D, Le Marec H (1996) Functional beta3-adrenoceptor in the human heart. J Clin Invest 98:556–562. doi:10.1172/JCI118823
Gesty-Palmer D, Chen M, Reiter E, Ahn S, Nelson CD, Wang S, Eckhardt AE, Cowan CL, Spurney RF, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ (2006) Distinct beta-arrestin- and G protein-dependent pathways for parathyroid hormone receptor-stimulated ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem 281:10856–10864. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513380200
Ghanouni P, Steenhuis JJ, Farrens DL, Kobilka BK (2001) Agonist-induced conformational changes in the G-protein-coupling domain of the beta 2 adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5997–6002. doi:10.1073/pnas.101126198
Granier S, Kim S, Shafer AM, Ratnala VR, Fung JJ, Zare RN, Kobilka B (2007) Structure and conformational changes in the C-terminal domain of the beta2-adrenoceptor: insights from fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies. J Biol Chem 282:13895–13905. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611904200
Green SA, Liggett SB (1994) A proline-rich region of the third intracellular loop imparts phenotypic beta 1-versus beta 2-adrenergic receptor coupling and sequestration. J Biol Chem 269:26215–26219
He J, Bellini M, Xu J, Castleberry AM, Hall RA (2004) Interaction with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-associated ligand (CAL) inhibits beta1-adrenergic receptor surface expression. J Biol Chem 279:50190–50196. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404876200
He J, Bellini M, Inuzuka H, Xu J, Xiong Y, Yang X, Castleberry AM, Hall RA (2006) Proteomic analysis of beta1-adrenergic receptor interactions with PDZ scaffold proteins. J Biol Chem 281:2820–2827. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509503200
Hu LA, Tang Y, Miller WE, Cong M, Lau AG, Lefkowitz RJ, Hall RA (2000) Beta 1-adrenergic receptor association with PSD-95. Inhibition of receptor internalization and facilitation of beta 1-adrenergic receptor interaction with N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem 275:38659–38666. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005938200
Hu LA, Chen W, Premont RT, Cong M, Lefkowitz RJ (2002) G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 regulates beta 1-adrenergic receptor association with PSD-95. J Biol Chem 277:1607–1613. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107297200
Hu LA, Chen W, Martin NP, Whalen EJ, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ (2003) GIPC interacts with the beta1-adrenergic receptor and regulates beta1-adrenergic receptor-mediated ERK activation. J Biol Chem 278:26295–26301. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212352200
Hung AY, Sheng M (2002) PDZ domains: structural modules for protein complex assembly. J Biol Chem 277:5699–5702. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100065200
Jans DA, Pavo I (1995) A mechanistic role for polypeptide hormone-receptor lateral mobility in signal-transduction. Amino Acids 9:93–109
Kenakin T (1995) Agonist-receptor efficacy. II. Agonist trafficking of receptor signals. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:232–238. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)89032-X
Kilts JD, Gerhardt MA, Richardson MD, Sreeram G, Mackensen GB, Grocott HP, White WD, Davis RD, Newman MF, Reves JG, Schwinn DA, Kwatra MM (2000) Beta(2)-adrenergic and several other G protein-coupled receptors in human atrial membranes activate both G(s) and G(i). Circ Res 87:705–709
Kim IM, Tilley DG, Chen J, Salazar NC, Whalen EJ, Violin JD, Rockman HA (2008) Beta-blockers alprenolol and carvedilol stimulate beta-arrestin-mediated EGFR transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14555–14560. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804745105
Kobayashi H, Narita Y, Nishida M, Kurose H (2005) Beta-arrestin2 enhances beta2-adrenergic receptor-mediated nuclear translocation of ERK. Cell Signal 17:1248–1253. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.12.014
Kursula P (2008) Structural properties of proteins specific to the myelin sheath. Amino Acids 34:175–185. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0479-7
Lavoie C, Mercier JF, Salahpour A, Umapathy D, Breit A, Villeneuve LR, Zhu WZ, Xiao RP, Lakatta EG, Bouvier M, Hebert TE (2002) Beta 1/beta 2-adrenergic receptor heterodimerization regulates beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization and ERK signaling efficacy. J Biol Chem 277:35402–35410. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204163200
Lazou A, Bogoyevitch MA, Clerk A, Fuller SJ, Marshall CJ, Sugden PH (1994) Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in adult rat heart preparations in vitro. Circ Res 75:932–941
Lumbreras M, Baamonde C, Martinez-Cue C, Lubec G, Cairns N, Salles J, Dierssen M, Florez J (2006) Brain G protein-dependent signaling pathways in Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Amino Acids 31:449–456. doi:10.1007/s00726-005-0272-z
Luttrell LM (2002) Activation and targeting of mitogen-activated protein kinases by G-protein-coupled receptors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80:375–382. doi:10.1139/y02-045
Luttrell LM, van Biesen T, Hawes BE, Koch WJ, Krueger KM, Touhara K, Lefkowitz RJ (1997) G-protein-coupled receptors and their regulation: activation of the MAP kinase signaling pathway by G-protein-coupled receptors. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res 31:263–277
Luttrell LM, Ferguson SS, Daaka Y, Miller WE, Maudsley S, Della Rocca GJ, Lin F, Kawakatsu H, Owada K, Luttrell DK, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1999) Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283:655–661. doi:10.1126/science.283.5402.655
Martin NP, Whalen EJ, Zamah MA, Pierce KL, Lefkowitz RJ (2004) PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the beta1-adrenergic receptor promotes Gs/Gi switching. Cell Signal 16:1397–1403. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.05.002
Massey KA, Blakeslee CH, Pitkow HS (1998) A review of physiological and metabolic effects of essential amino acids. Amino Acids 14:271–300. doi:10.1007/BF01318848
Maudsley S, Pierce KL, Zamah AM, Miller WE, Ahn S, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ, Luttrell LM (2000) The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via assembly of a multi-receptor complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 275:9572–9580. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9572
Molkentin JD, Dorn IGII (2001) Cytoplasmic signaling pathways that regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol 63:391–426. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.391
Pak Y, Pham N, Rotin D (2002) Direct binding of the beta1 adrenergic receptor to the cyclic AMP-dependent guanine nucleotide exchange factor CNrasGEF leads to Ras activation. Mol Cell Biol 22:7942–7952. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.22.7942-7952.2002
Pierce KL, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ (2001) New mechanisms in heptahelical receptor signaling to mitogen activated protein kinase cascades. Oncogene 20:1532–1539. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204184
Robidoux J, Kumar N, Daniel KW, Moukdar F, Cyr M, Medvedev AV, Collins S (2006) Maximal beta3-adrenergic regulation of lipolysis involves Src and epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem 281:37794–37802. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605572200
Shiina T, Kawasaki A, Nagao T, Kurose H (2000) Interaction with beta-arrestin determines the difference in internalization behavior between beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem 275:29082–29090. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909757199
Soeder KJ, Snedden SK, Cao W, Della Rocca GJ, Daniel KW, Luttrell LM, Collins S (1999) The beta3-adrenergic receptor activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in adipocytes through a Gi-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 274:12017–12022. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.17.12017
Spear JF, Prabu SK, Galati D, Raza H, Anandatheerthavarada HK, Avadhani NG (2007) Beta1-adrenoreceptor activation contributes to ischemia–reperfusion damage as well as playing a role in ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H2459–H2466. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00459.2006
Steinberg SF (1999) The molecular basis for distinct beta-adrenergic receptor subtype actions in cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 85:1101–1111
Suzuki T, Nguyen CT, Nantel F, Bonin H, Valiquette M, Frielle T, Bouvier M (1992) Distinct regulation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Mol Pharmacol 41:542–548
Swaminath G, Deupi X, Lee TW, Zhu W, Thian FS, Kobilka TS, Kobilka B (2005) Probing the beta2 adrenoceptor binding site with catechol reveals differences in binding and activation by agonists and partial agonists. J Biol Chem 280:22165–22171. doi:10.1074/jbc.M502352200
Takeishi Y, Huang Q, Abe J, Che W, Lee JD, Kawakatsu H, Hoit BD, Berk BC, Walsh RA (2002) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in failing human hearts with dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 53:131–137. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00438-2
Tang Y, Hu LA, Miller WE, Ringstad N, Hall RA, Pitcher JA, DeCamilli P, Lefkowitz RJ (1999) Identification of the endophilins (SH3p4/p8/p13) as novel binding partners for the beta1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12559–12564. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.22.12559
Tutor AS, Penela P, Mayor F Jr (2007) Anti-beta1-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies are potent stimulators of the ERK1/2 pathway in cardiac cells. Cardiovasc Res 76:51–60. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.05.022
Wang YC, Bachrach U (2002) The specific anti-cancer activity of green tea (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Amino Acids 22:131–143. doi:10.1007/s007260200002
Wisler JW, DeWire SM, Whalen EJ, Violin JD, Drake MT, Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ (2007) A unique mechanism of beta-blocker action: carvedilol stimulates beta-arrestin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16657–16662. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707936104
Xiao RP (2001) Beta-adrenergic signaling in the heart: dual coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to G(s) and G(i) proteins. Sci STKE 2001:RE15. doi:10.1126/stke.2001.104.re15
Xiao RP, Cheng H, Zhou YY, Kuschel M, Lakatta EG (1999) Recent advances in cardiac beta(2)-adrenergic signal transduction. Circ Res 85:1092–1100
Xiao RP, Zhu W, Zheng M, Cao C, Zhang Y, Lakatta EG, Han Q (2006) Subtype-specific alpha1- and beta-adrenoceptor signaling in the heart. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:330–337. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2006.04.009
Xu J, Paquet M, Lau AG, Wood JD, Ross CA, Hall RA (2001) Beta 1-adrenergic receptor association with the synaptic scaffolding protein membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted-2 (MAGI-2). Differential regulation of receptor internalization by MAGI-2 and PSD-95. J Biol Chem 276:41310–41317. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107480200
Yanagawa B, Nagaya N (2007) Adrenomedullin: molecular mechanisms and its role in cardiac disease. Amino Acids 32:157–164. doi:10.1007/s00726-005-0279-5
Yuan LQ, Lu Y, Luo XH, Xie H, Wu XP, Liao EY (2007) Taurine promotes connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) expression in osteoblasts through the ERK signal pathway. Amino Acids 32:425–430. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0380-4
Zou Y, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, Kudoh S, Uozumi H, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y (1999) Both Gs and Gi proteins are critically involved in isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 274:9760–9770. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9760
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (No: 30572183 and 30772573), the New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (NCET-06-0184), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20060025011), Foundation of Beijing Educational Committee (KZ200610025013), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No: 7082009) and Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China awarded to J. He, and fund for Excellent Talents in Beijing (20071D0501800253) awarded to JF Zheng. The manuscript correction of Julius Paul Pradeep John is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Zheng and H. Shen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J., Shen, H., Xiong, Y. et al. The β1-adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via Gαs. Amino Acids 38, 75–84 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0207-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0207-6