Abstract
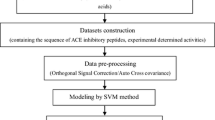
On the basis of exploratory factor analysis, six multidimensional patterns of 516 amino acid attributes, namely, factor analysis scales of generalized amino acid information (FASGAI) involving hydrophobicity, alpha and turn propensities, bulky properties, compositional characteristics, local flexibility and electronic properties, are proposed to represent structures of 48 bitter-tasting dipeptides and 58 angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Characteristic parameters related to bioactivities of the peptides studied are selected by genetic algorithm, and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) models are constructed by partial least square (PLS). Our results by a leave-one-out cross validation are compared with the previously known structure representation method and are shown to give slightly superior or comparative performance. Further, two data sets are divided into training sets and test sets to validate the characterization repertoire of FASGAI. Performance of the PLS models developed by training samples by a leave-one-out cross validation and external validation for test samples are satisfying. These results demonstrate that FASGAI is an effective representation technique of peptide structures, and that FASGAI vectors have many preponderant characteristics such as straightforward physicochemical information, high characterization competence and easy manipulation. They can be further applied to investigate the relationship between structures and functions of various peptides, even proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FASGAI:
-
Factor analysis scales of generalized amino acid information
- QSAR:
-
Quantitative structure–activity relationship
- PLS:
-
Partial least squares
- GA-PLS:
-
Genetic algorithm-partial least square
- BTD:
-
Bitter-tasting dipeptide
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
References
Agüero-Chapín G, Gonzalez-Díaz H, de la Riva G, Rodríguez E, Sanchez-Rodríguez A, Podda G, Vazquez-Padrón RI (2008) MMM-QSAR recognition of ribonucleases without alignment: comparison with an HMM model and isolation from Schizosaccharomyces pombe, prediction, and experimental assay of a new sequence. J Chem Inf Model 48:434–448
Agüero-Chapin G, González-Díaz H, Molina R, Varona-Santos J, Uriarte E, González-Díaz Y (2006) Novel 2D maps and coupling numbers for protein sequences: the first QSAR study of polygalacturonases; isolation and prediction of a novel sequence from Psidium guajava L. FEBS Lett 580:723–730
Andersson PM, Sjostrom M, Lundstedt T (1998) Preprocessing peptide sequences for multivariate sequence-property analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 42:41–50
Anfinsen CΒ (1973) Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science 181:223–230
Cocchi M, Johansson E (1993) Amino acids characterization by GRID and multivariate data analysis. Quant Struct Act Relat 12:1–8
Collantes ER, Dunn WJIII (1995) Amino acid side chain descriptors for quantitative structure–activity relationship studies of peptide analogues. J Med Chem 38:2705–2713
Crackower MA, Sarao R, Oudit GY, Yagil C, Kozieradzki I, Scanga SE, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, da Costa J, Zhang L, Pei Y, Scholey J, Ferrario CM, Manoukian AS, Chappell MC, Backx PH, Yagil Y, Penninger JM (2002) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 417:822–828
Fauchere JL, Charton M, Kier LB, Verloop A, Pliska V (1988) Amino acid side chain parameters for correlation studies in biology and pharmacology. Int J Pept Protein Res 32:269–278
Felipe-Sotelo M, Andrade JM, Carlosena A, Prada D (2003) Partial least squares multivariate regression as an alternative to handle interferences of Fe on the determination of trace Cr in water by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chem 75:5254–5261
Field A (2005) Discovering statistics using SPSS, 2nd edn. Sage, London
González-Díaz H, Uriarte E (2005) Proteins QSAR with Markov average electrostatic potentials. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:5088–5094
González-Díaz H, Molina R, Uriarte E (2005) Recognition of stable protein mutants with 3D stochastic average electrostatic potentials. FEBS Lett 579:4297–4301
González-Díaz H, Sánchez-González A, González-Díaz Y (2006) 3D-QSAR study for DNA cleavage proteins with a potential anti-tumor ATCUN-like motif. J Inorg Biochem 100:1290–1297
González-Díaz H, Pérez-Castillo Y, Podda G, Uriarte E (2007a) Computational chemistry comparison of stable/nonstable protein mutants classification models based on 3D and topological indices. J Comput Chem 28:1990–1995
González-Díaz H, Saíz-Urra L, Molina R, González-Díaz Y, Sánchez-González A (2007b) Computational chemistry approach to protein kinase recognition using 3D stochastic van der Waals spectral moments. J Comput Chem 28:1042–1048
González-Díaz H, Vilar S, Santana L, Uriarte E (2007c) Medicinal chemistry and bioinformatics: current trends in drugs discovery with networks topological indices. Curr Top Med Chem 7:1015–1029
González-Díaz H, Saiz-Urra L, Molina R, Santana L, Uriarte E (2007d) A model for the recognition of protein kinases based on the entropy of 3D van der Waals interactions. J Proteome Res 6:904–908
González-Díaz H, González-Díaz Y, Santana L, Ubeira FM, Uriarte E (2008) Proteomics, networks and connectivity indices. Proteomics 8:750–778
Gramatica P, Pilutti P, Papa E (2004) Validated QSAR prediction of OH tropospheric degradation of VOCs: splitting into training-test sets and consensus modeling. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 44:1794–1802
Hasegawa K, Funatsu K (1998) GA strategy for variable selection in QSAR studies: GAPLS and d-optimal designs for predictive QSAR model. J Mol Struct (Theochem) 425:255–262
Hasegawa K, Funatsu K (2000) Partial least squares modeling and genetic algorithm optimization in quantitative structure–activity relationships. SAR QSAR Environ Res 11:189–209
Hasegawa K, Miyashita Y, Funatsu K (1997) GA strategy for variable selection in QSAR Studies: GA based PLS analysis of calcium channel antagonists. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 37:306–310
Helland IS (2001) Some theoretical aspects of partial least squares regression. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:97–107
Hellberg S, Sjöström M, Skagerberg B, Wold S (1987) Peptide quantitative structure–activity relationships: a multivariate approach. J Med Chem 30:1126–1135
Hellberg S, Eriksson L, Jonsson J, Lindgren F, Sjöström M, Skagerberg B, Wold S, Andrews P (1991) Minimum analogue peptide sets (MAPS) for quantitative structure–activity relationships. Int J Pept Protein Res 37:414–424
Hunt PA (1999) QSAR using 2D descriptors and Tripos’ SIMCA. J Comput Aided Mol Des 13:453–467
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (2002) Applied multivariate statistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Kawashima S, Kanehisa M (2000) AAindex: amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res 28:374
Kidera A, Konishi Y, Poka M, Ooi T, Scheraga HA (1985) Statistical analysis of the physical properties of the 10 naturally occurring amino acids. J Protein Chem 4:23–55
Kowalski RB, Wold S (1982) Pattern recognition in chemistry. In: Krishnaiah PR, Kanal LN (eds) Handbook of statistics. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Lejon T, Svendsen JS, Haug BE (2002) Simple parameterization of non-proteinogenic amino acids for QSAR of antibacterial peptides. J Peptide Sci 8:302–306
Li S, Fu B, Wang Y (2001) On structural parameterization and molecular modeling of peptide analogues by molecular electronegativity edge vector (MEE): estimation and prediction for biological activity of dipeptides. J Chin Chem Soc 48:937–944
Mei H, Liao Z, Zhou Y, Li SZ (2005) A new set of amino acid descriptors and its application in peptide QSARs. Biopolymers (Pept Sci) 80:775–786
Molina E, Diaz HG, Gonzalez MP, Rodriguez E, Uriarte E (2004) Designing antibacterial compounds through a topological substructural approach. J Chem Inf Comp Sci 44: 515–521
Nakai K, Kidera A, Kanehisa M (1988) Cluster analysis of amino acid indices for prediction of protein structure and function. Protein Eng 2:93–100
Norinder U (1991) Theoretical amino acid descriptors: application to bradykinin potentiating peptides. Peptides 12:1223–1227
Ramos de Armas R, González-Díaz H, Molina R, Pérez-González M, Uriarte E (2004) Stochastic-based descriptors studying peptides biological properties: modeling the bitter tasting threshold of dipeptides. Bioorg Med Chem 12:4815–4822
Sandberg M, Eriksson L, Jonsson J, Sjöström M, Wold S (1998) New chemical descriptors relevant for the design of biologically active peptides: a multivariate characterization of 87 amino acids. J Med Chem 412:481–2491
Selassie CD, Mekapati SB, Verma RP (2002) QSAR: then and now. Cur Top Med Chem 2:1357–1379
Sewald N, Jakubke HD (2002) Peptides: chemistry and biology. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim
Sneath PH (1966) Relations between chemical structure and biological activity in peptides. J Theor Biol 12:157–195
Todeschini R, Consonni, V, Pavan M (2002) DRAGON software version 2.1. http://www.talete.mi.it/main_exp.htm
Tomii K, Kanehisa M (1996) Analysis of amino acid indices and mutation matrices for sequence comparison and structure prediction of proteins. Protein Eng 9:27–36
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar VK (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and inerpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb Sci 22:69–77
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001a) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:109–130
Wold S, Trygg J, Berglund A, Antti H (2001b) Some recent developments in PLS modeling. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:131–150
Zaliani A, Gancia E (1999) MS-WHIM scores for amino acids: a new 3D-description for peptide QSAM and QSPR studies. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 39:525–533
Acknowledgments
We thank the reviewers for the constructive comments. This work was supported by the National high-tech Research Program (The “863” Program) (2006AA02Z312), National 111 Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (0507111106) and Innovative Group Program for Graduates of Chongqing University, Science and Innovation Fund (200711C1A0010260).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, G., Yang, L., Kang, L. et al. Using multidimensional patterns of amino acid attributes for QSAR analysis of peptides. Amino Acids 37, 583–591 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0177-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0177-8