Summary.
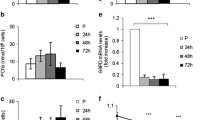
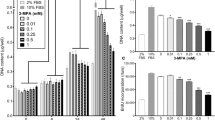
This study compared the effects of leucine and glutamine on the mTOR pathway, on protein synthesis and on muscle-specific gene expression in myogenic C2C12 cells. Leucine increased the phosphorylation state of mTOR, on both Ser2448 and Ser2481, and its downstream effectors, p70S6k, S6 and 4E-BP1. By contrast, glutamine decreased the phosphorylation state of mTOR on Ser2448, p70S6k and 4E-BP1, but did not modify the phosphorylation state of mTOR on Ser2481 and S6. Whilst the phosphorylation state of the mTOR pathway is usually related to protein synthesis, the incorporation of labelled methionine/cysteine was only transiently modified by leucine and was unaltered by glutamine. However, these two amino acids affected the mRNA levels of desmin, myogenin and myosin heavy chain in a time-dependant manner. In conclusion, leucine and glutamine have opposite effects on the mTOR pathway. Moreover, they induce modification of muscle-specific gene expression, unrelated to their effects on the mTOR/p70S6k pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SF Abcouwer PL Marjon RK Loper DL Vander Jagt (2002) ArticleTitleResponse of VEGF expression to amino acid deprivation and inducers of endoplasmic reticulum stress Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43 2791–2798 Occurrence Handle12147617
DR Alessi FB Caudwell M Andjelkovic BA Hemmings P Cohen (1996) ArticleTitleMolecular basis for the substrate specificity of protein kinase B; comparison with MAPKAP kinase-1 and p70 S6 kinase FEBS Lett 399 333–338 Occurrence Handle8985174 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(96)01370-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlahsw%3D%3D
L Bertrand DR Alessi J Deprez M Deak E Viaene MH Rider L Hue (1999) ArticleTitleHeart 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activation by insulin results from Ser-466 and Ser-483 phosphorylation and requires 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1, but not protein kinase B J Biol Chem 274 30927–30933 Occurrence Handle10521487 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.274.43.30927 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXntVSmurk%3D
C Brasse-Lagnel A Fairand A Lavoinne A Husson (2003) ArticleTitleGlutamine stimulates argininosuccinate synthetase gene expression through cytosolic O-glycosylation of Sp1 in Caco-2 cells J Biol Chem 278 52504–52510 Occurrence Handle14570901 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M306752200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvFGjs7o%3D
L Deldicque D Theisen M Francaux (2005) ArticleTitleRegulation of mTOR by amino acids and resistance exercise in skeletal muscle Eur J Appl Physiol 94 1–10 Occurrence Handle15702344 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00421-004-1255-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjslOmtrc%3D
M Du QW Shen MJ Zhu SP Ford (2007) ArticleTitleLeucine stimulates mammalian target of rapamycin signalling in C2C12 myoblasts in part through inhibition of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase J Anim Sci 85 919–927 Occurrence Handle17178807 Occurrence Handle10.2527/jas.2006-342 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXjslWlu7k%3D
E Erbay IH Park PD Nuzzi CJ Schoenherr J Chen (2003) ArticleTitleIGF-II transcription in skeletal myogenesis is controlled by mTOR and nutrients J Cell Biol 163 931–936 Occurrence Handle14662739 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.200307158 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvVaksrs%3D
HL Fox SR Kimball LS Jefferson CJ Lynch (1998) ArticleTitleAmino acids stimulate phosphorylation of p70S6k and organization of rat adipocytes into multicellular clusters Am J Physiol 274 C206–C213 Occurrence Handle9458729 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXotF2gug%3D%3D
LS Jefferson SR Kimball (2003) ArticleTitleAmino acids as regulators of gene expression at the level of mRNA translation J Nutr 133 2046S–2051S Occurrence Handle12771363 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXksFeqsb8%3D
MS Kilberg IP Barbosa-Tessmann (2002) ArticleTitleGenomic sequences necessary for transcriptional activation by amino acid deprivation of mammalian cells J Nutr 132 1801–1804 Occurrence Handle12097650 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xlt1egt78%3D
DH Kim DD Sarbassov SM Ali JE King RR Latek H Erdjument-Bromage P Tempst DM Sabatini (2002) ArticleTitlemTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery Cell 110 163–175 Occurrence Handle12150925 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00808-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvV2htr4%3D
SR Kimball RL Horetsky LS Jefferson (1998) ArticleTitleImplication of eIF2B rather than eIF4E in the regulation of global protein synthesis by amino acids in L6 myoblasts J Biol Chem 273 30945–30953 Occurrence Handle9812990 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.47.30945 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXns1egt7w%3D
SR Kimball LM Shantz RL Horetsky LS Jefferson (1999) ArticleTitleLeucine regulates translation of specific mRNAs in L6 myoblasts through mTOR-mediated changes in availability of eIF4E and phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 J Biol Chem 274 11647–11652 Occurrence Handle10206976 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.274.17.11647 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXislGmu7g%3D
N Kimura C Tokunaga S Dalal C Richardson K Yoshino K Hara BE Kemp LA Witters O Mimura K Yonezawa (2003) ArticleTitleA possible linkage between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway Genes Cells 8 65–79 Occurrence Handle12558800 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2443.2003.00615.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtFKmtQ%3D%3D
U Krause L Bertrand L Maisin M Rosa L Hue (2002) ArticleTitleSignalling pathways and combinatory effects of insulin and amino acids in isolated rat hepatocytes Eur J Biochem 269 3742–3750 Occurrence Handle12153571 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03069.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsVSitLs%3D
S Marshall (2006) ArticleTitleRole of insulin, adipocyte hormones, and nutrient-sensing pathways in regulating fuel metabolism and energy homeostasis: a nutritional perspective of diabetes, obesity, and cancer Sci STKE 2006 re7 Occurrence Handle16885148 Occurrence Handle10.1126/stke.3462006re7
AS Marsin L Bertrand MH Rider J Deprez C Beauloye MF Vincent G Van den Berghe D Carling L Hue (2000) ArticleTitlePhosphorylation and activation of heart PFK-2 by AMPK has a role in the stimulation of glycolysis during ischaemia Curr Biol 10 1247–1255 Occurrence Handle11069105 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00742-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotVSrsrw%3D
S Mordier C Deval D Bechet A Tassa M Ferrara (2000) ArticleTitleLeucine limitation induces autophagy and activation of lysosome-dependent proteolysis in C2C12 myotubes through a mammalian target of rapamycin-independent signalling pathway J Biol Chem 275 29900–29906 Occurrence Handle10893413 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M003633200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmvFKjur4%3D
T Nakajo T Yamatsuji H Ban K Shigemitsu M Haisa T Motoki K Noma T Nobuhisa J Matsuoka M Gunduz K Yonezawa N Tanaka Y Naomoto (2005) ArticleTitleGlutamine is a key regulator for amino acid-controlled cell growth through the mTOR signalling pathway in rat intestinal epithelial cells Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326 174–180 Occurrence Handle15567168 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.015 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVagsrvM
IH Park E Erbay P Nuzzi J Chen (2005) ArticleTitleSkeletal myocyte hypertrophy requires mTOR kinase activity and S6K1 Exp Cell Res 309 211–219 Occurrence Handle15963500 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.05.017 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXpt1ekt7c%3D
T Peng TR Golub DM Sabatini (2002) ArticleTitleThe immunosuppressant rapamycin mimics a starvation-like signal distinct from amino acid and glucose deprivation Mol Cell Biol 22 5575–5584 Occurrence Handle12101249 Occurrence Handle10.1128/MCB.22.15.5575-5584.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XltlGnt7g%3D
CG Proud (2002) ArticleTitleRegulation of mammalian translation factors by nutrients Eur J Biochem 269 5338–5349 Occurrence Handle12423332 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03292.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XptVymtr0%3D
MJ Rennie A Ahmed SE Khogali SY Low HS Hundal PM Taylor (1996) ArticleTitleGlutamine metabolism and transport in skeletal muscle and heart and their clinical relevance J Nutr 126 1142S–1149S Occurrence Handle8642447 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhvFansLo%3D
J Rohde J Heitman ME Cardenas (2001) ArticleTitleThe TOR kinases link nutrient sensing to cell growth J Biol Chem 276 9583–9586 Occurrence Handle11266435 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.R000034200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXis1OltLs%3D
Y Xia HY Wen ME Young PH Guthrie H Taegtmeyer RE Kellems (2003) ArticleTitleMammalian target of rapamycin and protein kinase A signalling mediate the cardiac transcriptional response to glutamine J Biol Chem 278 13143–13150 Occurrence Handle12522136 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M208500200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXislGrtbo%3D
G Xu G Kwon CA Marshall TA Lin JC Lawrence SuffixJr ML McDaniel (1998) ArticleTitleBranched-chain amino acids are essential in the regulation of PHAS-I and p70 S6 kinase by pancreatic beta-cells. A possible role in protein translation and mitogenic signalling J Biol Chem 273 28178–28184 Occurrence Handle9774438 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.43.28178 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntVCmu7Y%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Authors’ address: Marc Francaux, Département d’Education Physique et de Réadaptation, Université catholique de Louvain, Place Pierre de Coubertin 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deldicque, L., Sanchez Canedo, C., Horman, S. et al. Antagonistic effects of leucine and glutamine on the mTOR pathway in myogenic C2C12 cells. Amino Acids 35, 147–155 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-007-0607-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-007-0607-z