Abstract
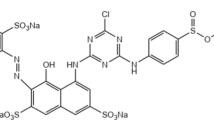
The non-covalent interaction of brilliant red (BR) with lysozyme was investigated by the UV spectrometry, circular dichroism (CD) and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). The thermodynamic characterization of the interaction was performed and the assembly complexes were formed: lysozyme(BR)17 at pH 2.03, lysozyme(BR)15 at pH 3.25 and lysozyme(BR)12 at pH 4.35, which corresponded to the physiological acidities. The ionic interaction induces a combination of multiple non-covalent bonds including hydrogen bond, hydrophobic interaction and van der Waals force. The two-step binding model of BR was found, in which one or two BR molecules entered the hydrophobic intracavity of lysozyme and the others bound to the hydrophilic outer surface of lysozyme. Moreover, BR binding resulted in change of the lysozyme conformation and inhibition of the lysozyme activity. The possible binding site and type of BR and the conformational transition of lysozyme were speculated and illustrated. This work provided a useful approach for study on enzyme toxicity of aromatic azo chemicals.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergamini CM (2007) Effects of ligands on the stability of tissue transglutaminase: studies in vitro suggest possible modulation by ligands of protein turn-over in vivo. Amino Acids 33:415–421
Collins MD, Hummer G, Quillin ML, Matthews BW, Gruner SM (2005) Cooperative water filling of a nonpolar protein cavity observed by high-pressure crystallography and simulation. PNAS 102:16668–16671
Cooper A, McAlpine A, Stockley PG (1994) Calorimetric studies of the energetics of protein–DNA interactions in the E. coli methionine repressor. Met J system. FEBS Lett 348:41–45
Cunningham FE, Lineweaver H (1967) Inactivation of lysozyme by native ovalbumin. Poult Sci 46:1471–1477
Derham BK, Harding JJ (2006) The effect of the presence of globular proteins and elongated polymers on enzyme activity. BBA Proteins Proteomics 1764:1000–1006
Desai A, Lee C, Sharma L, Sharma A (2006) Lysozyme refolding with cyclodextrins, structure–activity relationship. Biochimie 88:1435–1445
Diamond R (1974) Real-space refinement of the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol 82:371–391
Dominiak PM, Volkov A, Li X, Messerschmidt M, Coppens P (2007) Theoretical databank of transferable aspherical atoms and its application to electrostatic interaction energy calculations of macromolecules. J Chem Theory Comput 3:232–247
Eichmuller C, Tollinger M, Krautler B, Konrat R (2001) Mapping the ligand binding site at protein side-chains in protein-ligand complexes through NOE difference spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 20:195–202
Fang Y, Guo Y, Feng Y, Li M (2008) Predicting DNA-binding proteins: approached from Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition and other specific sequence features. Amino Acids 34:103–109
Gao HW, QianY, Hu ZJ (2004) Tetraiodophenolsuphonphthalein as a spectral substitute to characterize the complexation between cationic and anionic surfactant. J Colloid Interface Sci 279:244–252
Gao HW, Zhao JF, Yang QZ, Liu XH, Chen L, Pan LT (2006) Non-covalent interaction of 2′, 4′, 5′, 7′-tetrabromo−4, 5, 6, 7-tetrachlorofluorescein with proteins and its application. Proteomics 6:5140–5151
Goobes R, Minsky A (2001) Contextual equilibrium effects in DNA molecules. J Biol Chem 276:16155–16160
Hu HY, Xu GJ (1999) Structural transformation of proteins. Prog Biochem Biophys 1:9–12
Johnson LN, Phillips DC, Rupley JA (1968) The activity of lysozyme: an interim review of crystallographic and chemical evidence. Brookhaven Symp Biol 21:120–138
Jones RB, Gordus A, Krall JA, MacBeath G (2006) A quantitative protein interaction network for the ErbB receptors using protein microarrays. Nature 439:168–174
Kolandaivel P, Selvarengan P, Gunavathy KV (2006) Structure and potential energy surface studies on 310 helices of hen egg white lysozyme and Phaseolus vulgaris arcelin-1 proteins. BBA Proteins Proteomics 1764:138–145
Kraut DA, Carroll KS, Herschlag D (2003) Challenges in enzyme mechanism and energetics. Annu Rev Biochem 72:517–571
Lee YC, Yang D (2002) Determination of lysozyme activities in a microplate format. Anal Biochem 310:223–224
Liao ZY, Thibaut L, Jobson A, Pommier Y (2006) Inhibition of human tyrosyl––DNA phosphodiesterase by aminoglycoside antibiotics and ribosome inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol 70:366–372
Liu ST, Sugimoto T, Azakami H, Kato A (2000) Lipophilization of lysozyme by short and middle chain fatty acids. J Agric Food Chem 48:265–269
Marolia KZ, D’Souza SF (1999) Enhancement in the lysozyme activity of the hen egg white foam matrix by cross-linking in the presence of N-acetyl glucosamine. J Biochem Biophys Methods 39:115–117
Miller CM, Szegedi SS, Garrow TA (2005) Conformation-dependent inactivation of human betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase by hydrogen peroxide in vitro. Biochem J 392:443–448
Nelson TJ, Backlund PS, Alfred J, Yergey L, Alkon DL (2006) Isolation of protein subpopulations undergoing protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:253–259
Panigrahi SK, Desiraju GR (2007) Strong and weak hydrogen bonds in the protein-ligand interface. Proteins 67:128–141
Pible O, Guilbaud P, Pellequer JL, Vidaud C Quéméneur E (2006) Structural insights into protein–uranyl interaction: towards an in silico detection method. Biochimie 88:1631–1638
Piekarska B, Skowronek M, Rybarska J, Stopa B, Roterman I, Konieczny L (1996) Congo red-stabilized intermediates in the lambda light chain transition from native to molten state. Biochimie 78:183–189
Quinn SJ, Kifor O, Trivedi S, Diaz R (1998) Sodium and ionic strength sensing by the calcium receptor. J Biol Chem 273:19579–19586
Skipper PL, Tannenbaum SR (1994) Molecular Dosimetry of Aromatic Amines in Human Populations. Environ Health Perspect 102:17–21
Smeller L, Meersman F, Heremans K (2006) Refolding studies using pressure: the folding landscape of lysozyme in the pressure–temperature plane. BBA Proteins Proteomics 1764:497–505
Waehneldt TV (1975) Sodium dodecyl sulfate in protein chemistry. Biosystems 6:176–187
Wells MA, Jelinska C, Hosszu LLP, Craven CJ, Clarke AR, Collinge J, Waltho JP, Jackson GS (2006) Multiple forms of copper (II) co-ordination occur throughout the disordered N-terminal region of the prion protein at pH 7.4. Biochem J 400:501–510
Xie MX, Xu XY, Wang YD (2005) Interaction between hesperetin and human serum albumin revealed by spectroscopic methods. Biochim Biophys Acta 1724:215–224
Yang M (1998) Molecular recognition of DNA targeting small molecule drugs. J Beijing Med Univ 30:97–99
Yang XX, Hu ZP, Chan SY, Zhou SF (2006) Monitor drug-protein interaction. Clin Chim Acta 361:9–29
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Zhao-Feng Luo of USTC for his help with ITC measurement and Dr. Xue-Ling Ao of Microcal Co. for their assistance in use of the computer programs and data analysis. We also thank the Shanghai Fundamental Research Project (Grant No. 04JC14072) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20477030) for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, FF., Tang, YN., Wang, SL. et al. Binding of brilliant red compound to lysozyme: insights into the enzyme toxicity of water-soluble aromatic chemicals. Amino Acids 36, 399–407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0069-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0069-y